Table of Content
Introduction
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the way companies manufacture, improve and distribute their products. Manufacturers are integrating new technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, and AI and machine learning into their production facilities and throughout their operations.
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is the current trend of automation and digital transformation in manufacturing technologies. It involves the integration of advanced technologies into the manufacturing process such as:
- Internet Of Things (IoT)
- Artificial Intelligence (Ai) and Machine Learning (ML)
- Robotics
- Big Data Analytics
Smart manufacturing, a key component of Industry 4.0, refers to the use of these technologies to create a more efficient and effective manufacturing process. By integrating these technologies, manufacturers can improve their production processes, reduce waste and costs, and create more flexible and responsive supply chains.

The benefits of smart manufacturing are many. First, it enables manufacturers to optimize their operations, resulting in improved productivity, reduced downtime, and increased throughput. Second, it allows for real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, providing greater visibility into the production process and enabling rapid response to issues as they arise. Third, it can improve product quality and consistency by enabling tighter process controls and reducing the risk of errors.
In addition to these benefits, smart manufacturing can also enable more sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing waste and energy consumption. It can also help manufacturers to better understand customer needs and preferences, enabling them to create more customized products and services.
Overall, Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing represent a significant opportunity for manufacturers to improve their operations, reduce costs, and create new business opportunities. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, they will become increasingly important for manufacturers looking to stay competitive in a rapidly changing global marketplace.
Key Stats

- The global Smart Manufacturing market is expected to reach $573.8 billion by 2027.
- 87% of manufacturers believe that Smart Manufacturing will lead to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Smart Manufacturing can reduce production costs by up to 30%.
- 69% of manufacturers plan to invest in Smart Manufacturing technologies over the next year.
- 54% of manufacturers believe that Smart Manufacturing will improve their ability to compete in the global marketplace.
- The adoption of Smart Manufacturing technologies is expected to create 2.3 million new jobs by 2025.
- Smart Manufacturing can reduce unplanned downtime by up to 50%.
- 80% of manufacturers have reported improvements in quality as a result of Smart Manufacturing implementation.
- The use of IoT in Smart Manufacturing is expected to grow by 23% annually.
- Smart Manufacturing technologies can help reduce energy consumption by up to 20%.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a term used to describe the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing and other industries.
It represents a new era of technological advancement that combines traditional manufacturing with the latest digital technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, robotics, and big data analytics.
- Increased connectivity and communication between machines and devices, enabling greater automation and optimization of manufacturing processes
- The use of advanced sensors and analytics to collect and analyze data in real time allows for more efficient and effective decision-making
- The creation of “smart factories” where machines, equipment, and processes are connected and can be controlled and monitored remotely
- The potential for greater customization and personalization of products, as well as increased speed to market and reduced costs
- The need for a highly skilled workforce with expertise in digital technologies and data analysis
- The potential for significant economic and social impacts, including job displacement and the need for upskilling and reskilling of workers.
- Industry 4.0 represents a significant shift in the manufacturing industry, leveraging digital technologies to improve efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
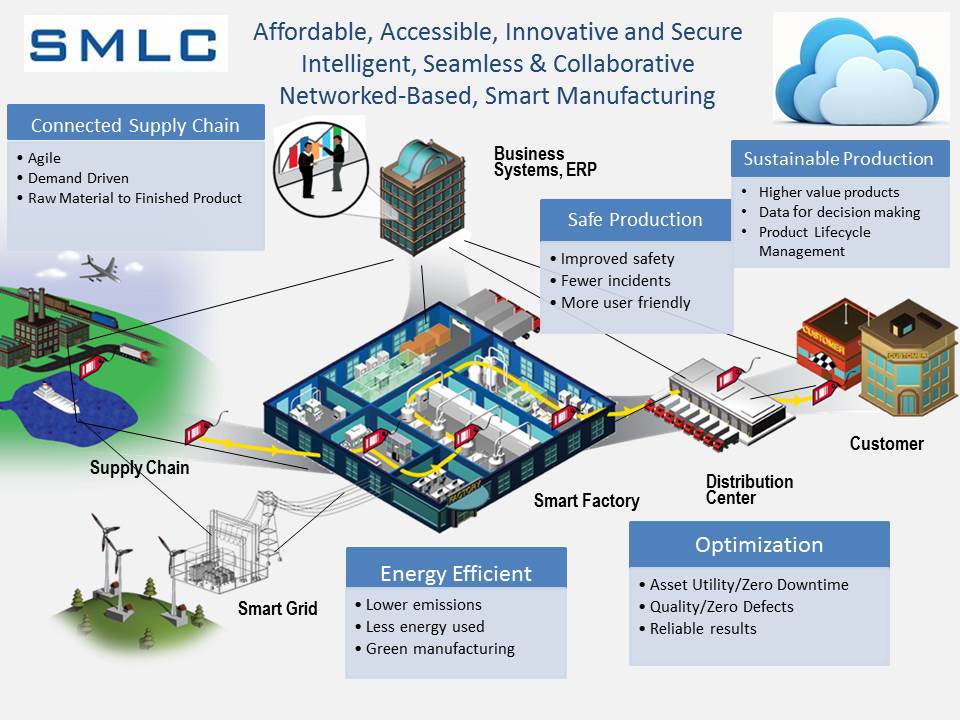
Smart Manufacturing
Smart Manufacturing is an advanced approach to manufacturing that uses cutting-edge digital technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and robotics to optimize production processes and improve efficiency, quality, and flexibility.
What is the Smart Factory?
A Smart Factory is a manufacturing facility that uses advanced digital technologies such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and robotics to optimize production processes and improve efficiency, quality, and flexibility.

