Table of Contents
Introduction
Marketing is all about making connections with people, and the more you know your target audience, the better you can customize your messages, offerings, and services to cater to their requirements.
Understanding your customers and identifying them is essential for an effective marketing strategy. Accurately identifying your customers assists you in concentrating your marketing endeavors, efficiently allocating resources, and generating more conversions and sales.
Grasping your customer goes beyond just their basic demographics – it involves delving into their behaviors, preferences, needs, and challenges. By gaining a profound understanding of your customers, you can craft pertinent marketing messages that deeply resonate with them.
The Basics of Customer Identification
Defining Your Target Audience
Defining your target audience is the first step in customer identification. This involves segmenting the broader market into smaller, more specific groups of potential customers who are most likely to benefit from your products or services. Key factors to consider when defining your target audience include:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level, education, occupation, and family status.
- Geographics: Location, climate, urban or rural setting.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, values, interests, attitudes, and personality traits.
- Behavioral Traits: Buying habits, brand loyalty, usage rate, and decision-making process.
By creating a detailed profile of your ideal customer, you can tailor your marketing strategies to better attract and engage this group.
To effectively identify and understand your customers, you need to employ various tools and techniques for customer research. These include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Collect direct feedback from your current or potential customers to understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Interviews and Focus Groups: Engage in deeper conversations with a small group of customers to gain insights into their motivations and challenges.
- Market Research Reports: Utilize existing industry reports and studies to gather information about market trends and consumer behaviors.
- Social Media Analytics: Analyze data from social media platforms to understand what your audience is talking about, their interests, and how they engage with your brand.
- Website Analytics: Use tools like Google Analytics to track visitor behavior on your website, including pages visited, time spent, and conversion paths.
- Customer Feedback and Reviews: Regularly monitor and analyze feedback and reviews from customers to identify common themes and areas for improvement.
- Competitor Analysis: Study your competitors to understand how they are meeting the needs of their customers and where there may be opportunities for differentiation.
By leveraging these tools and techniques, you can gather valuable data to create a comprehensive and accurate picture of your target audience. This information will guide your marketing strategies, ensuring they are customer-centric and effective.
The Buyer’s Journey Explained
Overview of the Buyer’s Journey Stages: Awareness, Consideration, Conversion
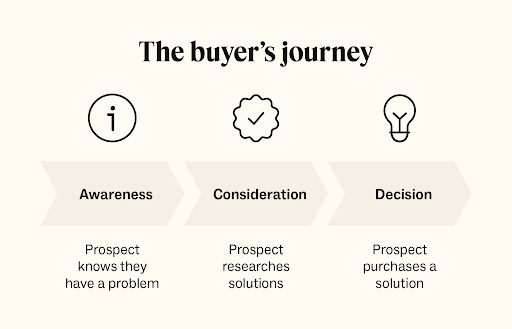
The buyer’s journey is the process that a potential customer goes through from becoming aware of a problem or need to making a purchase decision. It consists of three primary stages:
- Awareness Stage: In this initial stage, the potential customer realizes they have a problem or need but may not fully understand it. They begin to seek information and resources to grasp their situation better.
- Consideration Stage: At this stage, the potential customer has clearly defined their problem and is actively looking for solutions. They are comparing different products, services, or brands to determine which best meets their needs.
- Conversion Stage: In the final stage, the potential customer is ready to make a purchase decision. They have evaluated their options and are deciding which product or service to buy.
How Customer Identification Fits into Each Stage
Awareness Stage
- Identifying your customer helps you create content that resonates with their initial concerns and interests
- By understanding their demographics, psychographics, and pain points, you can craft messages that attract their attention and build awareness of your brand
Consideration Stage
- Knowing your customer allows you to provide tailored content that addresses their specific needs and questions
- Detailed buyer personas help you anticipate the criteria they use to evaluate solutions, enabling you to present your product or service as the ideal choice
Conversion Stage
- A deep understanding of your customer’s decision-making process helps you remove any barriers to purchase
- You can offer personalized incentives, address common objections, and provide a seamless buying experience that aligns with their expectations
Aligning Communication Strategies
Tailoring Messages to Each Stage of the Buyer’s Journey
Awareness Stage
- Content Focus: Educational and informative content that addresses the customer’s initial pain points and questions
- Message Tone: Friendly, helpful, and engaging to attract attention and build trust
- Examples: Blog posts, infographics, social media posts, introductory videos, and e-books
Consideration Stage
- Content Focus: In-depth information and comparisons that help customers evaluate their options and understand the benefits of your product or service
- Message Tone: Authoritative, detailed, and persuasive to guide customers toward your solution
- Examples: Whitepapers, case studies, product comparison guides, webinars, and demo videos
Conversion Stage
- Content Focus: Content that removes purchase barriers, provides reassurance, and prompts action
- Message Tone: Direct, confident, and urgent to encourage immediate decisions
- Examples: Testimonials, free trials, discount offers, detailed product pages, and clear calls to action
Choosing the Right Channels for Effective Communication
Awareness Stage
- Channels: Social media, content marketing (blogs, articles), SEO, paid advertising, and public relations
- Goal: Reach a broad audience and generate interest in your brand or product
Consideration Stage
- Channels: Email marketing, retargeting ads, detailed landing pages, and content hubs
- Goal: Nurture leads by providing valuable information that helps them evaluate your offering
Conversion Stage
- Channels: Direct email campaigns, personalized offers, sales calls, and remarketing
- Goal: Drive final purchase decisions and convert leads into customers
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Mistakes in Customer Identification
- Pitfall: Relying on assumptions instead of data to define your target audience.
