Table of Contents
Introduction
AI is everywhere now—from drafting emails to building apps and chatting like a human—thanks to Large Language Models (LLMs), enabled by training on vast amounts of text data and powered by cutting-edge neural networks and supercomputers.
As global enterprises increasingly embed AI across product development, customer experience, operations, and research, decision makers face a growing question: which AI model offers the right balance of capability, cost, and safety? With models like Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok, Perplexity, and DeepSeek pushing boundaries in context window size, multimodal inputs, real-time retrieval, and interpretability, understanding how each performs in enterprise settings is no longer optional.
We will explore top names that are leading AI LLMs : Claude.ai, ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Grok, Gemini, and Perplexity AI —highlighting their design, features, and best use cases to help you choose the right LLM for tasks like creativity, research, or app development.
Each one has unique features and capabilities,
- Claude.ai is safety-focused, large-context AI for advanced problem-solving
- ChatGPT is a real-time, citation-backed information provider via cloud integrations and plugins
- DeepSeek is a cost-efficient, open-source LLM with multilingual, multimodal prowess
- Grok is an AI with live web/Twitter access and “Think” modes for transparent reasoning
- Gemini is a fully multimodal, Google-integrated AI for deep reasoning and creation
- Perplexity AI is a citation-driven chat search engine with Pro tools for visuals and research
All of this innovation in large language models has been made possible, in large part, by the GPU chips from NVIDIA. With fast storage and strong networks, these GPUs work together in data centers to support today’s most advanced language models.
Looking ahead, new paradigms such as GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) are shifting how enterprises think about deploying AI. AIO refers to integrated platforms that combine multiple LLM modalities (text, image, voice, code) with built-in governance, safety, and deployment tools—allowing companies to avoid cobbling together multiple models for different tasks.
Understanding Large Language Models (LLM)
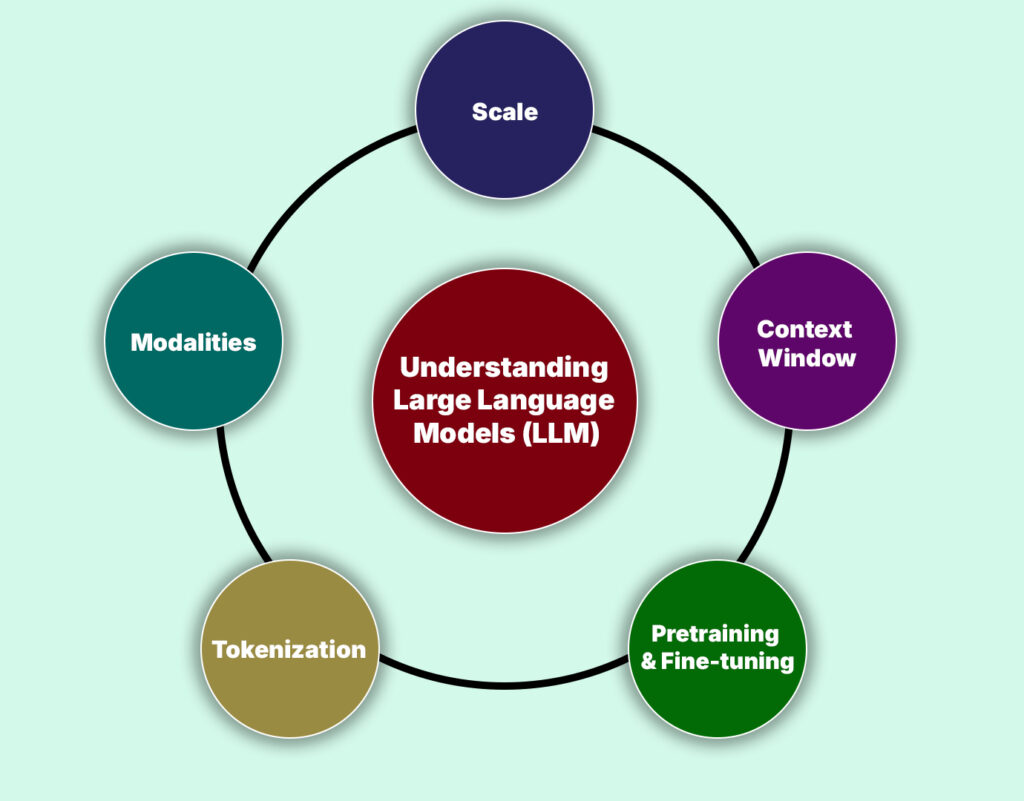
Large language models (LLMs) are neural networks trained on vast text data to predict the next token in a sequence, enabling tasks like text completion, summarization, question-answering, and code generation. Key characteristics of LLMs include:
- Scale: Modern LLMs often exceed hundreds of billions of parameters. Training such models demands hundreds of petaflop/s-days of compute across clusters of GPUs or specialized AI accelerators.
- Context Window: Each model has a maximum context length—how many tokens it can consider at once. Larger context windows enable handling longer documents or conversations without losing coherence.
- Pretraining & Fine-tuning: LLMs are pretrained on general web-scraped text and then fine-tuned (or instruction-tuned) on task-specific data or human feedback to improve their performance on downstream tasks.
- Modalities: Many recent models extend beyond pure text to incorporate images, audio, or code, yielding multimodal capabilities.
- Tokenization: Text is broken into tokens—subword units—so that the model’s vocabulary remains manageable while still representing rare words. Tokenization methods include byte-pair encoding (BPE), WordPiece, and SentencePiece.
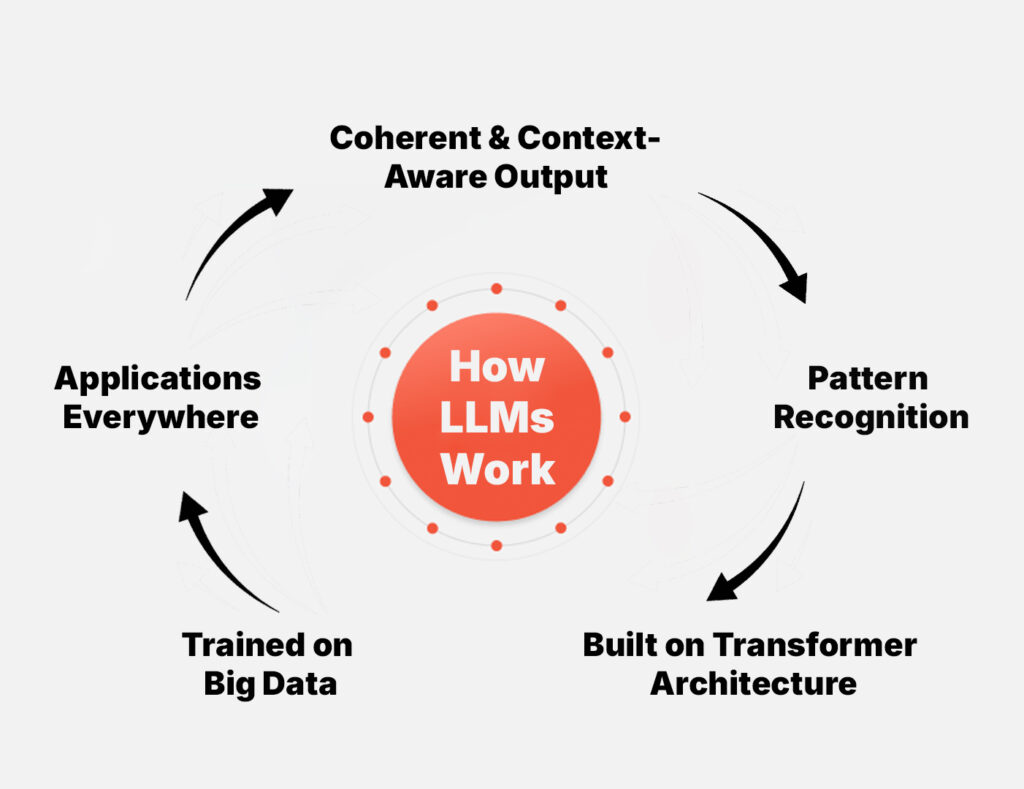
- Built on Transformer Architecture: LLMs use transformer blocks—the foundation of modern AI models.
- Pattern Recognition: These components help LLMs recognize vast patterns across massive datasets.
- Coherent & Context-Aware Output: LLMs generate and analyze text with an understanding of context, tone, and structure.
- Trained on Big Data: They learn from billions of words, enabling deep language comprehension.
- Applications Everywhere: From answering questions to writing content and coding—LLMs power everyday AI tools.
At their core, LLMs leverage transformer blocks composed of self-attention layers, feedforward networks, and layer normalization. The end result is a model that encodes vast patterns in data and can generate or analyze text in a coherent, context-aware manner.
Overview of Each LLM
Below is a high-level overview of the six LLMs—Claude.ai, ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Grok, Gemini, and Perplexity AI—with specific attention to their search capabilities and distinctive features.
Claude.ai

