Table of Contents
Introduction
Foundations of AI: 20th Century Beginnings
Early Theoretical Foundations
Alan Turing and the Turing Machine

Alan Turing, a British mathematician and logician, is often regarded as the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence.
- In 1936, Turing introduced the concept of the Turing Machine, a hypothetical computing device that could simulate the logic of any computer algorithm.
- The Turing Machine formalized the concepts of computation and algorithm, laying the groundwork for developing modern computers and AI.
- Turing’s work demonstrated that machines could, in principle, perform any task that a human could, given the right instructions and sufficient time.
Turing Test and the Concept of “Thinking Machines”

In 1950, Turing published a seminal paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” in which he proposed the idea of the Turing Test.
- The Turing Test was designed to assess a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human.
- In the test, a human evaluator interacts with both a machine and a human through a computer interface, without knowing which is which.
- If the evaluator is unable to distinguish between the machine and the human reliably, the machine is said to have passed the test.
- The Turing Test has since become a fundamental concept in AI, serving as a benchmark for evaluating machine intelligence and sparking debates about the nature of thinking machines.
Initial Developments and Key Figures
John McCarthy and the Coining of “Artificial Intelligence” in 1956

- The conference is widely considered the birth of AI as a distinct field of study.
- McCarthy’s vision for AI involved creating machines capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
- His contributions laid the foundation for AI research and development, inspiring subsequent generations of scientists and engineers.
- Logic Theorist: In 1955, Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon developed the Logic Theorist, one of the first AI programs. It successfully proved 38 of the first 52 theorems in Principia Mathematica.
- General Problem Solver (GPS): In 1957, Newell and Simon developed the General Problem Solver (GPS) as a universal problem-solving machine designed to simulate human problem-solving across various domains. It represented a significant step forward in understanding and modeling human cognition.
The Evolution of AI Research
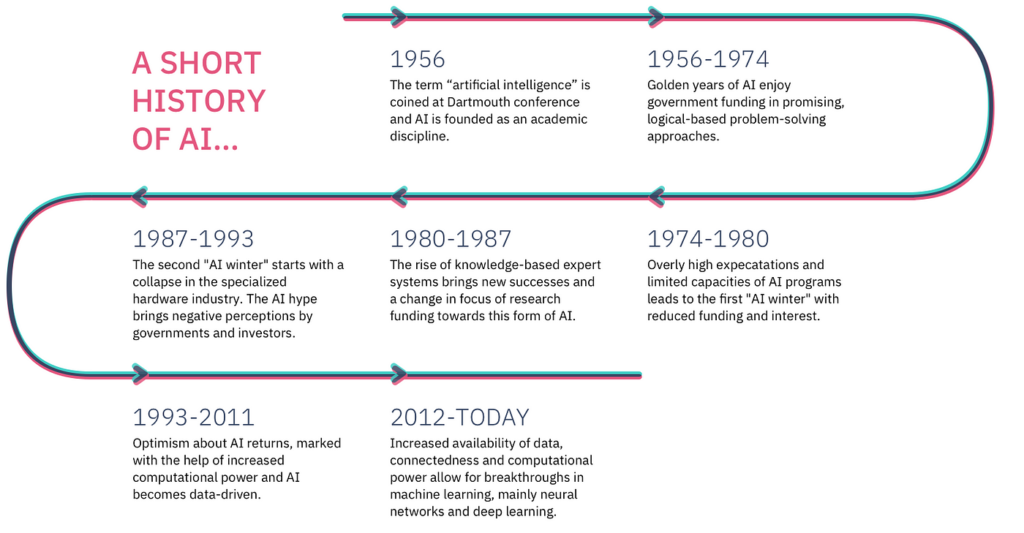
The Golden Years (1956-1974)
Early Successes in AI Research
The period from 1956 to 1974 is often referred to as the “Golden Years” of AI research, characterized by significant breakthroughs and optimistic expectations for the field.
- During this time, researchers made considerable progress in developing algorithms and systems that could perform tasks previously thought to be the exclusive domain of human intelligence.
- In 1958, Frank Rosenblatt introduced the perceptron, an early neural network model designed for pattern recognition.
- The perceptron could learn from data and adjust its weights to improve performance, laying the groundwork for future developments in machine learning.
The First AI Winter (1974-1980)