Key aspects of Smart Manufacturing include:
- The integration of data from across the manufacturing value chain to improve decision-making and drive continuous improvement
- The implementation of advanced sensors and automation technologies to enable real-time monitoring and control of production processes
- The creation of digital twins of manufacturing processes to enable virtual testing and optimization of production systems
- The development of agile and flexible manufacturing processes to enable rapid adaptation to changing customer demands
- Smart Manufacturing represents a major shift in the way that manufacturing is done, leveraging advanced digital technologies to create more efficient, flexible, and responsive production systems.
- It has the potential to significantly improve productivity, reduce costs, and enable greater customization of products to meet individual customer needs. However, it also requires a highly skilled workforce with expertise in digital technologies and data analysis to implement and operate effectively.
- Advanced sensors and automation technologies to enable real-time monitoring and control of production processes
- The use of data analytics and machine learning to optimize production processes and predict maintenance needs
- The integration of data from across the manufacturing value chain to improve decision-making and drive continuous improvement
- The implementation of digital twins of manufacturing processes to enable virtual testing and optimization of production systems
- The use of collaborative robots (cobots) to work alongside human workers to improve efficiency and safety
- Smart Factories are designed to be highly agile and flexible, able to quickly adapt to changing customer demands and market conditions.
- They are also capable of producing highly customized products at scale, using advanced technologies such as 3D printing and additive manufacturing.
- The Smart Factory represents a major step forward in the manufacturing industry, leveraging advanced digital technologies to create more efficient, flexible, and responsive production systems.
Smart Manufacturing offers benefits such as increased efficiency, improved quality, cost reduction, customization, flexibility, improved safety, and better decision-making.

Smart Manufacturing offers a range of benefits for manufacturers, including
Increased Efficiency: Smart Manufacturing technologies optimize production processes, reduce waste, and increase throughput, leading to higher efficiency.
Improved Quality: With real-time monitoring and control of production processes, Smart Manufacturing technologies help identify and address quality issues quickly, leading to improved product quality.
Cost Reduction: Smart Manufacturing technologies can help reduce costs through increased efficiency, reduced waste, and better use of resources, such as energy and raw materials.
Customization: Smart Manufacturing technologies enable mass customization, allowing manufacturers to create highly customized products at scale to meet individual customer needs.
Flexibility: Smart Manufacturing systems are highly agile and flexible, able to quickly adapt to changing market demands and production requirements.
Improved Safety: Advanced sensors and automation technologies can reduce the risk of workplace accidents and injuries, making manufacturing safer for workers.
Better Decision-Making: Smart Manufacturing systems provide real-time data and insights, enabling better decision-making and continuous improvement.
Smart Manufacturing technologies offer significant benefits for manufacturers, enabling them to operate more efficiently, effectively, and competitively in today’s fast-paced and rapidly changing market.
Challenges
The challenges of Smart Manufacturing include high implementation costs, the need for a highly skilled workforce, data privacy, and security concerns, the need for greater standardization and interoperability, and resistance to change. These challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential benefits of Smart Manufacturing

