Table of Contents
Introduction
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a business management system that helps companies manage their day-to-day business activities. ERP systems can help with a variety of business functions, including:
- Financial Management
- Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Supply Chain Management
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Manufacturing
- Inventory Management
- Project Management
- E-commerce
- Marketing Automation
- Procurement
- Order Management
- Warehouse Management
- Workforce Management
ERP systems connect a company’s business processes and share data between them. This provides a single source of truth and helps to eliminate data duplication. ERP systems can also streamline operations and encourage informed decision-making.
Some companies use a hybrid ERP system combining on-premises and cloud deployments. For example, a company might use an on-premises ERP system at headquarters and cloud systems for subsidiaries or regional offices.
Key Stats
- The ERP Software market is expected to be worth $300 billion by 2027
- ERP solutions will represent 16.8% of global software spending or $171.7 billion out of $1.02 trillion in 2023
- 70% of Large Businesses Use ERPs
- 86% of Employees Want Better Tools
- The Public Cloud ERP Market Is Growing at 15% Annually
- 40% of Businesses Achieve Reduced IT Costs
What is ERP software?
ERP systems streamline business processes by centralizing data and enhancing departmental efficiency. They also support activities like accounting and supply chain management, improving decision-making and productivity.
Modern ERPs are web-based, enabling remote access and integrating company operations onto a single platform. This ensures seamless communication and accurate, real-time data for effective resource planning.
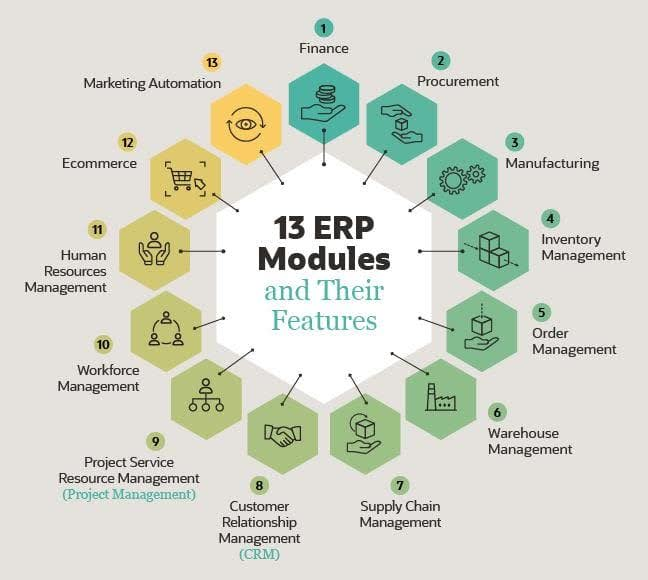
- Financial Management: The finance module manages the general ledger, accounts payable (AP), and accounts receivable (AR). It tracks all financial transactions, handles reconciliations, and generates detailed financial reports to ensure accuracy
- Human Resource Management (HRM): The HRM module stores employee records, tracks performance reviews and PTO, and identifies workforce trends across departments. It helps manage human capital and improve workforce productivity and planning
- Supply Chain Management: The supply chain management module oversees the flow of goods, ensures materials are available, schedules resources efficiently, and manages production from suppliers to customers for smooth operations
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): The CRM module tracks client interactions, assists in lead management, and enhances customer service. It helps boost sales and maintain strong relationships with customers through targeted communication
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing module coordinates production processes to meet demand, tracks in-progress and finished goods, and ensures production efficiency by effectively scheduling machinery and labor resources
- Inventory Management: The inventory management module monitors stock levels in real-time, down to SKU details. It helps optimize inventory based on demand, minimizing excess stock or shortages for better supply control
- Project Management: The module helps plan, track, and manage projects, resources, and time spent. It simplifies billing, promotes collaboration, and improves service-based business project delivery
- E-commerce: The e-commerce module manages online stores, enabling updates to product pages and site design. It supports order processing, inventory management, and customer experience optimization for retailers and brands
- Marketing Automation: The marketing automation module manages campaigns across email, web, and social channels. It personalizes messaging to increase lead generation, customer engagement, and sales, streamlining digital marketing efforts
- Procurement: The procurement module automates purchasing by managing quotes and purchase order requests. It helps avoid overbuying or underbuying and ensures optimal inventory levels based on demand planning
- Order Management: The module tracks customer orders across all channels, from placement to delivery. It prioritizes orders, speeds up fulfillment, and improves the customer experience with accurate tracking
- Warehouse Management: The warehouse management module optimizes receiving, picking, packing, and shipping activities. It identifies efficiencies in warehouse operations, reducing time and costs while improving productivity
- Workforce Management: A workforce management (WFM) module keeps track of attendance and hours worked; some can also manage payroll. This tool can record absenteeism and productivity by department, team, and individual employees
Why is ERP software important?

