Table of Contents
Introduction
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a thorough plan that delineates the steps to launch a product, ensuring it reaches the appropriate customers and attains its sales objectives.
The principal aims of a GTM strategy encompass identifying the target market, outlining the value proposition, devising a marketing scheme, establishing a sales approach, and setting up distribution channels.
A well-defined go-to-market (GTM) strategy aligns departments, optimizes resource utilization, enhances product launches, provides competitive insight, and helps with differentiation.
Market Research and Analysis

Effective market research and analysis are foundational to developing a successful go-to-market strategy. This involves identifying your target market, conducting thorough market research, and performing a competitive analysis.
Identifying Your Target Market
- Segmenting your target market is crucial for understanding who your potential customers are
- Demographic segmentation involves categorizing the market based on factors such as age, gender, income, education, and occupation
- Psychographic segmentation looks at lifestyle, values, interests, and attitudes.
- Behavioral segmentation focuses on customer behaviors, such as purchase patterns, brand loyalty, and product usage
- By understanding these segments, you can tailor your marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of different groups
- Buyer personas are semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers based on market research and real data about your existing customers
- They include detailed information about customer demographics, behaviors, motivations, and goals
- Creating detailed buyer personas helps you to understand your customers better and develop marketing strategies that resonate with them
Conducting Market Research
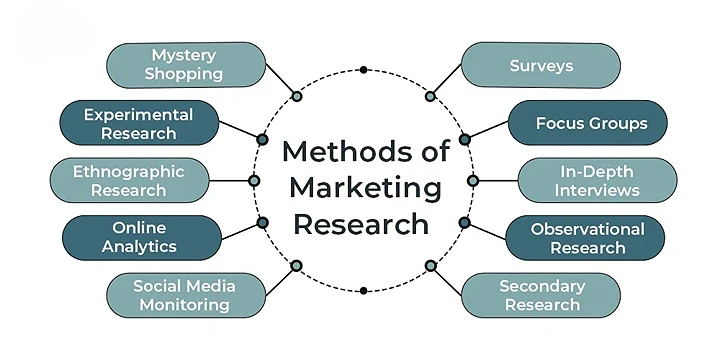
- Market research can be divided into primary and secondary research. Primary research involves collecting new data directly from the source, such as through surveys, interviews, and focus groups
- This type of research provides specific insights tailored to your business needs. Secondary research involves analyzing existing data from sources like industry reports, market studies, and public records
- For secondary research, industry reports, market analysis publications, and academic journals are valuable resources. Utilizing a combination of these tools ensures comprehensive market insights
Competitive Analysis
Understanding who your competitors are and what they offer is crucial for positioning your product effectively. Key competitors can be identified through market research, customer feedback, and industry reports.
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
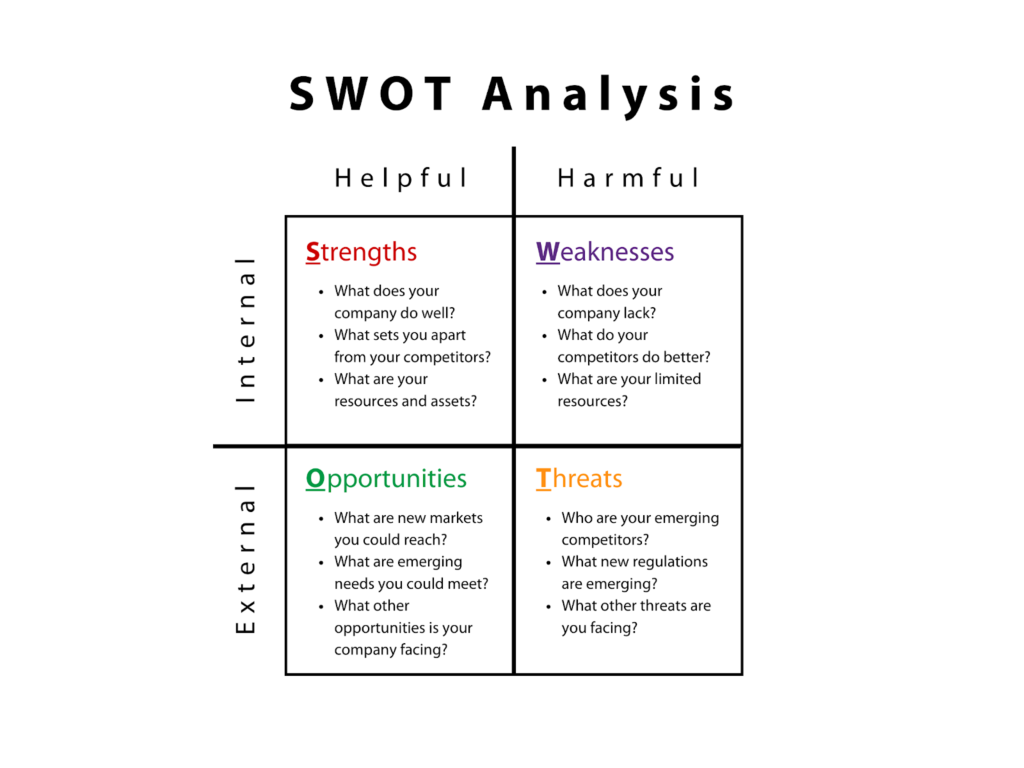
- SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats
- Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors, such as resources and capabilities, while opportunities and threats are external factors, such as market trends and competitive dynamics
- A SWOT analysis helps develop strategies that leverage strengths and opportunities while mitigating weaknesses and threats
Market Positioning and Differentiation
- Market positioning involves creating a distinct image of your product in the minds of your target customers, relative to competitors
- Differentiation is about offering unique features, benefits, or experiences that set your product apart
- Effective positioning and differentiation are achieved through clearly understanding your target market and competitive landscape and communicating your value proposition compellingly
By thoroughly researching the market, understanding your target audience, and analyzing competitors, you can develop a go-to-market strategy that effectively positions your product and meets customer needs.
Crafting Your Value Proposition
Understanding Customer Pain Points

