Table of Contents
Introduction
Becoming a successful CEO is about more than just having business skills; it’s about personal growth and self-awareness. CEOs need to understand their strengths and weaknesses, as this inner journey helps them inspire their teams, make smart decisions, and create a strong company culture.
- A CEO’s personal development directly affects the organization’s success
- This journey includes building emotional intelligence, staying resilient, and maintaining ethical values—all crucial for tackling challenges and taking advantage of new opportunities
- This guide will explore the key transformations CEOs go through to lead effectively
- We’ll look at personal development, strategic vision, ethical leadership, and empowering teams, offering a clear roadmap for both current leaders and those aspiring to be one
Understanding the Role of a CEO
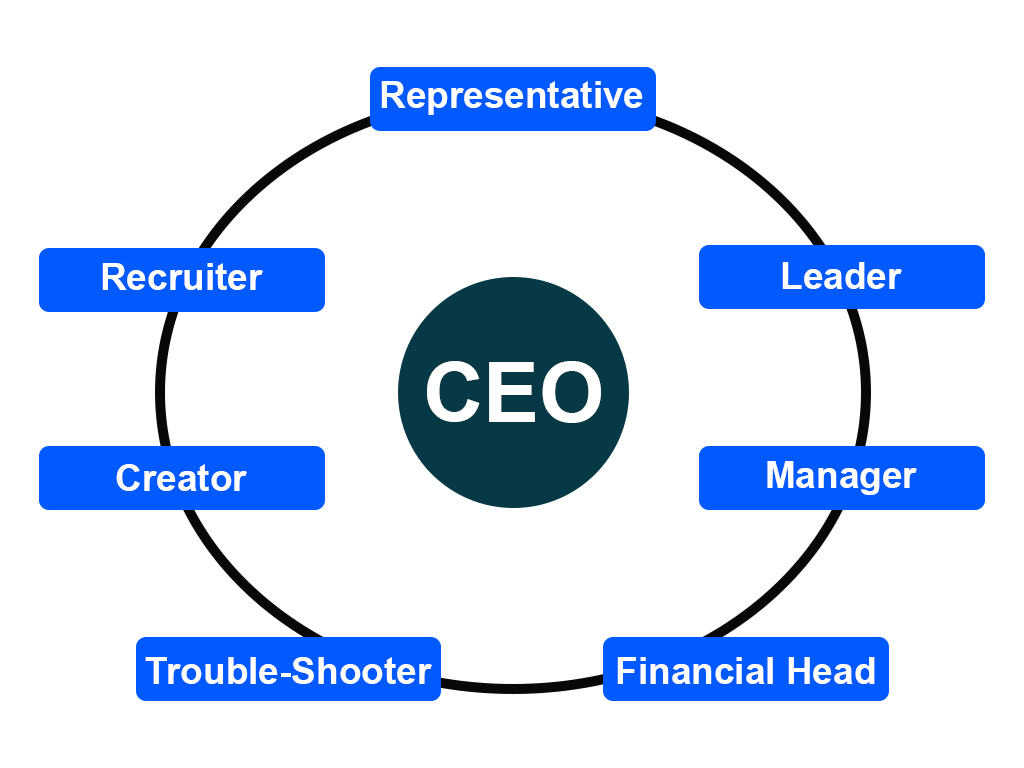
The CEO is the highest-ranking executive in a company. Their primary responsibilities include making major corporate decisions, managing operations and resources, and serving as the main point of communication between the board of directors and corporate operations.
In practice, a CEO’s time and expertise are most effectively utilized when they focus on a few high-impact, core responsibilities which include:
- Representative: The CEO serves as the face of the company, embodying its values and vision to stakeholders, partners, and the public.
- Leader: The CEO inspires and guides the organization, fostering a unified direction and motivating employees to achieve common goals.
- Manager: The CEO oversees the overall operations, ensuring that resources are efficiently utilized and that strategic objectives are met.
- Financial Head: The CEO is responsible for the financial health of the organization, making key decisions on budgeting, investments, and fiscal strategies.
- Troubleshooter: The CEO addresses and resolves critical issues and challenges, ensuring the organization remains resilient and adaptable in the face of adversity.
