Table of Contents
Introduction
Meditation is a practice that involves focusing your mind and eliminating distractions to achieve a state of mental clarity and inner peace. It has been used for centuries as a means to reduce stress, enhance self-awareness, and promote overall well-being.
This practice transcends mere silence; it involves training the mind to focus, relax, and fully engage with the present moment. Whether one seeks to alleviate stress, enhance concentration, or pursue spiritual growth, meditation offers a variety of benefits.
This comprehensive guide will delve into meditation’s origins, its many advantages, and provide practical techniques for both beginners and those seeking advanced practices.
What is Meditation?

Meditation is a practice that trains the mind to focus, relax, and achieve a state of mental clarity. It involves techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and concentration to cultivate inner peace and awareness.
- Meditation has been practiced for centuries in various cultures and spiritual traditions, but today, it is widely used for stress reduction, emotional well-being, and overall mental and physical health.
- Whether through guided sessions, silent contemplation, or movement-based practices like yoga, meditation helps individuals develop a calmer, more balanced mind.
Benefits of Meditation
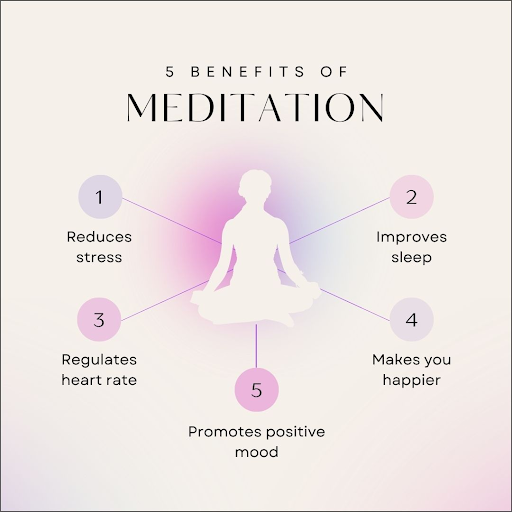
- Reduces Stress: Meditation lowers cortisol levels, helping to calm the nervous system, reduce anxiety, and promote relaxation.
- Improves Sleep: By quieting the mind and lowering stress, meditation helps improve sleep quality, making it easier to fall and stay asleep.
- Regulates Heart Rate: Deep breathing and mindfulness techniques support cardiovascular health by balancing the nervous system and lowering blood pressure.
- Makes You Happier: Meditation boosts serotonin and dopamine levels, enhancing overall happiness, gratitude, and emotional resilience.
- Promotes a Positive Mood: Regular meditation reduces negative emotions, fosters emotional balance, and helps maintain a more optimistic outlook on life.
Different Types of Meditation
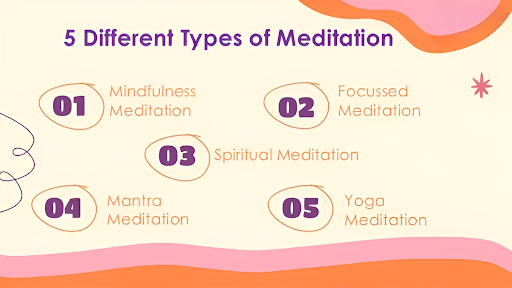
Meditation comes in many forms, each offering unique benefits for the mind, body, and soul. Whether you’re looking to enhance focus, deepen spiritual awareness, or simply find inner peace, different meditation techniques cater to various needs. Here’s a look at some popular meditation styles and how they can improve your well-being.
- Mindfulness Meditation: This practice involves staying fully present in the moment, observing thoughts without judgment. It helps reduce stress, improve concentration, and cultivate self-awareness.
- Focused Meditation: In this technique, you concentrate on a single object, sound, or sensation—such as your breath or a candle flame. It enhances focus, mental clarity, and patience.
- Spiritual Meditation: Often practiced in religious or spiritual settings, this form of meditation connects you with a higher power or inner self. It fosters inner peace, wisdom, and a sense of purpose.
- Mantra Meditation: This method involves repeating a specific word, phrase, or sound (like “Om”) to clear the mind. It promotes relaxation, mental clarity, and deeper meditation states.
- Yoga Meditation: Combining movement and mindfulness, yoga meditation synchronizes breath and body postures. It enhances flexibility, reduces stress, and promotes overall well-being.
How to Start Meditating as a Beginner