Despite the early successes, AI research faced significant challenges and setbacks during the mid-1970s. Some of the key obstacles included:
- Limited Computational Power: The hardware limitations of the time restricted the complexity and scale of AI systems, making it difficult to achieve practical and robust applications.
- Overly Optimistic Expectations: Early AI researchers and funding agencies had high expectations for rapid progress. When these expectations were not met, disappointment set in, leading to skepticism about the feasibility of AI.
- Theoretical Limitations: Researchers encountered fundamental challenges in understanding and replicating human intelligence, such as natural language understanding, common-sense reasoning, and learning from limited data.
The Expert Systems Boom (1980s)

- They rely on a knowledge base of rules and facts, along with an inference engine to draw conclusions and provide recommendations.
- Expert systems found practical applications in various industries, including medicine, finance, manufacturing, and customer support.
- Their ability to codify expert knowledge and provide consistent, high-quality advice made them valuable tools for businesses.
Geoffrey Hinton: Godfather of AI

Geoffrey Hinton is a leading figure in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and is often referred to as the “Godfather of AI” due to his significant contributions. Here is a timeline highlighting some of his key achievements:
- 1986: Hinton co-authored a groundbreaking paper on backpropagation titled “Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors,” which laid the foundation for training artificial neural networks.
- 1995: Hinton introduced the concept of the variational autoencoder (VAE), a generative model that learns to encode and decode data probabilistically.
- 2002: Hinton and his team developed the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM), which became a popular tool for unsupervised learning and deep learning pre-training.
- 2006: Hinton and his team published a paper on deep belief networks (DBNs), demonstrating an efficient method for training deep neural networks using greedy layer-wise pre-training.
- 2012: Hinton, along with his students Alex Krizhevsky and Ilya Sutskever, developed the deep learning model AlexNet, which significantly outperformed others in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC), bringing deep learning into the mainstream.
- 2014: Hinton co-authored a paper on the concept of “attention mechanisms” in neural networks, leading to advancements in natural language processing (NLP) models.
- 2015: Hinton, along with colleagues, introduced the concept of “capsules” and “capsule networks,” aiming to improve neural network architectures’ ability to understand spatial hierarchies.
- 2017: Hinton published work on dynamic routing between capsules, further advancing capsule network architecture.
- 2021: Hinton continued contributing to the field by researching alternative methods to backpropagation and exploring new ways to train neural networks more efficiently.
- 2022: Hinton’s research focused on understanding the limitations of deep learning models and addressing challenges related to interpretability and robustness.
Awards won by Geoffrey Hinton

- British-born artificial intelligence (AI) expert Geoffrey Hinton has won the Turing Award, sometimes referred to as “the Nobel Prize of computing”.
- Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in 1998 for his services to the field of computer science.
- Recipient of the Gerhard Herzberg Canada Gold Medal for Science and Engineering in 2010, which is Canada’s top honor for research excellence in science and engineering.
- Winner of the IEEE Frank Rosenblatt Award in 2011, which acknowledges exceptional contributions to biologically and linguistically motivated computational paradigms and systems.
- Recipient of the Killam Prize in 2012, one of Canada’s most prestigious awards for exceptional career accomplishments in engineering and natural sciences.
- Appointed Companion of the Order of Canada in 2019, one of Canada’s most esteemed civilian honors, in recognition of his contributions to the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Elected as a Royal Society Fellow in 1998, becoming a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) for his significant contributions to the advancement of natural knowledge.
- Named Foreign Member of the National Academy of Engineering in 2020, in acknowledgment of his contributions to neural networks and deep learning, which have profoundly influenced AI and its applications.
Companies Working on AI Technologies

