Table of Contents
“We need to do what has been done for airline safety, car safety, drug safety, medical device safety,” Blumenthal said. “AI safety is no different — in fact, potentially even more dangerous.”
Richard Blumenthal, US Senator
“I thought Satya Nadella from Microsoft said it best: ‘When it comes to AI, we shouldn’t be thinking about autopilot. You need to have copilots. ‘ So who’s going to be watching this activity and making sure that it’s done correctly?”
Maria Cantwell, US Senator
“My worst fear is that we, the industry, cause significant harm to the world. I think, if this technology goes wrong, it can go quite wrong and we want to be vocal about that and work with the government on that.”
Sam Altman
“The consequences of AI going wrong are severe so we have to be proactive rather than reactive.”
Elon Musk
Introduction
OpenAI and Google’s Bard are distinct artificial intelligence systems, each designed by separate organizations with their own set of features and capabilities. They are both fueled by advanced large language models (LLMs), enabling them to produce natural and coherent responses to various user inquiries. Additionally, these technologies can connect to the internet and other external resources, ensuring that they deliver information that is both current and pertinent.
However, they also differ in their features, advantages, and limitations, which are as follows:
Developer
- OpenAI: OpenAI is an AI research and deployment company that developed ChatGPT, and other AI models like DALL-E.
- Google’s Bard: Bard is developed by Google, a multinational technology company well-known for its search engine.
Capabilities:
- OpenAI: OpenAI’s models are known for text generation, conversation, and answering queries. DALL-E, another OpenAI creation, specializes in generating images from textual descriptions.
- Google’s Bard: Bard, as a product of Google, might integrate more deeply with Google’s ecosystem, including search, and could be designed to enhance conversational AI and answer complex queries.
Implementations:
- OpenAI: ChatGPT is used for conversation, content creation, coding assistance, and more. DALL-E is used for creative image generation.
- Google’s Bard: The exact applications of Bard would depend on Google’s strategy, but it could include enhancing Google’s search engine, integration into Google’s suite of products, and possibly new applications in AI-assisted tasks.
Availability and Accessibility:
- OpenAI: OpenAI’s products are generally available to the public, with some restrictions or waiting lists for certain models.
- Google’s Bard: The availability of Bard would depend on Google’s release strategy, which might initially involve limited access or specific use cases.
User Interface:
- OpenAI: OpenAI provides user-friendly interfaces for its tools, often accessible via web platforms.
- Google’s Bard: Google is known for its user-friendly designs, so Bard is likely to have an accessible and intuitive interface.
Ethics and Safety Guidelines:
- OpenAI: OpenAI emphasizes ethical AI development and deployment, with guidelines and safety measures to mitigate misuse and biases.
- Google’s Bard: Google, with its AI Principles, also focuses on responsible AI development, prioritizing fairness, safety, and privacy.
In summary, while both OpenAI and Google’s Bard are developed by leading organizations in the field of AI, their focus, applications, and integration with existing products and services might differ. The landscape of AI is rapidly evolving, so new developments and features might emerge beyond this comparison.
Key Statistics
OpenAI:
- In 2023 OpenAI is the 19th most popular website in the world with an average of 1.9 billion visits per month.
- Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI in 2019.
- In 2023 Microsoft invested an additional $10 billion among all the social media platforms YouTube (55.47%) and WhatsApp (11.26%) send the most traffic to OpenAI.
Bard AI:
- Google Bard was officially released on February 8, 2023. The access was opened up on March 21, 2023.
- The estimated reach of Google Bard is 1 billion users.
- Currently, Google Bard is available in 43 languages.
- The estimated reach of Google Bard is 1 billion users. That means almost 1 out of 8 people worldwide will use Google Bard.
OpenAI ChatGPT: An Overview
OpenAI is a non-profit organization focused on creating AI that is safe and beneficial. It was founded in December 2015 by notable figures such as Elon Musk, Sam Altman, Greg Brockman, and Ilya Sutskever.
The primary mission of OpenAI is to ensure that artificial general intelligence (AGI) is developed in a manner that benefits all of humanity.OpenAI is committed to achieving long-term safety, technical leadership, and cooperative orientation.