- Creator: The CEO drives innovation and creativity, spearheading the development of new products, services, and initiatives that propel the company forward.
- Recruiter: The CEO plays a pivotal role in attracting and retaining top talent, building a strong leadership team, and fostering a culture of excellence.
Learning Leadership from Inside Out
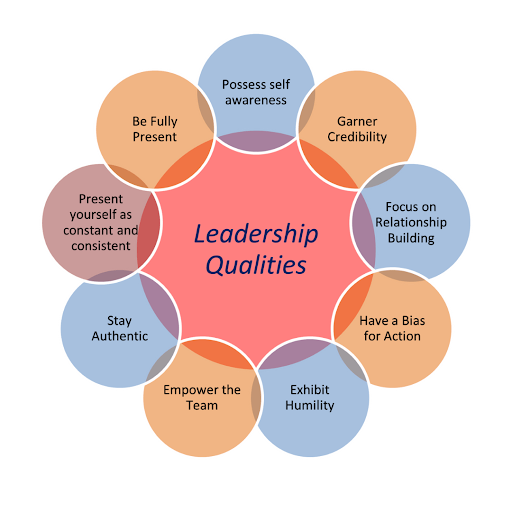
Effective leadership begins with self-awareness and personal growth. Leaders who understand their strengths, weaknesses, and motivations are better equipped to inspire and guide their teams.
Core Principles
- Possess Self-Awareness: Develop a deep understanding of your strengths and weaknesses to lead with clarity and confidence from within.
- Garner Credibility: Build trust by consistently demonstrating integrity and reliability in all your actions.
- Focus on Relationship Building: Cultivate meaningful connections to create a supportive and collaborative team environment.
- Have a Bias for Action: Drive progress by proactively taking initiative and making decisive moves when opportunities arise.
- Exhibit Humility: Lead with modesty, valuing others’ contributions, and remaining open to feedback and growth.
- Empower the Team: Foster an environment where team members feel valued, trusted, and encouraged to take ownership of their roles.
- Stay Authentic: Maintain genuine behavior and be true to your values, ensuring your leadership is both sincere and relatable.
- Present Yourself as Constant and Consistent: Demonstrate reliability by being steady and predictable in your actions and decisions.
- Be Fully Present: Engage completely in interactions and tasks, showing your team that their presence and input are valued.
Personal Development in Leadership
Personal development is a cornerstone of effective leadership. It involves a commitment to continuous learning and self-improvement, enabling leaders to navigate complex challenges and seize growth opportunities.
Self Awareness and Reflection
Self-awareness involves understanding one’s emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and the impact of one’s actions on others. Regular reflection allows leaders to evaluate their performance, learn from experiences, and make informed adjustments to their leadership approach.
- Journaling: Maintaining a journal to track thoughts, decisions, and experiences.
- 360-Degree Feedback: Gathering comprehensive feedback from peers, subordinates, and superiors.
- Meditation: Incorporating meditation practices to enhance focus and emotional regulation.
Emotional Intelligence

Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s emotions and those of others. High EI is linked to better leadership outcomes, including improved communication, conflict resolution, and team cohesion.
Components of EI
- Self-Regulation: Managing emotions in healthy ways.
- Empathy: Understanding and considering others’ perspectives.
- Social Skills: Building strong interpersonal relationships.
Enhancing emotional intelligence enables CEOs to connect with their teams on a deeper level, fostering an environment of mutual respect and collaboration.
Building Resilience and Adaptability

Resilience is the capacity to recover quickly from setbacks, while adaptability refers to the ability to adjust to new conditions. These traits are essential for navigating challenges and sustaining organizational growth in a volatile business environment.
- Stress Management: Implementing techniques to handle stress effectively.
- Positive Mindset: Cultivating optimism and a solution-oriented approach.
- Support Systems: Establishing strong support networks both professionally and personally.
- Flexibility: Being open to change and willing to pivot strategies as needed.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with industry trends and emerging technologies.
By fostering resilience and adaptability, CEOs can lead their organizations through uncertain times with confidence and poise.
Strategic Vision and Execution
A CEO’s ability to craft and execute a strategic vision is paramount to an organization’s success. This involves setting ambitious goals and developing actionable plans to achieve them.