- Description: Claude.ai is a family of AI assistants (Haiku, Sonnet, Opus) designed around Anthropic’s emphasis on safety and alignment. It is trained to follow user instructions carefully while minimizing harmful outputs.
- Search Capabilities: Claude.ai supports external retrieval through plugins for web searches or knowledge-base lookups, with newer “Opus” versions enabling real-time browsing.
- Strengths: Claude.ai focuses on delivering safe, reliable responses with strong long-form reasoning supported by extended context windows—up to 200K tokens, and even 1 million for enterprise users. It excels at summarization, explanation, and coding tasks.
ChatGPT

- Description: ChatGPT (in its GPT-4.1 and GPT-4o variants) is one of the most widely adopted LLMs, known for versatility in chat-based interactions, code generation, and creative writing.
- Search Capabilities: ChatGPT has optional “plugins” enabling real-time web access, including a built-in browsing plugin that fetches up-to-date information. Additionally, specialized retrieval-augmented setups allow integration with private knowledge bases or document stores.
- Strengths: GPT-4.1 offers a large context window of up to 1 million tokens, making it ideal for handling lengthy or complex inputs. It’s well-tuned for instruction-following and conversational tasks, ensuring accurate and coherent responses.
DeepSeek

- Description: DeepSeek specializes in open-source, high-performance reasoning models. Its flagship, DeepSeek R1, focuses on mathematical reasoning, code generation, and logic-intensive tasks.
- Search Capabilities: DeepSeek R1 does not natively browse the web but can be integrated into retrieval-augmented pipelines. Custom builds often combine DeepSeek with vector search indexes (e.g., FAISS or Elasticsearch) to fetch documents dynamically.
- Strengths: This model offers cost-effective pricing, strong performance on academic and coding benchmarks, and open-source weights that support on-premise deployment and customization.
Grok

- Description: Grok is xAI’s in-house LLM brand, trained on their Colossus supercluster. Grok versions progressively expand reasoning abilities and context window sizes.
- Search Capabilities: Grok 3 comes with built-in real-time search via xAI’s proprietary data pipeline, allowing it to fetch and cite up-to-the-minute information (e.g., news, social media). This search integration differentiates Grok from many static models.
- Strengths: Grok offers real-time web search with citations via its “Grok it!” feature, supports up to 1M-token context windows, and excels at multi-step reasoning and complex code tasks.
Gemini

- Description: Gemini (versions 2.0, 2.5 Pro) is Google’s next-generation multimodal AI, optimized for text, images, audio, video, and code. The “Deep Think” capability in 2.5 Pro allows extended chain-of-thought reasoning.
- Search Capabilities: Gemini ties into Google’s existing search infrastructure. Via Google Search APIs or a specialized retrieval layer, Gemini can query web index data and knowledge graphs, returning grounded, citation-backed responses.
- Strengths: Gemini supports true multimodality—text, image, audio, video, and code—along with deep integration with Google Search for improved accuracy. Its 1M-token context window handles long and complex inputs with ease.
Perplexity AI