- Identifying and understanding customer pain points is crucial for creating a value proposition that resonates with your target audience
- Pain points are specific problems or challenges that your customers face
- These can be identified through customer feedback, surveys, interviews, and market research
- By understanding what frustrates or hinders your customers, you can tailor your product or service to address these issues directly, providing solutions that genuinely add value
Developing a Compelling Value Proposition
A compelling value proposition communicates the unique benefits your product or service offers. It should answer the question, “Why should customers choose your product over competitors?” Key elements of a strong value proposition include:
- Clear Benefits: Explain what benefits the customer will gain
- Unique Differentiators: Highlight what sets your product apart from competitors
- Target Audience: Specify who will benefit from your product
A well-crafted value proposition is concise, memorable, and aligns with the needs and desires of your target audience.
Testing and Refining Your Value Proposition
Once you have developed a value proposition, it’s essential to test it with your target audience.
- Methods such as A/B testing, surveys, and focus groups can provide valuable feedback on how your value proposition is perceived
- Based on this feedback, refine and iterate your value proposition to ensure it resonates with your audience and effectively communicates the unique value your product offers
Building Your Product Messaging and Positioning
Creating Clear and Consistent Messaging
- Clear and consistent messaging is vital for ensuring that your target audience understands your product’s value
- Your messaging should reflect your value proposition and be consistent across all marketing channels and touchpoints
- This includes your website, social media, advertising, and sales materials
- Consistent messaging helps to build brand recognition and trust with your audience
Positioning Your Product in the Market
- Product positioning involves defining how your product fits within the market and how it is perceived relative to competitors
- This requires a deep understanding of your target audience and the competitive landscape
- Positioning statements should highlight your product’s unique features and benefits and articulate why it is the best choice for your target audience
- Effective positioning differentiates your product and creates a clear, compelling narrative that resonates with potential customers
Aligning Messaging with Target Audience
- Tailoring your messaging to align with the specific needs, preferences, and pain points of your target audience is crucial
- This involves segmenting your audience and creating tailored messages for each segment
- Understanding the language, tone, and style that appeals to different segments helps to make your messaging more relevant and engaging, leading to higher conversion rates and stronger customer relationships
Selecting Your Marketing Channels
Understanding Different Marketing Channels