Crafting a Strategic Vision
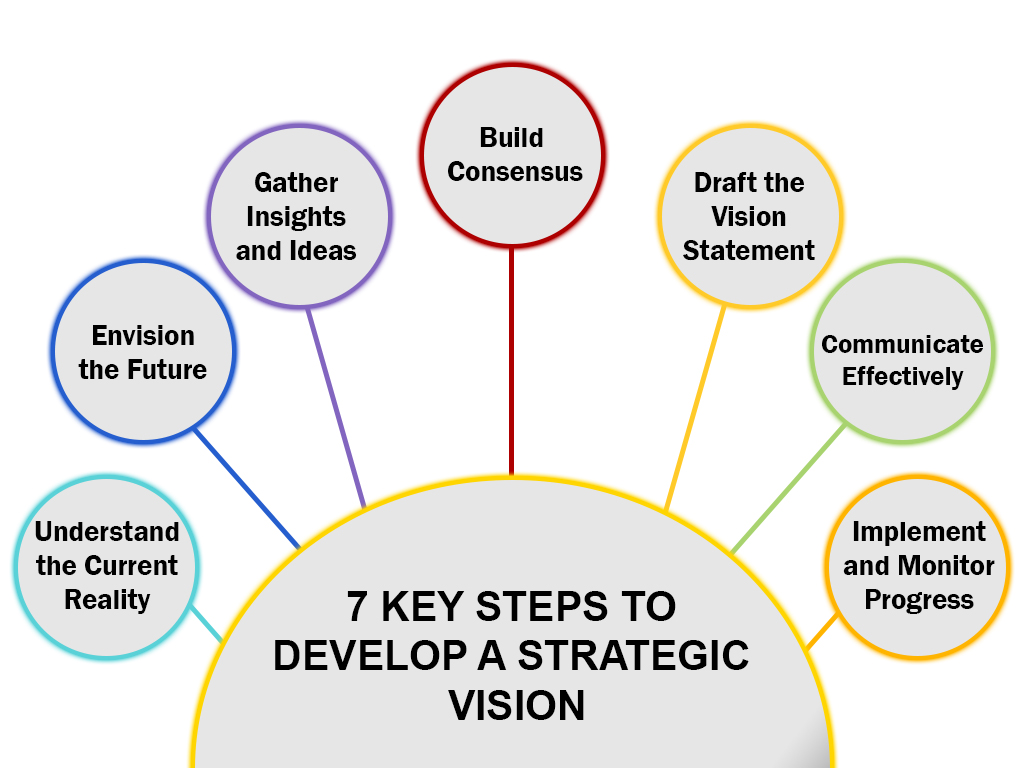
Creating a strategic vision requires a deep understanding of the market, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities. It serves as a roadmap, guiding the organization toward its desired future state.
Steps to Develop a Strategic Vision
- Understand the Current Reality: Assess the organization’s current position, including strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, to establish a clear baseline.
- Envision the Future: Define a compelling and aspirational picture of where the organization aims to be in the long-term future.
- Gather Insights and Ideas: Collect diverse perspectives and innovative ideas from stakeholders to inform the vision development process.
- Build Consensus: Engage key stakeholders to align their interests and secure collective agreement on the strategic vision.
- Draft the Vision Statement: Articulate the strategic vision in a clear, concise, and inspiring statement that reflects the organization’s goals and values.
- Communicate Effectively: Share the vision statement widely and consistently to ensure understanding and buy-in across the organization.
- Implement and Monitor Progress: Develop actionable plans to execute the vision and regularly track progress to ensure objectives are being met.
Leading with Integrity and Ethics
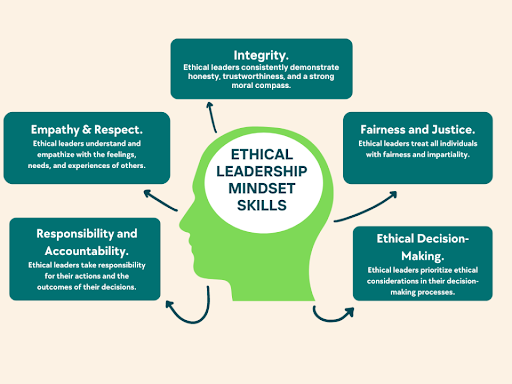
Integrity and ethics form the bedrock of effective leadership. Leaders who prioritize ethical behavior set the tone for the entire organization, fostering a culture of trust and accountability.
