Table of Contents
Introduction
The Panama Canal united two oceans, dramatically transforming maritime trade. This article will explore the extensive history of the Panama Canal and its influence on the social, political, and economic landscape of Panama.
Since its construction, the Panama Canal has linked the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It has significantly influenced the development of international commerce and the transportation of goods and resources.
- Panama Canal is a short cut between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- It’s considered one of the Man-Made Wonders of the World
- It’s over 100 years old.
- Over 1 Million Vessels have transited the canal since it opened.
- The Panama Canal was expanded for bigger ships in 2016
In this article, we explore the rich history of the canal and its profound impact on Panama’s social, political, and economic landscape. We will also examine the associated costs and revenues, as well as the future challenges that lie ahead.
What is the Panama Canal?

The Panama Canal stands out as one of the most significant construction endeavors ever, demanding engineering feats of an unparalleled magnitude and creative approaches to challenges that seemed impossible to overcome.
The purpose of constructing the Panama Canal was to establish a direct shipping pathway between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, as ships from the East Coast previously had to navigate around South America to access the West Coast, a journey that was lengthy and time-consuming.
Panama Canal History

The story of the Panama Canal is one of aspiration, innovation, and conflict. Its establishment revolutionized global commerce, but it incurred significant human and environmental costs.
- Initial Attempts (1880s): The canal’s history started with a failed venture by the French engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps, who had previously constructed the Suez Canal. Obstacles such as tropical illnesses (malaria and yellow fever) and engineering challenges resulted in the project’s abandonment.
- U.S. Involvement (1904-1914): In 1904, the United States took control of the project, spearheaded by President Theodore Roosevelt. The canal’s completion in 1914 showcased advanced engineering methods and the successful elimination of disease-carrying mosquitoes by Dr. William C. Gorgas.
- Opening and Strategic Significance: When it opened on August 15, 1914, the canal became a vital connection between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, cutting the travel distance for vessels by about 8,000 nautical miles. It quickly acquired considerable military and economic significance during World War II.
- Panama Canal Agreement (1977): In a landmark agreement between U.S. President Jimmy Carter and Panamanian leader Omar Torrijos, the Panama Canal Treaties facilitated the gradual transfer of canal control to Panama by December 31, 1999.
Initial Trade Routes in Panama
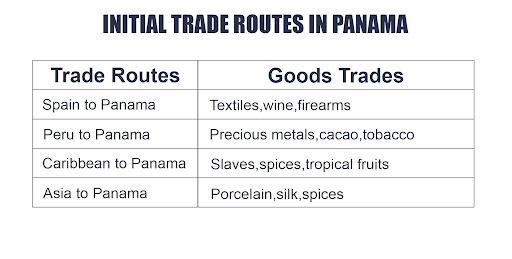
Before the construction of the Panama Canal, the region played a vital role in global commerce by serving as a key transit route and trade hub. Over time, Panama’s significance grew through various developments that connected the Atlantic and Pacific, laying the groundwork for one of the world’s most ambitious engineering projects.
- Trade Hub Origins: Spanish Portobelo Fairs fostered vibrant trade among colonies in the 17th and 18th centuries.
- Early Global Commerce: The fairs acted as bustling marketplaces for diverse products and cultural exchange.
- Strategic Route: Panama’s location made it an essential natural corridor for the transit of goods and people.
- Railway Breakthrough: The Panama Railroad, built in 1855, linked the Atlantic and Pacific coasts.
- Accelerated Trade: The railroad offered a faster, more efficient means of transport between oceans.
- Economic Catalyst: These early trade routes bolstered Panama’s role in international commerce.
- Foundation for Innovation: The region’s established significance set the stage for the eventual construction of the Panama Canal.
Oceanic Link: A Revolutionary Step in Canal Development

Construction commenced in 1881 with an original design that did not include locks, allowing ships to navigate at sea level. It quickly became apparent that traversing the continental divide, which rises to 110 meters above sea level, would be impractical without locks.
Consequently, the design was updated in 1887 to incorporate two sets of locks. The canal was opened to shipping traffic in 1914. Due to the increasing demand for capacity over the following century, a project to widen the canal and build new, larger locks was launched and completed in 2016.
- Lock Canal Innovation: Chief Engineer John F. Stevens championed the lock canal design, redirecting French plans and paving the way for a groundbreaking engineering solution that connected two major oceans.
- Navigating Challenges: Overcoming obstacles during construction, including the development of an intricate lock system and the management of the unpredictable Chagres River.
- Revolutionary Lock Design: Introducing a system of locks that raised and lowered vessels, ensuring smooth and efficient transit across varying elevations.
- Expansive Vessel Capacity: The canal’s dimensions and design were tailored to accommodate a wide range of ships, from small boats to massive cargo vessels.
- Gatun Lake Creation: Damming the Chagres River to form Gatun Lake—the largest artificial lake of its time—secured a vital water source and helped regulate water flow and prevent flooding.
- Global Engineering Achievement: The completed Panama Canal stands as a testament to human creativity and determination, uniting thousands of workers from around the world and continuing to serve as a critical artery for global maritime trade.
Engineering Marvel: The Lock Canal