- Consequence: Marketing messages that fail to resonate, leading to low engagement and conversion rates.
- Tip: Conduct thorough market research and continuously update your customer personas based on real data and feedback.
Consequences of Misaligned Marketing Strategies

- Pitfall: Using a one-size-fits-all approach for all stages of the buyer’s journey.
- Consequence: Inefficient use of marketing resources and missed opportunities to connect with potential customers.
- Tip: Tailor your communication strategies to each stage of the buyer’s journey to ensure relevant and effective messaging.
Tips for Staying on Track
- Regular Review: Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing strategies. Use analytics and performance metrics to make informed adjustments.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop with your sales and customer service teams to gain insights into customer interactions and challenges.
- Agility: Stay flexible and be prepared to pivot your strategies based on new data, market trends, and customer feedback.
- Consistency: Ensure consistent messaging across all channels and touchpoints to build a cohesive brand experience.
Utilizing Data and Analytics
Gathering Data to Refine Customer Understanding
Behavioral Data
- Track customer interactions on your website, including page views, time spent on site, click-through rates, and conversion rates
- Use this data to understand how customers navigate your site and what content or products they engage with most
Demographic Data
- Collect demographic information such as age, gender, location, and income level to segment your audience effectively
- Tailor your marketing messages to address the specific needs and preferences of each segment
Psychographic Data
- Gather insights into customers’ values, interests, lifestyles, and attitudes through surveys, social media listening, and customer interviews
- Use this information to create more personalized and relevant marketing campaigns
Leveraging Analytics for Ongoing Improvement
Performance Tracking
- Use analytics tools to monitor the performance of your marketing campaigns, tracking KPIs such as ROI, CAC, and LTV
- Regularly review these metrics to identify successful strategies and areas needing improvement.
A/B Testing
- Conduct A/B tests to compare different versions of your marketing materials (emails, landing pages, ads) and determine which performs better
- Implement the winning variations to optimize your marketing efforts.
Customer Journey Analysis
- Map out the customer journey to identify touchpoints where customers drop off or need additional support
- Use this analysis to improve the customer experience and increase conversions
The Role of Customer Feedback
Importance of Listening to Your Customers
- Customer Insights: Feedback provides valuable insights into customer needs, preferences, and pain points
- Customer Loyalty: Actively seeking and responding to feedback fosters stronger customer relationships and loyalty
- Continuous Improvement: Use feedback to continuously improve your products, services, and overall customer experience.
Methods for Collecting and Analyzing Feedback
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Gather direct feedback on specific aspects of your products or services
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Monitor and analyze reviews on your website, social media, and third-party review sites
- Social Media Listening: Track mentions and conversations about your brand on social media platforms
- Focus Groups and Interviews: Conduct in-depth interviews and focus groups to gain deeper insights
- Customer Support Interactions: Analyze data from customer support emails, chats, and calls.
Implementing Feedback into Your Marketing Strategy
- Prioritize Feedback: Focus on addressing the most critical areas first
- Actionable Insights: Translate feedback into specific plans for improvement
- Communicate Changes: Inform customers about the changes you’ve made based on their feedback
- Continuous Improvement: Establish a regular feedback loop to continuously refine your strategy
Measuring Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Customer-Centric Marketing
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost of acquiring a new customer
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV): The total revenue a customer is expected to generate over their lifetime
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): A measure of how satisfied customers are with your products or services
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A measure of customer loyalty and the likelihood of customers recommending your brand
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase
Tools for Tracking and Measuring Success
- Google Analytics: For tracking website and campaign performance
- CRM Systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot): For managing customer interactions and tracking sales performance
- Email Marketing Platforms: For monitoring email campaign metrics
- Social Media Analytics Tools: For tracking social media engagement and performance
- Customer Feedback Tools (e.g., SurveyMonkey, Typeform): For collecting and analyzing customer feedback.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Performance Metrics
- Regular Review: Continuously monitor and evaluate your marketing performance metrics
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use the insights gained from performance metrics to make informed adjustments to your marketing strategies
- Agility: Stay flexible and be prepared to pivot your strategies based on new data, market trends, and customer feedback.
Conclusion
Utilizing data and analytics, actively listening to customer feedback, and measuring success through key performance indicators are essential for creating a responsive, customer-centric marketing strategy.
By continuously gathering, analyzing, and implementing insights from data and feedback, you can optimize your marketing efforts, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive long-term success for your business.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