- Description: Perplexity is a search-centric LLM that merges an internal GPT-based engine with real-time search results. It emphasizes concise, citation-backed answers akin to a modern “AI search engine.”
- Search Capabilities: Perplexity’s core differentiator is native web grounding—each query invokes an internal browsing routine that retrieves relevant pages, summarizes content, and provides linked citations.
- Strengths: This model provides real-time citations and source attribution, making it well-suited for research-style Q&A and fact validation. It also offers lightweight deployment tiers, allowing for quick and efficient integration into various workflows.
Company Profiles Behind the Models
Building and operating a state-of-the-art LLM requires massive infrastructure investments. Below, we outline each organization’s data center footprint and overarching infrastructure commitments.
Anthropic (Claude.ai)
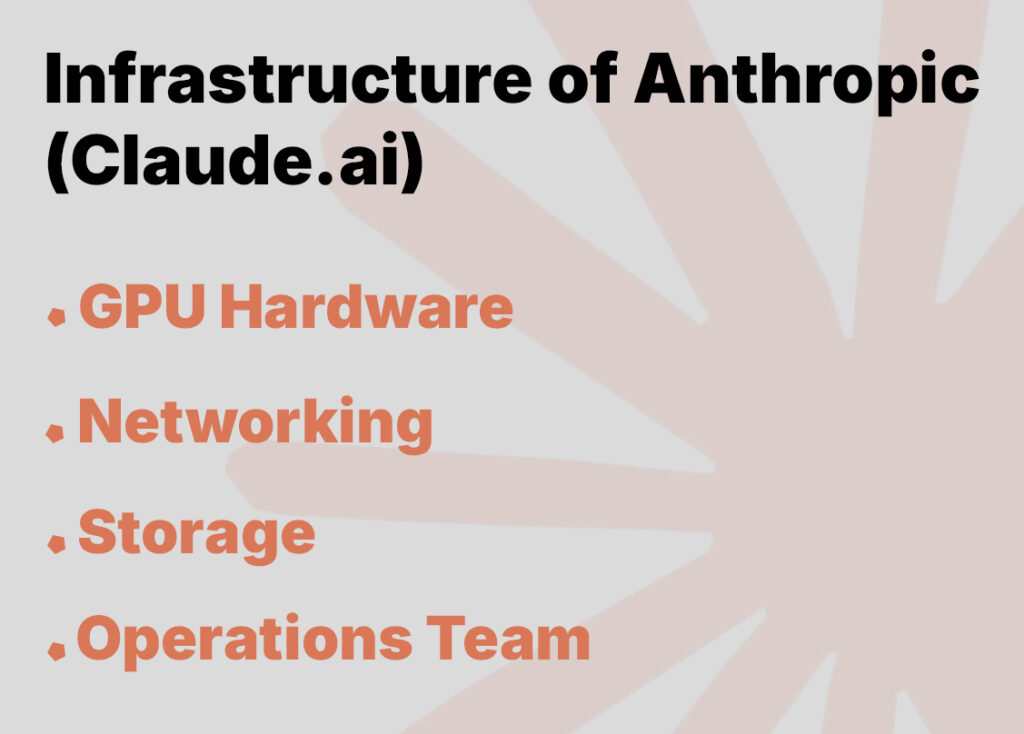
Anthropic maintains several private data centers in North America and Europe, each densely packed with NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD clusters. Their infrastructure includes:
- GPU Hardware: Primarily NVIDIA H100 and A100 GPUs for training and inference.
- Networking: High-speed InfiniBand fabric (200 Gbps) to interconnect GPU nodes, reducing training times.
- Storage: Petabyte-scale NVMe SSD arrays for training data, model checkpoints, and retrieval indexes.
- Operations Team: A dedicated site reliability engineering (SRE) group oversees 24/7 monitoring, automated scaling, and failsafe redundancies.
OpenAI (ChatGPT)
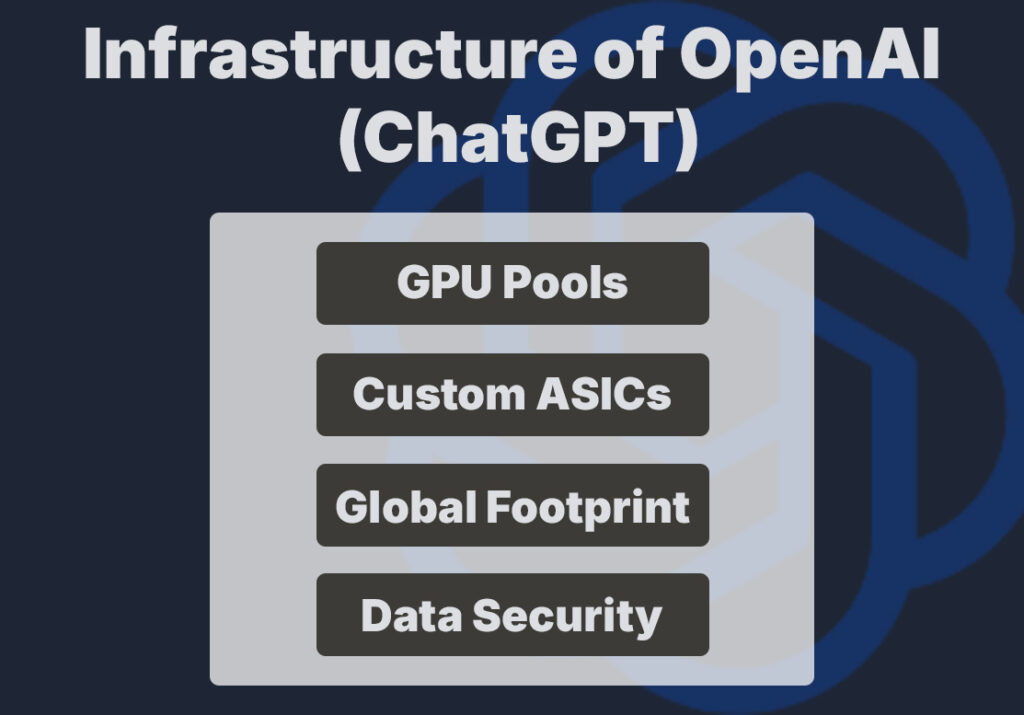
- GPU Pools: Thousands of NVIDIA GPUs (H100, A100), often in cluster form for distributed training.
- Custom ASICs: Early experiments with custom inference chips to accelerate production workloads.
- Global Footprint: Via Azure, OpenAI can run inference endpoints close to end users, minimizing latency.