Principles of Ethical Leadership
- Transparency: Being open about decision-making processes and organizational changes.
- Accountability: Taking responsibility for actions and outcomes.
- Fairness: Ensuring equitable treatment of all employees and stakeholders.
Ethical leadership not only enhances the organization’s reputation but also builds long-term trust and loyalty among employees and customers.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to a company’s commitment to contribute positively to society and the environment. It encompasses a range of activities, from sustainable business practices to community engagement initiatives.
Key Areas of CSR

- Environmental Sustainability: Implementing practices that reduce the organization’s environmental footprint.
- Community Engagement: Supporting local communities through philanthropy, volunteering, and partnerships.
- Ethical Supply Chain: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor and environmental standards.
Embracing CSR not only benefits society but also enhances the company’s brand image and stakeholder relationships.
Ethical Decision Making
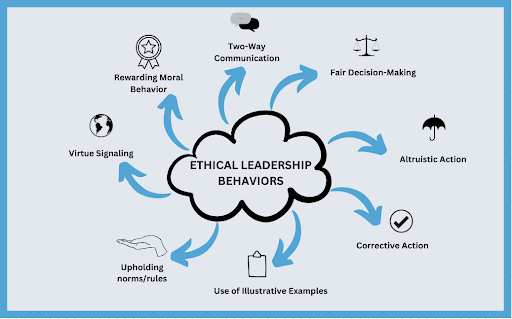
Ethical decision-making involves evaluating choices through a moral lens, and considering the potential impact on all stakeholders. It requires a structured approach to ensure that decisions align with the organization’s values and ethical standards.
Steps for Ethical Decision-Making
- Identify the Issue: Recognize the ethical dilemma or conflict.
- Gather Information: Collect relevant facts and perspectives.
- Evaluate Alternatives: Assess the potential consequences of each option.
- Make a Decision: Choose the course of action that aligns with ethical principles.
- Implement and Reflect: Execute the decision and reflect on its outcomes to inform future actions.
By prioritizing ethical decision-making, CEOs can cultivate a culture of integrity that permeates the entire organization.
Developing and Empowering Others

A CEO’s effectiveness is amplified by their ability to develop and empower their team members. Empowered employees are more engaged, innovative, and committed to the organization’s success.
Building High-Performing Teams
Creating high-performing teams involves assembling individuals with complementary skills, fostering collaboration, and maintaining a positive team dynamic.
Strategies for Building High-Performing Teams
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Defining each team member’s role to ensure accountability and efficiency.
- Effective Communication: Promoting open and honest communication to facilitate collaboration.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Encouraging diversity of thought and fostering an inclusive environment where all voices are heard.
High-performing teams are the engine of organizational success, driving innovation and achieving ambitious goals.
Mentorship and Coaching
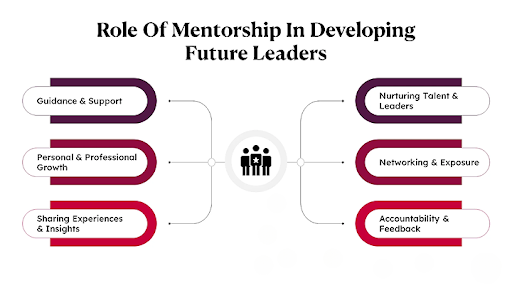
Mentorship and coaching are vital for nurturing talent and facilitating professional growth. They provide employees with guidance, support, and opportunities to develop their skills and careers.
Benefits of Mentorship and Coaching
- Skill Development: Enhancing employees’ competencies and expertise.
- Career Advancement: Assisting employees in navigating their career paths and achieving their goals.
- Increased Engagement: Boosting employee morale and commitment through personalized support.
By investing in mentorship and coaching programs, CEOs can cultivate a culture of continuous learning and development.
Teamwork and Communication
Effective leadership is built on a foundation of strong teamwork and clear communication. A great leader not only sets a vision but also fosters collaboration and ensures that every team member is aligned with common goals.