Companies choose ERP systems for operational improvement, business expansion, and cost reduction. Choosing ERP for small businesses enables them to modernize their legacy systems and enhance the customer experience.
- Better Collaboration: ERP for your company improves cooperation across departments and reduces communication delays, especially for organizations with distributed affiliates
- Improved Productivity: Companies can automate routine tasks, save time, reduce duplication, and integrate other systems to enhance employee performance
- Faster Decision-making: Provides real-time data and easy reporting, helping employees make informed decisions and identify efficient or costly workflows
- Built-in Compliance: ERP systems track industry regulations and changes in compliance. This allows businesses to stay ahead and comply with guidelines, relevant laws, and specifications
- Better Customer Service: Centralized data enables faster customer support and smoother communication with clients, making it easier to communicate with clients and reducing delays in offering customer services
- Scalability and Flexibility: ERP adapts to a company’s growth or reduction, handling changes like production increases, new services, or more users
- Enhanced Reports: ERP streamlines report generation, improving communication and reducing paperwork
- Better Availability of Information: Advanced ERP systems streamline information management by centralizing data into a single system, eliminating the need for multiple databases and redundant data checks
Understanding Your Business Needs
Before diving into ERP solutions, assessing your company’s needs is essential. ERP can be powerful solution that integrates an e-commerce platform with comprehensive business management systems.
For example, by using ERP for Shopify stores, you can automate and streamline critical business processes such as inventory management, order processing, accounting, and customer relationship management (CRM). Here are some key questions to consider:
- What are your business objectives? Growth, efficiency, customer satisfaction, or compliance might drive your need for an ERP
- Which processes need integration? ERP for dummies is a simplified introduction to the concept of ERP systems, which are software solutions designed to manage and integrate core business processes like finance, HR, inventory, and sales.
- Do you need industry-specific features? Certain industries, such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare, require tailored solutions
- What is your budget and timeline? Define a realistic budget for ERP implementation and understand the timeline for deployment
Key Criteria for Selecting an ERP

Once you’ve outlined your needs, the following criteria should guide your ERP selection process:
- Scalability: Your ERP should be able to grow with your business. As your operations expand, the system should support additional users, increased data volumes, and more complex processes
- Customization and Flexibility: Look for ERPs that offer customization options. This allows the system to align with your business processes rather than forcing you to adapt to the software’s predefined workflows
- Cloud vs. On-Premise: Cloud ERPs have lower upfront costs, quicker implementation, and easier updates. On-premise ERPs offer more data control, which is ideal for businesses with strict regulations
- Integration with Existing Systems: Your ERP should seamlessly integrate with existing software systems, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM), e-commerce platforms, or supply chain management tools
- Vendor Support and Training: ERP implementation can be complex and challenging. Whether you’re seeking advice on implementing an ERP system, integrating specific features, or optimizing performance, ERP for forums provides access to a diverse pool of expertise.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider long-term costs like maintenance, upgrades, and training beyond the initial purchase. Calculate total costs over the system’s lifespan to prevent surprises.
What are the Types of ERP?

Some of the main types of ERP systems are –
On-premise: On-premise ERP systems offer complete control and security, needing dedicated IT for maintenance. They provide significant advantages in terms of system management and security.
- Offers strong integration with various other systems already used by any organization
- The system can be easily customized per the users’ specific business requirements
- This type of ERP module can handle the firm’s sensitive and confidential data, so there is no need for a third-party
Cloud-based: Cloud-based ERP, a SaaS managed by third-party providers, offers a flexible design suitable for any organization. It simplifies data storage and access across devices and offers various advantages.
- Users don’t need to make a substantial initial investment to gain access to the system
- No specialized skills are required from the team members to implement the system into the firm, as a third party handles everything
Hybrid: Hybrid ERP combines on-premise and cloud-based solutions, offering flexibility and vendor expertise without full data access. It is also known as two-tier ERP, and it benefits businesses by efficiently meeting diverse needs.
- It offers innovation and responsiveness to business requirements
- The processes carried out by this model are simpler, making the workflow less complex
Open Source: This affordable system allows businesses to download free software, pay a minimal annual fee for cloud access, and manage their configuration. It offers limited provider support and self-managed configuration
- The cost of ownership in the open-source ERP system is next to zero
- There is no vendor dependency on anything
Leading ERP Vendors for All Business Sizes
Microsoft Dynamics 365

Microsoft Dynamics 365 merges ERP and CRM into one platform, offering cloud and on-premise solutions. It serves as an ERP application, offering comprehensive financial solutions such as handling ledger, payments, cash flows, assets, and debts. Being part of the business edition, this module is built on Microsoft Azure and can be accessed through the cloud.
Odoo: The Modular and Open-Source ERP

Odoo is an open-source ERP solution designed for small to mid-sized businesses. It offers a modular approach, allowing companies to implement only the needed features, such as ERP for accounting , inventory, or project management. Odoo provides seamlessly integrated functional business apps called Odoo apps that form an ERP solution when combined.
NetSuite: Cloud-Based Management Platform

NetSuite is an AI-powered cloud business management solution that helps organizations enhance effectiveness by automating core processes. It operates on a cloud infrastructure that ensures security, availability, and robust data management. It helps organizations operate more effectively by automating core processes and providing real-time visibility.
SAP ERP: The Market Leader for Large Enterprises

SAP enables Fortune 500 and large enterprises to run profitably, adapt continuously, and grow sustainably. Their flagship, SAP S/4HANA, suits complex enterprises, while SAP Business One serves small and mid-sized businesses with cloud and on-premise options.