Marketing channels are the various platforms and mediums through which you can reach your target audience. These can be broadly categorized into:
- Online Channels: Social media, email marketing, search engine marketing, content marketing, and online advertising.
- Offline Channels: Print advertising, events, direct mail, and public relations.
- Owned, Earned, and Paid Media: Owned media includes your website and social media profiles, earned media encompasses organic mentions and shares, and paid media includes advertising and sponsorships.
Choosing the Right Channels for Your Audience
Selecting the right marketing channels involves understanding where your target audience spends their time and how they prefer to receive information.
- This requires research into audience behaviors and preferences
- Consider factors such as demographics, psychographics, and media consumption habits
- Choosing the right mix of channels ensures that your marketing efforts are effective and efficient.
Developing a Multi-Channel Strategy
A multi-channel strategy leverages multiple marketing channels to reach your audience at various touchpoints.
- This approach ensures a broader reach and more opportunities to engage with potential customers
- Integrating your messaging across channels is important to provide a cohesive brand experience
- Tracking and measuring the performance of each channel allows you to optimize your strategy, allocate resources effectively, and achieve better results
By understanding customer pain points, developing a strong value proposition, building clear and consistent messaging, and selecting the right marketing channels, you can create a comprehensive go-to-market strategy that effectively reaches and engages your target audience.
Sales Strategy and Planning
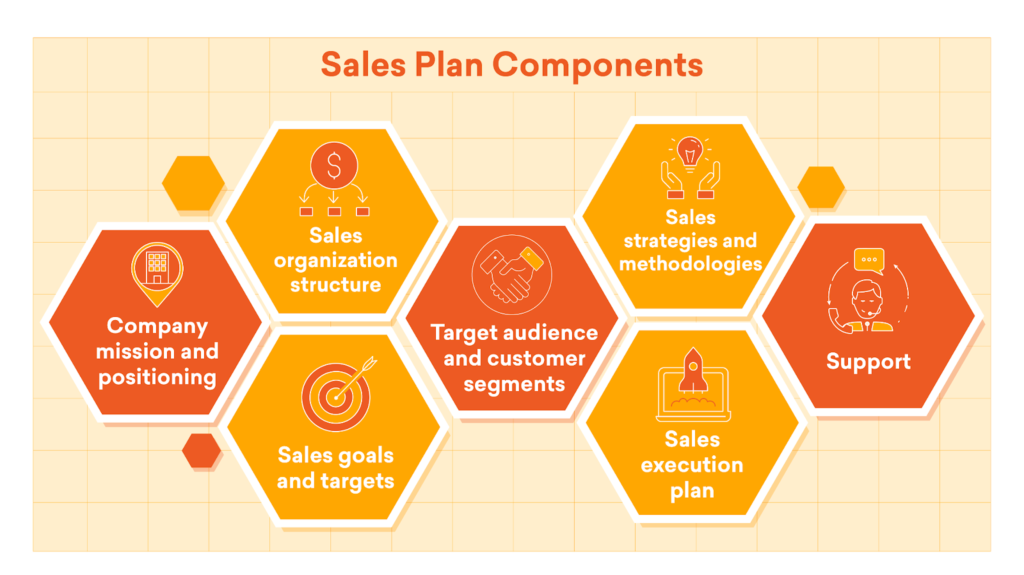
Setting Sales Goals and Objectives
Setting clear, achievable sales goals and objectives is the first step in building an effective sales strategy
- Goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART)
- These goals could include revenue targets, market penetration rates, or customer acquisition numbers
- Establishing clear objectives directs your sales team and helps measure progress and success
Building Your Sales Team
A strong sales team is crucial for executing your sales strategy.
- This involves recruiting individuals with the right skills and experience, providing thorough training, and fostering a collaborative and motivated team culture
- Clear role definitions, performance expectations, and incentives help to align the team’s efforts with your sales goals
- Continuous professional development ensures that your sales team remains knowledgeable and effective.
Developing a Sales Process
A structured sales process is essential for guiding your sales team through each stage of the sales cycle.
- This process typically includes lead generation, qualification, pitching, handling objections, closing, and follow-up
- Implementing a customer relationship management (CRM) system can streamline this process by tracking interactions and managing sales pipelines
- A well-defined sales process ensures consistency, efficiency, and higher conversion rates.
Creating a Customer Success Strategy
Onboarding and Training
Effective onboarding sets the tone for the customer relationship and helps ensure customer success.
- A comprehensive onboarding program should introduce customers to your product, demonstrate its value, and provide the necessary training to use it effectively
- Tailored onboarding experiences that cater to different customer segments can enhance satisfaction and reduce churn
Customer Relationship Management
Building and maintaining strong relationships with customers is critical for long-term success.
- This involves regular communication, personalized support, and proactive engagement to address customer needs and concerns
- Implementing a CRM system helps track customer interactions, manage accounts, and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling
Gathering and Utilizing Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is invaluable for improving your product and services.
- Regularly collecting feedback through surveys, interviews, and customer support interactions provides insights into customer satisfaction and areas for improvement.
- Analyzing this feedback allows you to make informed decisions, enhance the customer experience, and foster loyalty.
Measuring Success and Adjusting Your Strategy

Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Identifying and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of your go-to-market strategy
- KPIs may include metrics such as sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and conversion rates
- Regularly monitoring these KPIs helps assess performance and identify areas needing improvement
Data-Driven Decision Making

- Data-driven decision-making involves using data and analytics to inform your strategic choices
- This includes analyzing market trends, customer behaviors, and sales performance to make evidence-based adjustments to your strategy
- Leveraging business intelligence tools and dashboards can provide real-time insights and support more accurate forecasting and planning.
Continuous Improvement
- A successful go-to-market strategy requires continuous evaluation and refinement
- Regularly reviewing performance data, soliciting feedback from stakeholders, and staying informed about industry trends help identify opportunities for improvement
- Implementing a culture of continuous improvement ensures your strategy remains effective and adaptable to changing market conditions.
Conclusion
Developing and executing a comprehensive go-to-market strategy involves multiple steps, from market research and value proposition development to sales planning and customer success strategies.
By setting clear objectives, understanding your target market, and continuously refining your approach, you can achieve successful product launches and gain a competitive advantage. Remember, the key to a successful go-to-market strategy lies in alignment, adaptation, and ongoing improvement. With a well-crafted plan, your business can navigate the complexities of the market and drive sustained growth and success.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