It aims to directly build safe and beneficial AI while also contributing to the larger global AI community.OpenAI is a community of brilliant minds, collaborating and sharing knowledge to unlock the full potential of AI. It is a haven for open-source research, fostering transparency and driving progress on a global scale.
OpenAI believes that AI when developed ethically and thoughtfully, can pave the way for a brighter future. It is not just a company, but a movement towards a future where AI empowers, inspires, and solves the challenges we face as a global community.
Google Bard: An Overview
Bard is a powerful language model developed by Google Research that can produce highly creative and contextually relevant text. It employs advanced techniques, such as neural architecture search and reinforcement learning, contributing to its exceptional performance in generating state-of-the-art content.
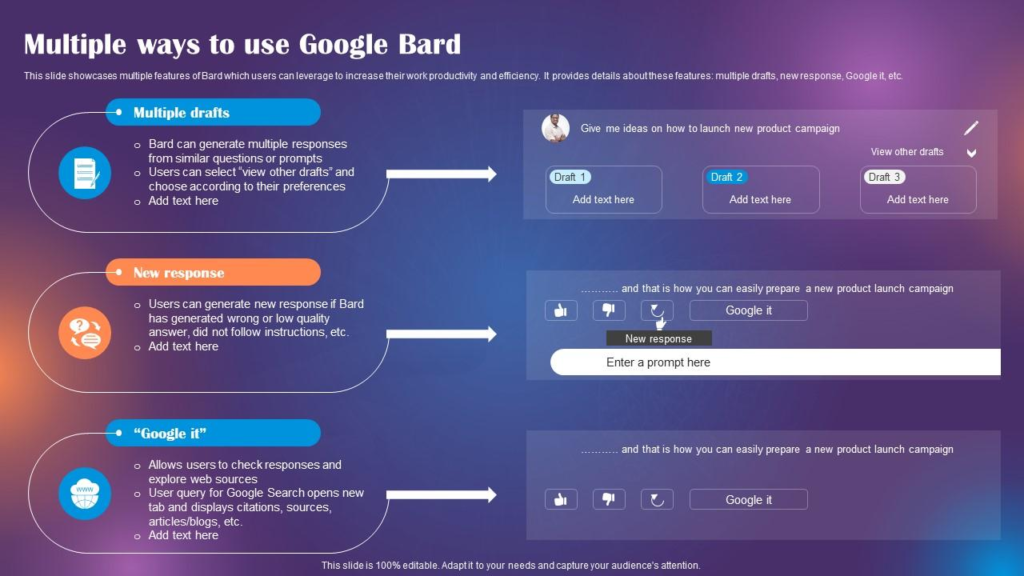
Bard represents a new era of AI that places conversations at the forefront and allows knowledge to flow freely. It has unparalleled access to information, enabling it to answer questions, fulfill requests, and engage in conversations with a depth and breadth rarely seen in AI.
Bard’s capabilities extend beyond textual communication, as it can leverage Google’s image recognition and understanding to analyze pictures, summarize videos, and even generate visuals based on your descriptions. Bard represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with AI, opening the door to a more natural, human-like dialogue.
Comparison of Open AI and Bard AI

In terms of Model Size:
Open AI:
- GPT-4: OpenAI’s GPT-4 is a language model that boasts an impressive number of 175 billion parameters, making it one of the largest models in existence.
- Its massive size allows it to excel in various natural language processing tasks, such as generating coherent text, translating languages, and writing code.
- The model’s advanced linguistic capabilities make it a valuable tool for businesses and academics seeking to improve their language-based applications.
- DALL-E 3: OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 is not just a collection of words; it’s a visual alchemist with an astounding 137 billion parameters that enable it to bring breathtaking images to life from simple text descriptions.
- This cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the way we generate images and has opened up endless creative possibilities for artists and designers alike.
Bard AI:
- 137 billion parameters: It’s interesting to note that Bard has the same number of parameters as OpenAI’s DALL-E 3, despite still being in its developmental stage. This is a testament to Google’s strong dedication to AI research, as well as its vast computational resources.
- Evolving Architecture: Bard is an AI model that stands out from OpenAI’s dedicated models due to its flexible architecture. It can easily handle various tasks, such as text generation, image analysis, and code creation, making it a versatile solution. This jack-of-all-trades approach allows for seamless switching between tasks.