- Data Security: Strict data governance policies, encryption at rest and in transit, and isolated compute for sensitive tasks.
DeepSeek AI
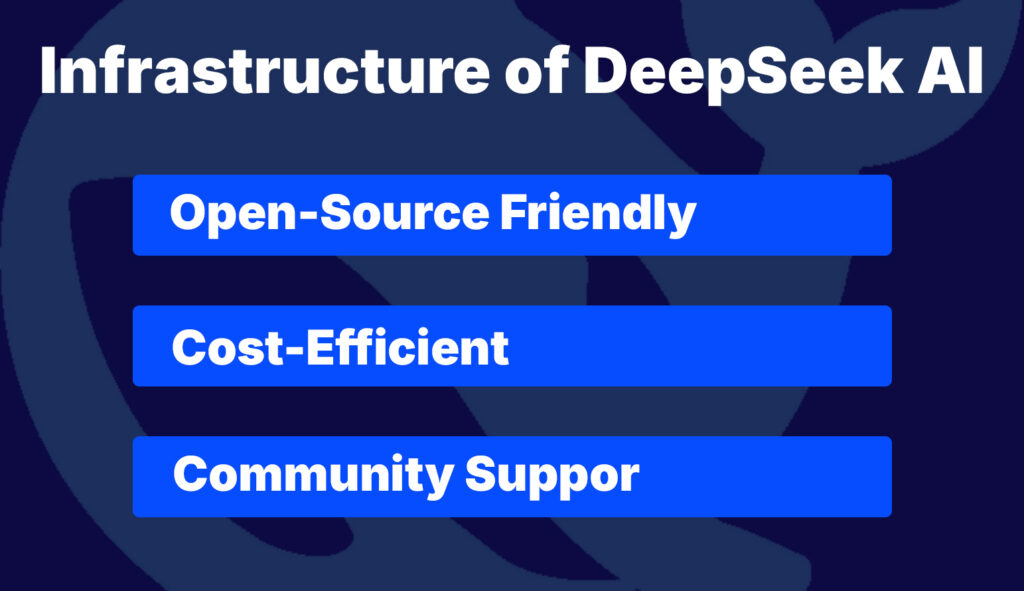
DeepSeek focuses on making LLMs accessible via open-source releases and smaller compute footprints. Their infrastructure model:
- Open-Source Friendly: Models are released in Docker containers optimized for single-node GPU inference (e.g., 8×A100).
- Cost-Efficient: Rather than sprawling data centers, DeepSeek partners with cloud providers (AWS, GCP) for on-demand GPU rentals, passing savings to end users.
- Community Support: A growing ecosystem of researchers and hobbyists contribute to model improvements, extending inference options to smaller clusters or even high-end consumer GPUs.
xAI (Grok)
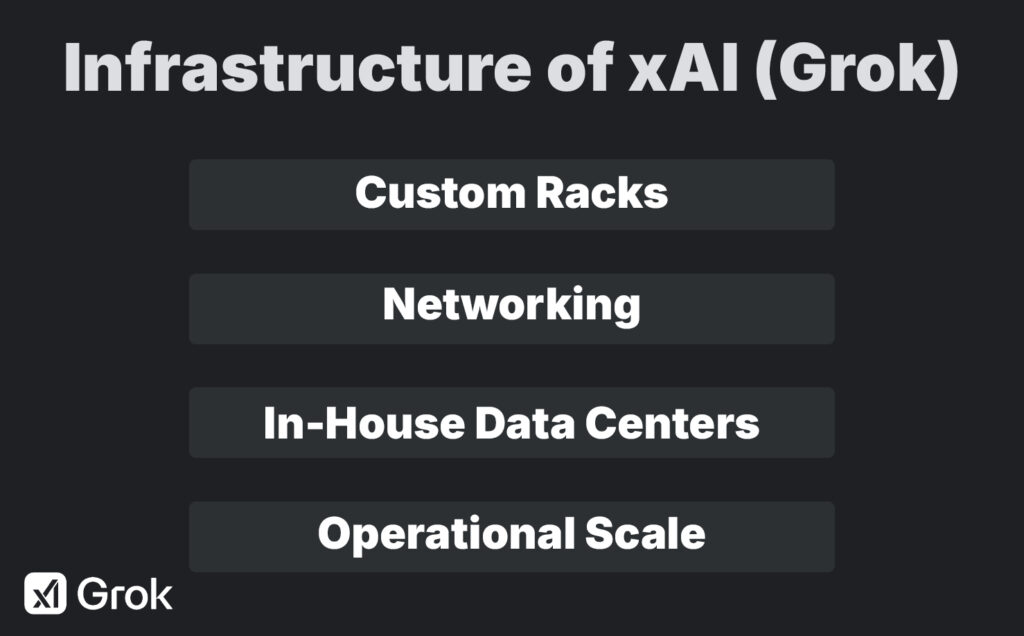
Elon Musk’s xAI operates its own “Colossus” supercluster:
- Custom Racks: Over 10,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs, arranged in bespoke liquid-cooled racks.
- Networking: Proprietary high-bandwidth interconnects (Custom NVLink + InfiniBand) for sub-microsecond communication.
- In-House Data Centers: xAI leases dedicated floors in secure colocation facilities near major cloud hubs (Silicon Valley, Texas).
- Operational Scale: Designed for both massive pretraining runs and low-latency inference serving, with ability to burst into additional capacity on partner cloud regions.
Google DeepMind (Gemini)
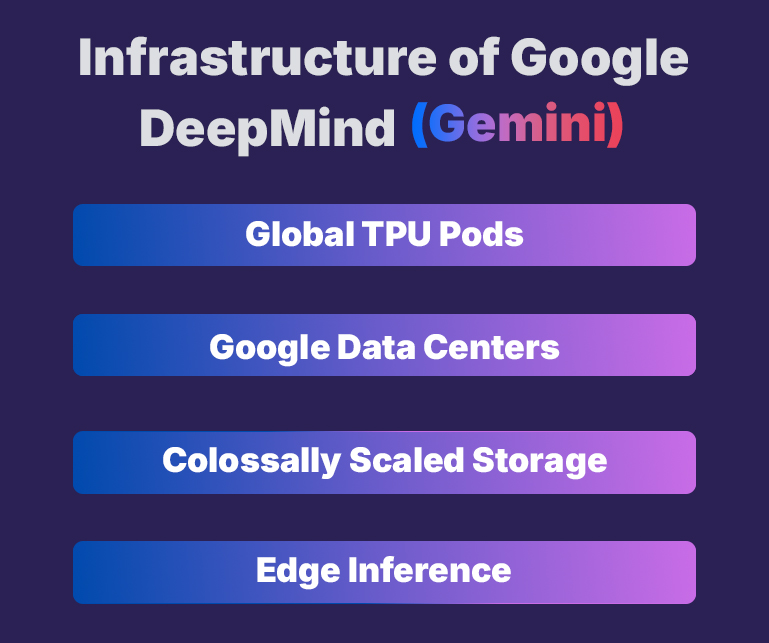
- Global TPU Pods: Google developed Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) for training. Gemini 2.5 Pro was trained on TPU v5 pods (512 TPU “chips” per pod).
- Google Data Centers: Massive, distributed data-center presence across North America, Europe, and Asia, with redundant power, cooling, and microservices for AI workloads.
- Colossally Scaled Storage: Exabyte-level file systems (Colossus) store training corpora, fine-tuning data, and large model checkpoints.