- Google AI, DeepMind: Google uses AI in products like Google Search, Assistant, and Photos, and conducts AI research through its Google AI and DeepMind divisions, focusing on advanced AI models, ethical AI practices, and AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- Microsoft AI, Azure AI: Microsoft offers AI-powered cloud services, NLP, computer vision, and AI for enterprise solutions through its Azure platform. They also develop AI solutions for industries like healthcare and finance.
- Tencent AI Lab, WeChat AI: Tencent utilizes AI in social media, gaming, healthcare, and finance. They invest in AI for various sectors, leveraging their extensive data ecosystem.

- Amazon AI, Alexa AI: E-commerce recommendations, voice recognition, cloud AI services (AWS), and robotics. Amazon uses AI for personalized e-commerce recommendations, and voice recognition through Alexa, and offers AI and machine learning services through AWS.
- Facebook AI Research (FAIR), Meta AI: Facebook uses AI for content recommendation, moderation, and enhancing user experiences. Meta is also exploring AI applications in AR and VR technologies for the metaverse.
- Nvidia AI, Deep Learning GPUs: Nvidia is a leader in developing AI hardware, particularly GPUs used for deep learning. They are involved in AI research and applications in autonomous driving, healthcare imaging, and other AI-intensive fields.
- Siri, Apple AI Research: Apple integrates AI into its products for features like Siri, facial recognition, and photo categorization. They emphasize privacy-preserving on-device AI and are investing in AI for health and wellness applications.

- IBM Watson: IBM Watson provides AI-powered solutions for industries including healthcare, finance, and cybersecurity. IBM focuses on developing AI that can interpret large datasets, assist in decision-making, and improve business processes.
- GPT-3, DALL-E, Codex: OpenAI is known for its cutting-edge NLP models like GPT-3, creative AI tools like DALL-E, and code generation models like Codex. They focus on developing advanced AI while ensuring safety and ethical considerations.
- Baidu AI, Apollo (autonomous driving): Baidu integrates AI into its search engine, develops autonomous driving technology through Apollo, and works on AI applications in healthcare and voice recognition.

- Intel AI, Nervana Systems: Intel focuses on AI hardware and applications in autonomous systems and healthcare.
- Salesforce Einstein: Salesforce integrates AI into its CRM platform for enhanced analytics and customer service.
- Oracle AI, Oracle Cloud AI: Oracle provides AI solutions for enterprise applications, database management, analytics, and cloud services. The company is known for offering a wide range of enterprise AI solutions and cloud services, making it a comprehensive choice for businesses looking to integrate AI into their operations.
- SAP Leonardo: SAP uses AI to enhance its enterprise applications, optimize supply chain management, analytics, and IoT solutions, and improve operational efficiencies across industries.

- Adobe Sensei Applications: Adobe utilizes AI in its creative and marketing tools to improve productivity, automate repetitive tasks, enhance image recognition, provide intelligent suggestions, personalize customer experiences, and streamline campaign management.
- Alibaba DAMO Academy, Alibaba Cloud AI: Alibaba leverages AI for e-commerce, cloud computing, logistics, and financial services.
- Samsung Research AI: Samsung integrates AI into consumer electronics, smart home devices, and healthcare applications.
- Tesla AI, Autopilot: Tesla focuses on AI for autonomous driving, energy solutions, and manufacturing processes.