SAP B1, also known as SAP Business One, is a powerful business management software or ERP solution. It assists small and medium-sized businesses in streamlining their operations and improving results. SAP Business One enables companies to efficiently handle key functions like finance, procurement, customer relations, analytics, and reporting in a unified platform.

SAP S/4HANA is an advanced, in-memory, column-oriented database for real-time analytics and fast transactions. Fortune 500 companies widely use it for operational efficiency and innovation. SAP S/4HANA’s solutions span the entire ecosystem of sales, from direct sales management to customer analytics.
Infor ERP: Industry-Specific Solutions

Infor is known for its industry-specific ERP solutions for manufacturing, healthcare, distribution, and other sectors. Its flagship product, Infor CloudSuite, is a cloud-based ERP designed for large enterprises and global operations. Infor is built on an open-source technology stack which enables manufacturers to connect software systems and processes throughout the entire enterprise.
Acumatica

Acumatica is a cloud-based ERP software designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It helps you manage accounting, operations, customers, vendors, employees, and many other aspects of running a business efficiently and effectively. Acumatica’s unique ERP platform offers open APIs, a low-code/no-code framework, and mobility, empowering businesses to customize and scale their operations quickly.
Sage Intacct

Sage Intacct is a cloud-based financial management platform offering accounting, inventory, accounts payable/receivable, cash management, and advanced reporting for business insights. It provides automation and trusted insights across financials, planning, HR, and payroll.
Aptean

Aptean provides industry-specific enterprise software solutions for ERP, supply chain, manufacturing, and compliance. Serving sectors like food, manufacturing, and distribution, its cloud and on-premise tools enhance efficiency, productivity, and regulatory compliance.
Epicor

Epicor is a global ERP leader offering cloud and on-premise solutions to streamline operations and optimize supply chains. Its software drives growth, reduces costs, and boosts efficiency for businesses. Most important, Epicor software is built to manage, organize and improve how all company resources are used.
Case Studies: ERP Impact on Business Growth
Numerous companies in different sectors utilize ERP systems to optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and better understand their business procedures. Here are some instances of businesses effectively employing ERP systems:

- Jawbone, a wearable tech firm, utilized NetSuite’s cloud ERP for its financial operations worldwide. This system enhanced global supply chain visibility, facilitating more efficient growth. With real-time data and automation, Jawbone was able to streamline processes and reduce manual errors across its international operations.

- Komatsu Mining Corp. implemented SAP S/4HANA to streamline its global operations. The ERP helped the company standardize processes across 14 countries, improving efficiency and reducing costs. This integration also provided Komatsu with enhanced analytics and forecasting capabilities, allowing for better decision-making at scale.

- Fossa Apparel, a small clothing manufacturer, used Odoo to streamline its production and inventory management processes. Odoo’s modular design’s flexibility allowed the company to scale its ERP system as it grew. This adaptability enabled Fossa to efficiently manage increasing demand while maintaining control over its operations and resources.

- Sub-Zero Group utilized Epicor Kinetic to enhance manufacturing and inventory processes, reducing production lead times and boosting supply chain efficiency. This showcases the impact of ERP on luxury appliance manufacturing, allowing the company to meet high customer demand while maintaining product quality and operational excellence.

- Honest Brew, a craft beer firm in the UK, adopted NetSuite to streamline its e-commerce and distribution. This ERP automation led to a 40% cut in operational costs and higher-order accuracy. By automating key processes, Honest Brew was able to focus more on customer satisfaction and expanding its product offerings.

- Ferrari implemented Infor CloudSuite to optimize its manufacturing processes. The ERP provided real-time data on production, helping Ferrari maintain its high standards of quality and efficiency. With improved visibility into the supply chain, Ferrari was able to enhance its responsiveness to market changes and customer demands.

- Renault Group adopted Microsoft Dynamics 365 for its global operations, enhancing real-time data sharing, decision-making, and collaboration across divisions, significantly improving operational efficiency. The system also empowered Renault to innovate faster by providing insights into market trends and customer preferences.

- Hershey’s replaced its outdated system with SAP ERP, resulting in better production planning, reduced supply chain inefficiencies, and increased profitability. This transformation significantly improved operational efficiency by providing real-time insights into inventory and demand, enabling the company to optimize resources and meet customer demand more effectively.
Conclusion
Choosing the right ERP system is vital for your business’s long-term success. It’s not just about addressing your current operational needs; it’s also about ensuring the system can adapt as your company grows and the industry evolves.
Aligning ERP selection with long-term goals improves efficiency, scalability, and competitiveness. A suitable ERP enhances processes, drives innovation, and supports growth.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