In terms of Features: - Open AI:
Language Mastery: OpenAI is a leader in text generation, with GPT-4 as its crown jewel. GPT-4 can produce poems, code, and scripts with remarkable accuracy and fluency.
Beyond the Canvas: OpenAI’s reach extends beyond text and images. They delve into robotics, crafting machines that learn and dance and explore game development, building virtual worlds brimming with intelligence.
Bard AI:
- Conversational Chameleon: Bard excels at natural language processing, seamlessly engaging in dialogue, interpreting nuances, and responding with wit. Whether you seek factual answers, playful banter, or creative prompts, Bard keeps the conversation flowing.
- Knowledge Ocean: Bard has a never-ending passion for knowledge, which derives from Google’s extensive knowledge base. It is capable of gathering facts, simplifying complicated topics, and providing updates on various topics of interest. Additionally, Bard is always up-to-date on current events.
In terms of Pricing:
Open AI:
- Tiered Approach: OpenAI offers a tiered pricing structure, ranging from free access for researchers and educators to paid subscriptions for businesses and developers. This caters to diverse needs and budgets, fostering responsible development while ensuring commercial viability.
- API Access: OpenAI offers paid API access to their models for advanced users, which enables developers to incorporate them into their projects and applications. This collaboration and innovation allow for the expansion of what AI can accomplish.
Bard AI:
- Currently in Beta: As a project still under development, Bard offers free public access. This open beta phase allows users to explore its capabilities, provide feedback, and contribute to its growth.
- Future Monetization: Bard’s upcoming pricing strategy is not yet fully defined, but it may involve joining forces with Google’s existing services or experimenting with subscription models. This approach would enable a gradual implementation process and better alignment with Google’s established ecosystem.
Applications of Open AI and Bard
OPENAI APPLICATIONS
Bing Copilot:

Bing Copilot is an AI-powered digital assistant that offers a more natural and efficient way of browsing the internet. It’s more than just a search engine as it understands user queries and provides comprehensive and summarized answers. Formerly known as Bing Chat, it helps users navigate the web with ease. Here’s a breakdown of what Bing Copilot can do:
- Go beyond keywords: With Bing Copilot, you can ask open-ended questions instead of typing in a string of keywords.
- Get consolidated answers: Bing Copilot provides accurate information by presenting a single answer with cited sources.
- Ask follow-up questions: Bing Copilot provides in-depth answers to your follow-up questions, like talking to a knowledgeable friend.
- Get things done: Bing Copilot is more than an information gatherer. It can book flights, find restaurants, and write emails for you. Just tell it what you need, and it will help.
- Available on multiple platforms: Bing Copilot is easily accessible through the Microsoft Bing website, Edge browser, and Microsoft 365 apps.
Copilot and ChatGPT are two AI-powered chatbots that are rivals in the market. Each of them has its unique strengths. Copilot offers free web access, GPT-4, and well-crafted responses, while ChatGPT has a higher character limit and faster processing speed. Ultimately, choosing between them depends on personal preferences – if you value robust features, Copilot might be your choice. But if you prioritize a fast and free experience, ChatGPT might be the better option for you.
Google Gemini AI:

In January 2023, Google AI announced the launch of Google Gemini AI, a new artificial intelligence model. This model is a large language model (LLM) that has been trained on an extensive dataset of text, images, and audio. As a result, it is capable of comprehending and answering a broad range of prompts and questions, including those that are challenging, open-ended, or unusual.
Gemini AI has many potential applications, including:
- Natural language understanding and generation: Gemini AI can understand text, translate languages, create various content, and answer your questions.
- Image and audio recognition: Gemini AI can be used to identify objects and scenes in images, and to understand the meaning of audio.
- Machine translation: Gemini AI can be used to translate text from one language to another.
- Code generation: Gemini AI can be used to generate code for different programming languages.
- Creative content generation: Gemini AI can be used to generate different creative text formats, like poems, code, scripts, musical pieces, emails, letters, etc.
The integration of Gemini with Google’s Bard chatbot has significantly improved user interaction. By leveraging the advanced capabilities of Gemini, Bard is now able to better understand user intent, leading to more accurate and high-quality responses. Additionally, the multimodal processing enabled by Gemini allows Bard to handle various types of media including text, images, audio, and video, seamlessly.