Whether managing a small team or leading a large organization, mastering teamwork and communication is essential for driving productivity, innovation, and overall business success.
The Role of Teamwork in Leadership
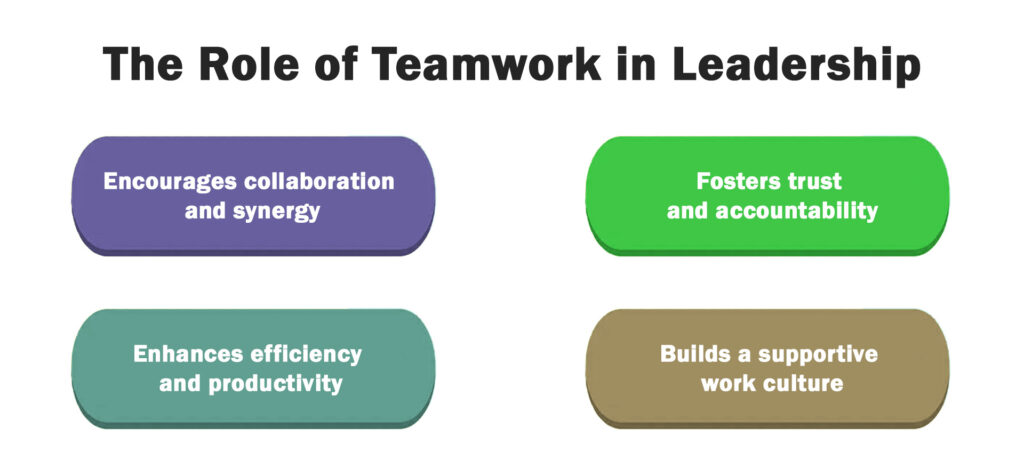
- Encourages collaboration and synergy: Strong teams leverage diverse skills and perspectives to generate innovative solutions.
- Fosters trust and accountability: Leaders who promote teamwork ensure that responsibilities are shared, and everyone is committed to achieving success together.
- Enhances efficiency and productivity: When team members work together effectively, tasks are completed more efficiently, reducing bottlenecks and redundancies.
- Builds a supportive work culture: A leader who values teamwork nurtures an environment where employees feel valued, motivated, and engaged.
Importance of Communication in Leadership
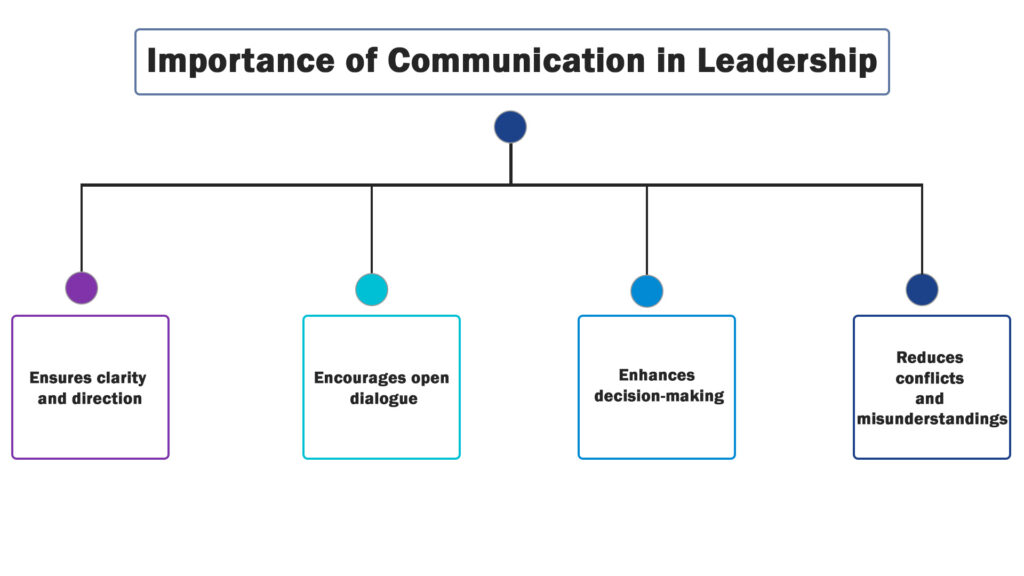
- Ensures clarity and direction: Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and aligns the team with the organization’s objectives.