Smart Manufacturing also presents several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential, including:
- Implementation Costs: The upfront costs of implementing Smart Manufacturing technologies can be significant, requiring significant investments in equipment, software, and training.
- Workforce Skills and Training: Smart Manufacturing requires a highly skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining advanced technologies, which may require additional training and education.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: As Smart Manufacturing systems collect and analyze large amounts of data, there are concerns about data privacy and security, and the need to ensure that sensitive data is protected from cyber threats.
- Interoperability and Standardization: As Smart Manufacturing systems are highly complex and diverse, there is a need for greater standardization and interoperability to ensure that different systems can work together seamlessly.
- Resistance to Change: The adoption of Smart Manufacturing technologies requires significant changes to traditional manufacturing processes, which can be met with resistance from workers and managers who may be reluctant to embrace new technologies.
While Smart Manufacturing offers significant benefits, there are also significant challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential.
Case Studies
There are several brands that have implemented Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 technologies and processes to improve their manufacturing operations. Here are some case studies:
Tesla

Tesla’s Smart Manufacturing approach is centered around its advanced automation capabilities and cutting-edge technologies, including the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning.

Tesla’s Gigafactory in Nevada, which produces battery packs for its electric vehicles, is a prime example of the company’s Smart Manufacturing strategy in action.
Tesla has implemented real-time monitoring and data analytics to monitor production performance and identify areas for improvement. Through its Smart Manufacturing initiatives, Tesla has been able to increase production capacity, reduce costs, and improve overall quality, helping to drive the growth of the electric vehicle market.
General Electric (GE)

General Electric has implemented Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 technologies such as sensors, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) in its factories to improve productivity, reduce downtime, and optimize its supply chain.

For example, GE’s Brilliant Factory in Greenville, South Carolina, uses data analytics and machine learning to predict and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime by up to 20%.
Ford Motor Company

Ford has implemented Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, and virtual reality (VR) in its factories to improve efficiency and quality.

For example, Ford’s Advanced Manufacturing Center in Michigan uses VR to simulate assembly processes, enabling workers to identify and address potential issues before production begins.
Caterpillar Inc

Caterpillar has implemented Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 technologies such as robotics, IoT, and AI in its factories to improve productivity and safety.

For example, Caterpillar’s Smart Iron program uses IoT sensors and data analytics to monitor equipment performance and identify potential issues, reducing downtime and improving safety.
Procter & Gamble (P&G)

Procter & Gamble (P&G) has implemented Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 technologies such as sensors and big data analytics in its factories to improve quality and reduce waste.

For example, P&G’s Baby Care plant in Mexico uses sensors to monitor diaper production in real-time, enabling workers to identify and address quality issues quickly and reduce waste.
These brands have demonstrated the benefits of Smart Industry Manufacturing 4.0 in improving efficiency, quality, safety, and sustainability in manufacturing operations.
The Future
The future of Smart Manufacturing looks bright, with ongoing advances in technology and increasing adoption by companies across various industries
Some of the key trends and developments that are expected to shape the future of Smart Manufacturing include:
- Greater integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies to optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and increase efficiency.
- Increased use of the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to create interconnected systems and enable real-time monitoring and analysis of manufacturing processes.
- The development of more advanced robotics and automation technologies that can work alongside humans to improve productivity and safety.
- Greater use of 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing technologies to enable rapid prototyping and customization of products.
- The adoption of digital twin technologies, which use virtual simulations to test and optimize manufacturing processes.
- The future of Smart Manufacturing is expected to be characterized by continued innovation and technological advancements, leading to even greater improvements in efficiency, productivity, and cost reduction.
Conclusion
Smart Manufacturing is transforming the manufacturing industry by leveraging advanced technologies to optimize production processes, reduce costs, and improve quality. While there are some challenges to implementing Smart Manufacturing, such as high costs and the need for a skilled workforce, the benefits are numerous, including increased efficiency, productivity, and flexibility.
American brands such as Ford, GE, P&G, and Caterpillar demonstrate the success of Smart Manufacturing in improving operations and reducing costs. Looking to the future, ongoing advances in technology are expected to drive even greater improvements in Smart Manufacturing, enabling companies to remain competitive and meet the changing needs of consumers.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