Future of AI

Future of Artificial Intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) has a bright future, but it also faces several difficulties. AI is predicted to grow increasingly pervasive as technology develops, revolutionizing sectors including healthcare, banking, and transportation.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to become more pervasive and integrated into our daily lives over the next 10 years. Some experts believe that AI has a bright future, with continuous advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
Some say that AI will enhance various industries and transform the way we live and work. For example, AI can help analyze medical images and potentially save a patient’s life. AI is also expected to play a crucial role in the field of transportation, with self-driving cars becoming more popular. However, others say that the development of AI capable of doing different tasks similar to human intelligence is far away. They say that it will take years or centuries to create such AI applications and that the efficiency of such AI is not predictable at the current stage.
Here’s a glimpse into the anticipated trajectories and key themes in the future of AI:
- Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Language models are getting better, making interactions more natural and context-aware. Translation and summarization abilities are also improving, allowing for a better understanding of nuanced human language. - AI in Healthcare:
AI-powered diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. Predictive analytics for disease prevention and early intervention. Accelerated drug discovery and development through AI algorithms. - Autonomous Systems and Robotics:
The transportation and logistics industry is seeing a rise in the use of autonomous vehicles and drones. Meanwhile, industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and services are increasingly adopting AI-powered robotics. Additionally, advancements in humanoid robots are allowing for more complex tasks to be performed. - AI in Education:
Individualized learning experiences personalized to each student’s needs. AI-powered assessments provide a more accurate evaluation of progress. Virtual assistants and tutors support educators in the classroom. - Ethical AI and Responsible Development:
There has been a growing focus on tackling bias, promoting fairness, and ensuring transparency in AI systems. To that end, ethical guidelines and regulations are being developed to govern AI applications. Additionally, there is an increased awareness and collaboration among stakeholders to ensure the responsible deployment of AI. - Human-AI Collaboration:
The use of AI assistance is on the rise, as it helps augment human capabilities across various domains. We can also see an increase in AI integration in decision-making processes across different industries. By collaborating with AI systems, humans can achieve more efficient and effective outcomes.
Conclusion
OpenAI and Google Bard are two impressive language models that have their distinct strengths and limitations. OpenAI is particularly adept at handling dynamic conversations and can retrieve a vast range of knowledge, making it ideal for applications that require extensive data retrieval.
On the other hand, Google Bard’s strength lies in its ability to craft compelling and engaging narratives, making it a top choice for applications that require a narrative-driven approach. By understanding the differences between these two models, you can pick the one that best suits your specific needs. As natural language processing continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and contextually-aware models to emerge.
FAQ's
While both are large language models, their objectives differ. OpenAI focuses on general-purpose AI aiming for artificial general intelligence. Bard prioritizes information retrieval and factual accuracy, drawing information from the real world through internet access. This leads to contrasting development approaches, with OpenAI emphasizing self-learning and exploration, while Bard leverages Google’s vast data and knowledge graph.
Both can do creative writing, but their strengths differ. OpenAI’s ChatGPT is known for its imaginative and engaging narratives, while Bard excels at generating specific formats like poems and scripts due to its access to external information and structure libraries. Ultimately, the “better” choice depends on your desired stylistic tone and level of factual accuracy.
Bard emphasizes factual accuracy by accessing and referencing real-world information. OpenAI prioritizes generating fluent and engaging text, which can occasionally lead to factual inconsistencies. Both models are trained on massive datasets and susceptible to biases present in that data. However, Bard’s focus on factual sources and Google’s efforts to mitigate bias might give it an edge in factual accuracy.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT is currently more accessible with a publicly available free tier and various third-party integrations. Bard’s access is currently limited through research partnerships and internal Google testing. ChatGPT focuses on user interaction and open-ended conversation, while Bard’s strengths lie in information retrieval and task completion.
OpenAI aims to advance towards artificial general intelligence, creating AI capable of reasoning, learning, and adapting like humans. Bard’s future likely lies in integrating deeper with Google’s products and services, enhancing information access and task automation capabilities. Both are expected to contribute significantly to the ongoing advancements in the field of artificial intelligence.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