- Uber AI Labs: Uber uses AI to optimize ride-hailing, develop autonomous driving technology, and enhance its food delivery services.
- Huawei AI, HiAI: Huawei uses AI in telecommunications, cloud services, consumer electronics, and smart city solutions.
- Siemens: Siemens is developing AI solutions primarily for industrial automation and smart infrastructure, focusing on optimizing production processes and enhancing energy efficiency.
- Bosch: Bosch is leveraging AI for automotive applications, smart home technologies, and industrial IoT, with an emphasis on autonomous driving and intelligent sensors.
- Perplexity: Perplexity specializes in AI-based natural language processing and conversational AI, aiming to improve human-computer interactions and provide advanced query understanding capabilities.
AI Smart Devices
Here are some examples of AI-integrated smart devices categorized under smartphones and smart PCs, along with their brand names:
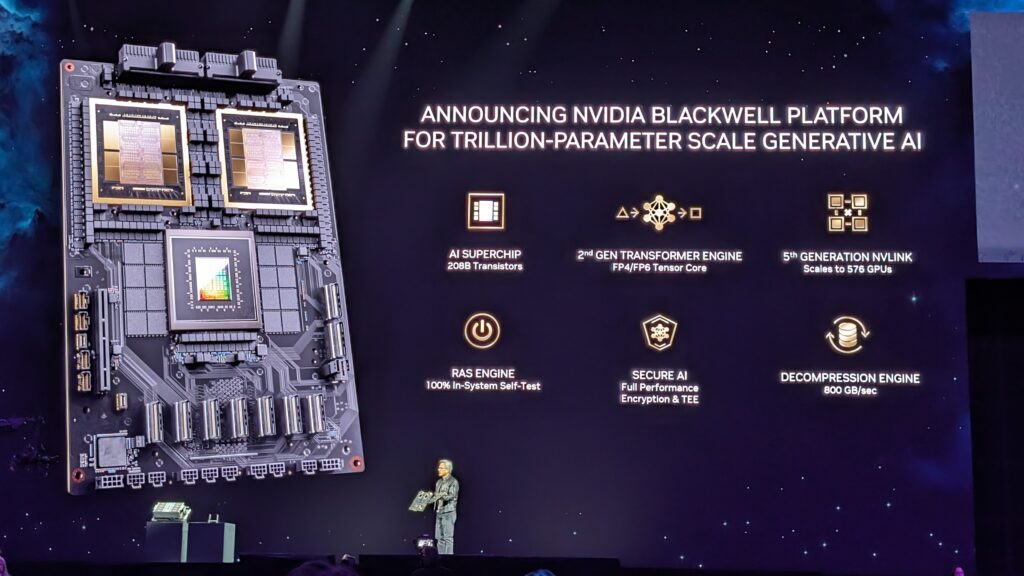
Nvidia Blackwell AI Chip

- During the GTC event in March, Nvidia introduced the Nvidia Blackwell AI chip.
- It consists of generative AI using trillion-parameter large language models (LLMs) at a reduced cost and energy consumption of up to 25 times less than the Nvidia Hopper architecture.
- The Blackwell GPU architecture incorporates six innovative technologies for accelerated computing that will enable significant advancements in data processing, engineering simulation, electronic design automation, computer-aided drug design, quantum computing, and generative AI.
Qualcomm and AI

AI-Enabled Chipsets
- Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors incorporate AI engines that enhance the performance and efficiency of smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
- These processors use AI for tasks like image processing, voice recognition, and battery management.
- The Hexagon Digital Signal Processor (DSP) is designed to handle AI workloads efficiently, enabling real-time AI processing on edge devices.
AI for 5G and IoT
- Qualcomm leverages AI to optimize 5G network performance, including dynamic spectrum sharing, predictive maintenance, and network traffic management.
- AI is integrated into IoT platforms to enhance device interoperability, security, and data analytics.
Smartphones
Apple iPhone
- Models: iPhone 13, iPhone 14, iPhone 15
- Key AI Features: Siri, advanced camera algorithms, Face ID, predictive text, and personalized app suggestions.
Samsung Galaxy