- Encourages open dialogue: Leaders who foster transparent communication create a workplace where employees feel comfortable sharing feedback, ideas, and concerns.
- Enhances decision-making: Effective leaders use communication to gather insights from their teams, leading to well-informed and strategic decisions.
- Reduces conflicts and misunderstandings: Clear and respectful communication helps in resolving disputes quickly and maintaining harmony in the workplace.
Continuous Learning and Growth
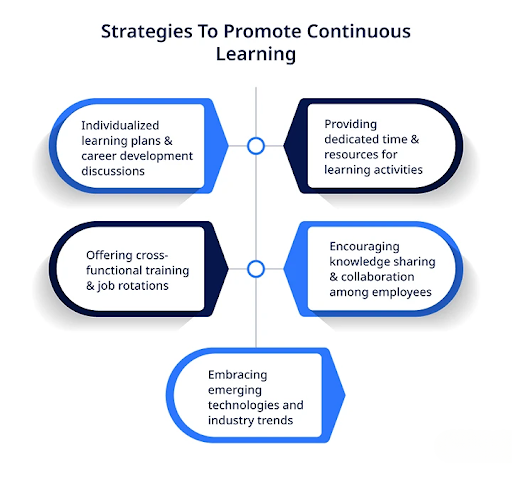
In a rapidly changing business environment, continuous learning is essential for both personal and organizational growth. Encouraging a culture of learning ensures that the organization remains agile and competitive.
Approaches to Foster Continuous Learning
- Professional Development Programs: Offering training and development opportunities to enhance skills.
- Knowledge Sharing: Promoting the exchange of ideas and best practices within the organization.
- Encouraging Innovation: Creating an environment where experimentation and innovation are valued.
Continuous learning not only enhances individual capabilities but also drives organizational excellence and adaptability.
Leveraging External Networks and Resources

In addition to internal development, leveraging external networks and resources is crucial for a CEO’s effectiveness. External networks provide access to diverse perspectives, expertise, and opportunities for collaboration.
Benefits of External Networks
- Knowledge Exchange: Gaining insights from industry peers, mentors, and experts.
- Business Opportunities: Identifying potential partnerships, collaborations, and market expansion opportunities.
- Resource Access: Accessing resources such as funding, technology, and talent through external partnerships.
By effectively leveraging external networks and resources, CEOs can enhance their strategic capabilities and drive organizational success.
Measuring Leadership Effectiveness
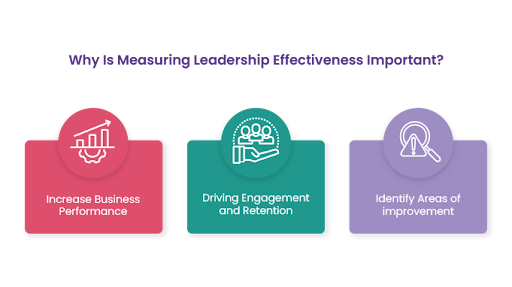
Assessing the effectiveness of leadership is essential for continuous improvement and ensuring that the organization is on the right path to achieving its goals.
Key Metrics to Measure Leadership Effectiveness
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: High levels of engagement and satisfaction indicate effective leadership.
- Retention Rates: Low turnover rates suggest a positive work environment and strong leadership.
- Performance Metrics: Achieving or exceeding business goals reflects successful leadership.
- Feedback and Surveys: Regular feedback from employees and stakeholders provides insights into leadership performance.
Conclusion
The role of a CEO is both challenging and rewarding, requiring a delicate balance of strategic vision, personal development, ethical integrity, and team empowerment. Effective leadership is not a static trait but a dynamic process of continuous learning and adaptation. By focusing on self-awareness, emotional intelligence, resilience, strategic execution, ethical decision-making, and the development of others, CEOs can navigate the complexities of modern business and steer their organizations toward enduring success. Ultimately, the art of CEO leadership lies in the harmonious integration of personal growth and strategic acumen, creating a legacy of positive impact and sustainable achievement.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