- Edge Inference: Google’s edge network deploys distilled versions of Gemini for low-latency on-device or regional serving.
Perplexity AI
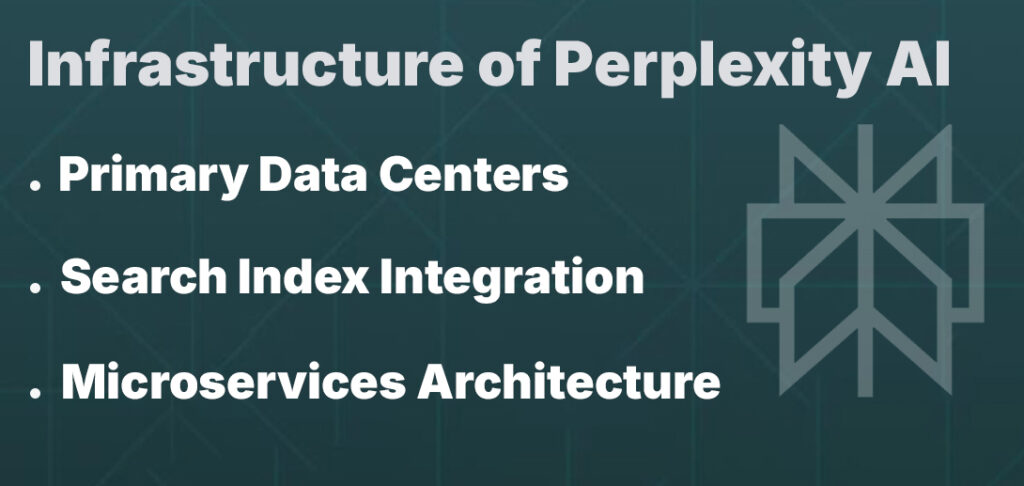
Perplexity operates a hybrid infrastructure:
- Primary Data Centers: Co-located in North America (primary) and Europe (backup), each housing NVIDIA A100-based GPU clusters.
- Search Index Integration: Close collaboration with web-crawling partners to maintain fresh indexes; ephemeral retrieval nodes run lightweight crawlers.
- Microservices Architecture: Each query spins up a microservice that orchestrates retrieval, summarization, and response generation in under a second.
Key Metrics for Comparison
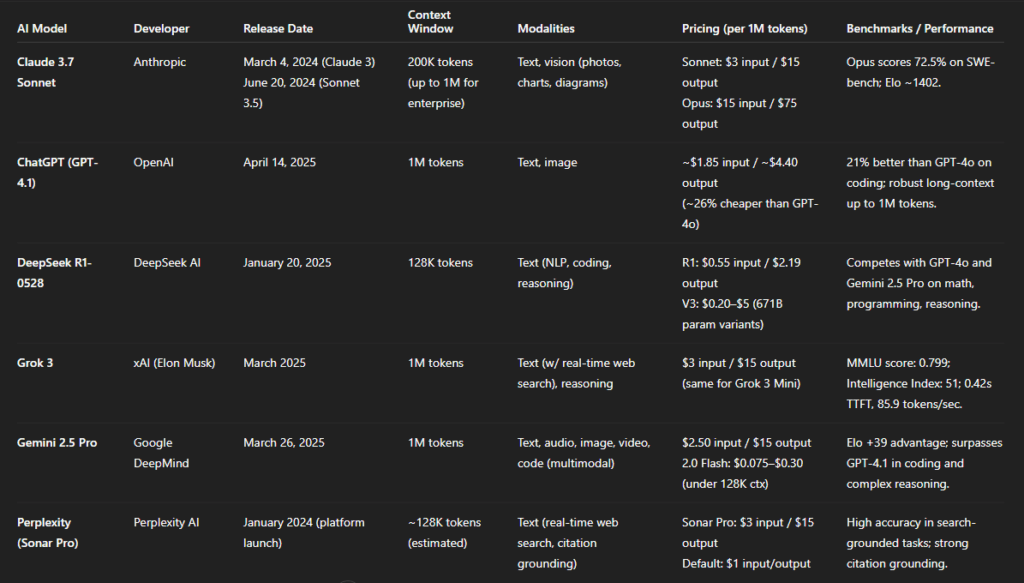
Claude 3.7 Sonnet (Anthropic)
- Developer: Anthropic
- Release Date: Claude 3 family launched March 4, 2024 (Claude 3 Haiku, Sonnet, Opus).Sonnet 3.5 released June 20, 2024.
- Context Window: 200 K tokens (expandable to 1 M for enterprise).
- Modalities: Text and vision (photos, charts, diagrams).
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): Sonnet 4 costs $3 for input and $15 for output, while Opus 4 costs $15 for input and $75 for output.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: Opus 4 scores 72.5% on SWE-bench coding and has an Elo score of ~1402, ranking it among the top reasoning models.
ChatGPT (GPT-4.1) (OpenAI)
- Developer: OpenAI
- Release Date: April 14, 2025.
- Context Window: 1 M tokens.
- Modalities: Text and image.
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): Approximately 26 % cheaper than GPT-4o; estimated around $1.85 input / $4.40 output.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: It outperforms GPT-4o by 21% on coding tasks and supports robust long-context retrieval up to 1 million tokens.
DeepSeek R1-0528 (DeepSeek AI)
- Developer: DeepSeek AI
- Release Date: January 20, 2025 (R1).
- Context Window: 128 K tokens.
- Modalities: Text (NLP, coding, reasoning).