Meditation doesn’t have to be complicated. By practicing a few simple techniques, you can cultivate inner peace, reduce stress, and enhance mindfulness in just a few minutes each day. Here are some effective methods to get started:
- Set a Timer for 2-3 Minutes: If you’re new to meditation, start small. Setting a short timer helps you stay focused without worrying about the time.
- Focus on Your Breathing: Your breath is a natural anchor for your mind. Pay attention to the sensation of air entering and leaving your nose or the rise and fall of your chest.
- Be Aware of Your Thoughts: It’s normal for thoughts to arise during meditation. Instead of resisting them, observe them like passing clouds in the sky.
- Inhale to the Count of 3: Breathe in slowly and deeply, counting to three. Feel your lungs expand and your body fill with fresh oxygen, energizing and calming you at the same time.
- Exhale to the Count of 5: Release your breath gradually, counting to five as you exhale. This longer exhalation activates your parasympathetic nervous system, which helps your body relax and reduces stress.
- Use Sound or a Mantra: Repeating a calming phrase like “I am peace” or using a gentle sound can enhance your meditation. Mantras help keep the mind focused and reinforce a sense of calm and positivity.
- Keep a focussed mind: It’s natural for your mind to drift to thoughts, worries, or distractions. Instead of feeling frustrated, simply notice the wandering and gently redirect your attention back to your breath.
The Science Behind Meditation
The tradition of meditation has been around for millennia, yet we are just starting to understand the science that explains how this straightforward mental practice can lead to substantial transformations in both our bodies and minds.
Similar to physical workouts, the more consistently you engage in meditation, the greater the benefits you will experience, and the longer these effects will persist..
How Meditation Changes the Brain
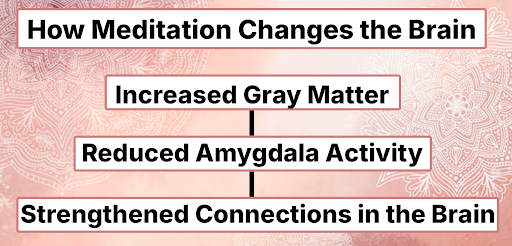
Meditation triggers neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize itself. Key changes include:
- Increased Gray Matter: Studies show that regular meditation increases gray matter density in areas linked to memory, learning, and emotional regulation, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
- Reduced Amygdala Activity: The amygdala, responsible for stress and fear responses, shrinks with consistent meditation practice. This leads to better emotional regulation and reduced anxiety.
- Strengthened Connections in the Brain: Meditation enhances connectivity between different regions of the brain, particularly those involved in focus, self-awareness, and empathy.
Scientific Studies on Meditation and Mental Health

Research confirms the profound impact of meditation on mental well-being:
- A Harvard study (2011) found that an 8-week mindfulness meditation program increased cortical thickness in the hippocampus, improving learning and memory while reducing stress.
- A Johns Hopkins meta-analysis (2014) reviewed 47 studies and found that meditation can significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and pain.
- A University of California study found that long-term meditators had better cognitive function and a lower risk of age-related brain decline.
Meditation and Breathing Techniques

Breathing is an essential part of meditation, serving as a bridge between the body and mind. It directly influences the nervous system, emotional state, and mental clarity. By focusing on breath control, meditation enhances relaxation, reduces stress, and improves overall well-being.
How Breathing Affects Meditation
Breath control is central to meditation because it regulates physiological and psychological states. Different breathing patterns affect the nervous system in unique ways:
- Slow, deep breathing stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” response. This reduces stress, slows heart rate, and promotes relaxation.
- Shallow, rapid breathing activates the sympathetic nervous system, triggering the “fight or flight” response. This can increase anxiety, raise blood pressure, and cause mental restlessness.
- Conscious breathing enhances oxygen flow to the brain, improving focus, emotional regulation, and cognitive function. It also helps bring awareness to the present moment, deepening the meditation experience.
By practicing controlled breathing techniques, meditators can shift their mental state, achieve greater relaxation, and enhance mindfulness.
Popular Breathing Techniques in Meditation