- Models: Galaxy S21, Galaxy S22, Galaxy S23, Galaxy S24
- Key AI Features: Bixby, smart camera features, voice recognition, and intelligent battery management.
Google Pixel
- Models: Pixel 6, Pixel 6 Pro, Pixel 7
- Key AI Features: Google Assistant, advanced computational photography, and real-time language translation.
Huawei Mate
- Models: Mate 40, Mate 50
- Key AI Features: AI-driven camera features, voice assistant, and performance optimization.
Smart PCs
Apple MacBook
- Models: MacBook Air (M1, M2), MacBook Pro (M1, M2)
- Key AI Features: Siri, advanced machine learning for performance optimization, and integrated security features.
Microsoft Surface

- Models: Surface Laptop 4, Surface Pro 8, Surface Book 3
- Key AI Features: The Microsoft Surface Laptop Studio, with Copilot AI, combines cutting-edge hardware with intelligent software features to provide a versatile and powerful tool for professionals, creatives, and everyday users.
- Models: XPS 13, XPS 15, XPS 17
- Key AI Features: Dell Optimizer (AI-based performance and battery management), voice recognition, and enhanced security features.
- Models: Spectre x360, Spectre Folio
- Key AI Features: AI noise removal, smart power management, and HP Command Center for personalized performance.
- Models: ThinkPad X1 Carbon, ThinkPad X1 Yoga
- Key AI Features: AI-based noise cancellation, security features like ThinkShield, and Lenovo Vantage for system optimization.
AI in Different Facets of Life
Artificial Intelligence has made significant inroads into various industries, driving innovation and improving efficiency. Below are some notable applications of AI in different sectors:
Healthcare
- Diagnostics: AI algorithms are used to analyze medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) to detect conditions like tumors, fractures, and infections with high accuracy. Tools such as IBM Watson Health assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more quickly and accurately.
- Personalized Medicine: AI helps tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. This approach improves treatment efficacy and reduces adverse effects.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates the drug discovery process by predicting how different compounds will interact with targets in the body, significantly reducing the time and cost involved in bringing new drugs to market.
Finance

- Fraud Detection: AI systems analyze transaction patterns in real time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Machine learning models can identify anomalies that may indicate fraud, enhancing security for financial institutions and customers.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of financial data to make trading decisions at speeds and accuracies beyond human capabilities. These systems can optimize investment strategies and maximize returns.
- Risk Management: AI helps in assessing and managing financial risks by analyzing market trends, economic indicators, and historical data. This enables better decision-making and strategic planning for financial institutions.
Transportation

- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use AI to interpret sensory data from cameras, radar, and lidar to navigate roads safely. Companies like Tesla and Waymo are at the forefront of developing autonomous driving technologies.
- Traffic Management: AI systems analyze traffic patterns and control traffic signals to reduce congestion and improve traffic flow in urban areas. This results in more efficient transportation systems and reduced travel times.
- Logistics Optimization: AI optimizes supply chain and logistics operations by predicting demand, managing inventory, and optimizing delivery routes. Companies like Amazon use AI to streamline their logistics and improve efficiency.
Future Direction and Challenges
As AI continues to evolve, it raises important ethical considerations and societal implications that must be addressed:
Bias and Fairness
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair outcomes. Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI algorithms is crucial to prevent discrimination and promote equity.
- Inclusive Data: Efforts must be made to include diverse data sets in AI training to ensure that AI systems serve all demographic groups fairly and accurately.
Privacy and Security
- Data Privacy: The widespread use of AI involves the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data. Safeguarding privacy and ensuring that data is used ethically is paramount to protect individuals’ rights.
- Cybersecurity: AI can both enhance and threaten cybersecurity. AI-driven systems can detect and respond to cyber threats more effectively, but they can also be used to develop sophisticated cyber attacks. Balancing these aspects is critical for secure AI deployment.
Conclusion
AI has already made significant strides in various facets of life, from healthcare and finance to transportation and entertainment. As the field continues to advance, ongoing research and emerging trends will drive further innovations, transforming industries and society.
However, the ethical and societal implications of AI must be carefully managed to ensure that its benefits are realized equitably and responsibly. By addressing these challenges and fostering human-AI collaboration, we can harness the power of AI to create a better future for all.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