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): Pricing ranges from $0.20 to $5 for V3 (671B parameters) variants, with R1 costing $0.55 per input and $2.19 per output.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: Competes closely with GPT-4o and Gemini 2.5 Pro on math, programming, and reasoning benchmarks.
Grok 3 (xAI)
- Developer: xAI (Elon Musk)
- Release Date: March 2025.
- Context Window: 1 M tokens.
- Modalities: Text (with integrated real-time web search), advanced reasoning.
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): Grok 3 and Grok 3 Mini both cost $3 per million input tokens and $15 per million output tokens, with the Mini version optimized for lower latency.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: With an MMLU score of 0.799 and Intelligence Index of 51, it delivers fast performance at 0.42s TTFT and 85.9 tokens/s throughput.
Gemini 2.5 Pro (Google DeepMind)
- Developer: Google DeepMind
- Release Date: March 26, 2025.
- Context Window: 1 M tokens.
- Modalities: Text, audio, image, video, and code (multimodal).
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): 2.5 Pro costs $2.50 per input and $15 per output, while 2.0 Flash (under 128K context) ranges from $0.075 to $0.30.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: It leads benchmarks with an Elo advantage of +39 and outperforms GPT-4.1 in coding and complex reasoning tasks.
Perplexity (Sonar Pro) (Perplexity AI)
- Developer: Perplexity AI
- Release Date: Platform launched January 2024.
- Context Window: Approximately 128 K tokens (inferred from search context limits)
- Modalities: Text (integrated with real-time web search and citation grounding).
- Pricing (per 1 M tokens): Sonar Pro costs $3 per input and $15 per output, while the default Sonar version is $1 for both input and output.
- Notable Benchmarks / Performance: Excels at search-grounded tasks with high accuracy and inline citations.
Target Market