Different breathing techniques have unique benefits and applications. Here are some of the most effective ones:
Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
Also known as abdominal breathing, this technique focuses on deep, intentional breaths using the diaphragm.
How to Practice:
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly.
- Inhale deeply through your nose, expanding your belly while keeping your chest still.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth or nose, feeling your belly contract.
- Repeat for a few minutes, maintaining a steady rhythm.
Box Breathing (4-4-4-4 Method)
Box breathing is a technique used by athletes, military personnel, and meditation practitioners to improve focus and calm the mind.
How to Practice:
- Inhale deeply through the nose for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 4 seconds.
- Exhale slowly through the mouth for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath again for 4 seconds.
- Repeat this cycle for a few minutes.
Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
This ancient yogic breathing technique is believed to balance the brain’s hemispheres and improve mental clarity.
How to Practice:
- Sit in a comfortable meditation posture.
- Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale deeply through your left nostril.
- Close your left nostril with your ring finger, release the right nostril, and exhale through the right nostril.
- Inhale through the right nostril, then switch and exhale through the left.
- Continue alternating for a few minutes.
4-7-8 Breathing
This breathing technique, popularized by Dr. Andrew Weil, is designed to induce deep relaxation and aid sleep.
How to Practice:
- Inhale deeply through the nose for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds.
- Exhale slowly and completely through the mouth for 8 seconds.
- Repeat for 4–8 cycles.
Integrating meditation into your daily routine doesn’t require hours of practice. Small, consistent efforts can make a significant impact on your well-being.
Tips to Incorporate Meditation into Daily Life

Starting a meditation practice can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. The key is to begin with small, manageable steps and gradually build consistency. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to deepen your practice, these simple strategies can help you integrate meditation into your daily routine effortlessly.
- Start Small: Begin with just a few minutes of meditation each day. Short, consistent sessions are more effective than long, irregular ones.
- Set a Regular Schedule: Establishing a fixed time for meditation, whether in the morning or before bed, helps create a habit and makes practice easier to maintain.
- Use Guided Meditations: If you’re unsure where to start, guided meditations can provide structure and help you stay focused, especially as a beginner.
- Pair Meditation with Daily Activities: Integrate meditation into existing routines, such as after brushing your teeth, during a lunch break, or before bedtime, to make it a natural part of your day.
- Create a Dedicated Space: Designate a quiet, comfortable space for meditation to signal your mind that it’s time to relax and focus. A peaceful environment enhances the experience.
- Practice Mindful Breathing Anytime: You don’t have to set aside a specific time to meditate. Practicing mindful breathing during daily activities like walking or waiting in line can help bring calmness and presence to any moment.
Connection of Meditation and Mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present in the moment without judgment. Meditation is one of the most effective ways to cultivate mindfulness, but mindfulness can also be practiced in everyday activities.
How Meditation Enhances Mindfulness

- Improves Focus: Meditation strengthens attention, making it easier to stay present.
- Reduces Stress: By training the brain to observe thoughts without reacting, meditation lowers stress and emotional reactivity.
- Enhances Self-Awareness: Regular meditation fosters a deeper understanding of thoughts and emotions.
- Encourages Gratitude: Mindfulness meditation promotes appreciation for simple moments.
- Increases Emotional Resilience: Meditation helps regulate emotions, reducing anxiety and negative thought patterns.
Ways to Practice Mindfulness in Daily Life
- Eat mindfully: Pay attention to the taste, texture, and aroma of your food.
- Listen actively: Fully engage in conversations without distractions.
- Observe surroundings: Take a few moments to notice sights, sounds, and sensations around you.
- Practice gratitude: Reflect on things you appreciate daily.
By combining meditation with everyday mindfulness, you can create a more peaceful and fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Meditation is a powerful tool for mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall well-being. By incorporating simple breathing techniques, mindfulness, and daily meditation practices, you can experience lasting benefits such as reduced stress, improved focus, and greater self-awareness.
You don’t need hours of practice—just a few minutes each day can transform your mindset and bring more peace into your life. Whether through guided meditation, mindful breathing, or movement-based techniques, meditation is a lifelong skill that enhances both personal and professional life.
Start small, be consistent, and enjoy the journey toward a calmer, more mindful life.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