- Claude.ai: Ideal for enterprises in regulated sectors (finance, healthcare), academic researchers valuing reasoning and safety, and startups balancing performance with alignment.
- ChatGPT: Serves a broad audience—developers, educators, enterprises, and hobbyists—via ChatGPT, Azure OpenAI, and API integrations for assistants and content pipelines.
- DeepSeek: Targets researchers, open-source enthusiasts, and privacy-conscious orgs needing on-premise control or customizable LLMs for niche tasks like scientific modeling.
- Grok: Best for early adopters seeking real-time, citation-backed answers; developers in the xAI ecosystem; and fans of Elon Musk–led tech ventures.
- Gemini: Tailored for Google Cloud users, media and research institutions, and developers building multimodal apps with video, audio, or AR/VR capabilities.
- Perplexity AI: Suited for users needing fast, citation-rich answers—students, researchers, librarians, and product teams integrating lightweight Q&A agents.
Case Studies
Microsoft

Microsoft is a long-time champion of ChatGPT and a major investor it OpenAI, the company that created it. The large language models (LLMs) that power the ChatGPT chatbot – GPT-3 and GPT-4 – now power its Bing search engine, allowing users to search and receive results through a conversational interface rather than the traditional list of web links.
Slack

Collaborative workspace platform Slack has created an app allowing its users to leverage the power of ChatGPT to help with managing workflows, boosting productivity, and communicating with colleagues. Users of the plugin have an assistant on-hand at all times to answer questions and offer suggestions on the best way to move forward with the projects they’re working on.
Amazon

Amazon has integrated DeepSeek R1 into its Bedrock and SageMaker AI platforms, allowing AWS customers to leverage this AI model for building applications with enhanced efficiency and lower costs.
IBM Watson

General Motors

General Motors’ OnStar has been augmented with new AI features, including a virtual assistant powered by Google Cloud’s conversational AI technologies that are better able to recognize the speaker’s intent.
Thoughtworks

Thoughtworks is a global technology consultancy that helps businesses use technology to solve problems and innovate. They use Google Workspace with Gemini to improve internal and external communication across their company, including in non-native languages — from emails to documents and blogs.
Beyond

Beyond is a global technology consultancy that creates cloud- and AI-based solutions that help companies unlock productivity and drive growth. They’re a member of Next15, a network of agencies, software companies, and consulting firms that help clients leverage AI in marketing, data, tech platforms, and business transformation projects. They’ve been a Google partner for 15 years.
Devoteam

The Future of AI LLM
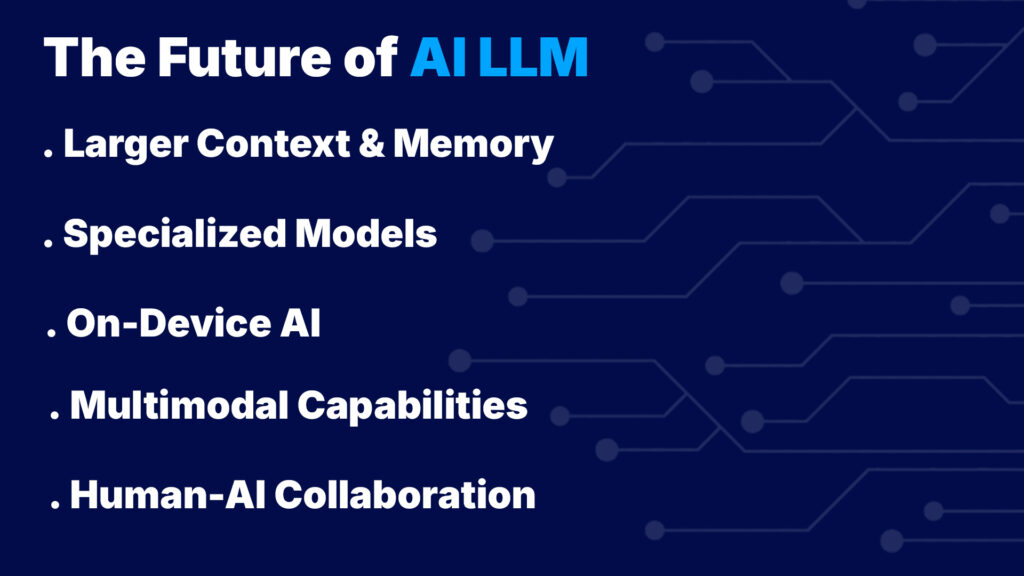
- Larger Context & Memory: LLMs will support multi-million-token windows for full-document reasoning and use memory modules to retain user context across sessions.
- Specialized Models: Industry-specific LLMs (e.g., legal, medical) and hybrid systems with general and task-focused micro-models will gain traction.
- On-Device AI: Compression techniques will enable LLMs on smartphones and IoT devices, enhancing privacy and reducing cloud dependence.
- Multimodal Capabilities: Future models will integrate text, images, audio, video, and sensor data—enabling rich, real-time, multimodal interaction.
- Human–AI Collaboration: AI will shift from reactive assistants to proactive co-authors and workflow partners, in immersive, mixed-reality interfaces.
Conclusion
The AI landscape in 2025 offers diverse tools, each excelling in different areas. Rather than declaring a single winner, the best LLM depends on your specific needs and budget.
ChatGPT excels as an all-around performer for everyday tasks and creative writing. Claude stands out for thoughtful analysis and complex reasoning. DeepSeek offers cutting-edge performance at lower costs or free access. Gemini provides seamless Google ecosystem integration. Perplexity excels for real-time research with proper citations. Grok offers unique personality with X (Twitter) integration.
The key to success lies in understanding which tool aligns with your workflow and objectives. Consider adopting a multi-model approach: use ChatGPT for daily tasks, Claude for analysis, Perplexity for research, and DeepSeek for cost-effective performance.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