The innovative lock canal design used in the Panama Canal stands as a testament to groundbreaking engineering.
- By incorporating a system of locks, engineers were able to facilitate the movement of vessels across the Isthmus of Panama, effectively bridging the elevation gap between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- Massive gates and complex hydraulic mechanisms within the lock chambers allowed ships to be safely elevated and lowered, ensuring a seamless journey through the canal.
Harnessing Nature: The Chagres River and Gatun Lake
A major obstacle during the canal’s construction was the formidable Chagres River, notorious for its unpredictable floods that threatened the canal’s stability.
- To address this challenge, engineers created Gatun Lake, an expansive man-made reservoir that serves as a natural buffer against the river’s force.
- This strategic innovation not only subdued the Chagres River but also provided a consistent water supply for the canal’s locks, while simultaneously nurturing the surrounding ecosystem.
Panama’s Social and Political Transformation

The building and operation of the Panama Canal significantly transformed the nation on both social and political fronts.
Enhanced sanitation practices during construction dramatically improved public health, reducing the incidence of diseases such as yellow fever and malaria by eliminating stagnant water, controlling mosquitoes, and establishing efficient sewage systems.
- The canal’s development spurred economic growth by attracting an international workforce and generating new opportunities.
- Moreover, the transfer of canal authority from the United States to Panama in 1999 marked a pivotal moment in the country’s history, empowering Panama to manage and reap the benefits of this monumental asset. The creation and management of the Panama Canal provided Panama with various economic prospects.
- The arrival of workers from across the globe resulted in the expansion of local enterprises and industries.
- Furthermore, the canal’s strategic positioning and significance in international commerce have placed Panama prominently on the world stage, establishing it as an essential participant in the maritime sector.
The canal’s social and political effects have been substantial. As Panama continues to oversee and benefit from the canal, it strengthens its role as an important center for global trade and as a source of national pride.
Economic Impact on International Trade
The Panama Canal is an essential conduit for global commerce, linking the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- With over 140 trade routes converging at this strategic location, the canal facilitates the movement of raw materials and manufactured goods, thereby driving global economic growth and development.
- Its prime location and efficient operations have made it a favored route for shipping companies worldwide.
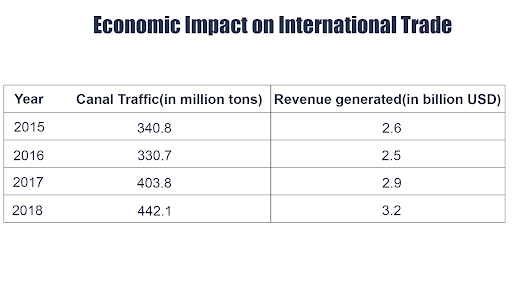
The data above illustrates the steady growth in canal traffic over the years, marked by an increasing number of vessels passing through its waters.
- This surge in activity has had a significant economic impact on Panama, underpinning the country’s development and supporting major infrastructure projects.
- The economic benefits of the canal extend beyond Panama, as it helps lower transportation distances and enhances trade between regions.
The efficient transit of goods through the canal ultimately contributes to reduced costs for shipping companies and consumers alike, while fostering greater economic integration on a global scale.
The Canal Expansion Project
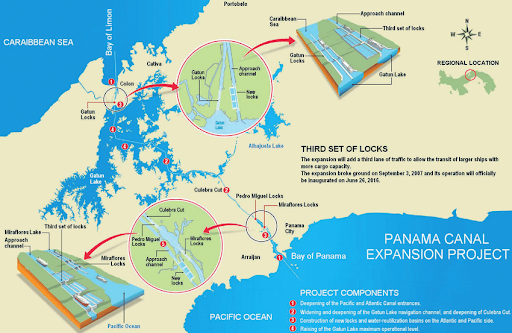
The Panama Canal experienced a significant expansion project to accommodate the increasing requirements of global trade.
- Finished in 2016, this initiative aimed to enhance the canal’s capacity, allowing for the passage of larger vessels, referred to as neo-Panamax and some post-Panamax ships.
- The expansion introduced new traffic lanes, providing a more efficient transit experience and alleviating congestion.
- With the enlarged canal, maritime traffic in Latin America and the Caribbean region has notably risen.
- This surge, in turn, prompted considerable investments in port upgrades and infrastructure improvement in nearby areas.
The expansion project opened up new avenues for trade and economic development in the region, enabling the transport of goods on a broader scale.
Impact on Latin America and the Caribbean Ports

The expansion of the Panama Canal has profoundly impacted Latin American and Caribbean ports, reshaping trade dynamics and prompting significant investments in port infrastructure to handle larger vessels and increased maritime commerce.
- Enhanced Vessel Capacity: The canal now accommodates larger ships, prompting ports to upgrade facilities to manage increased vessel sizes efficiently.
- Revitalized Trade Dynamics: The expanded canal has transformed regional trade, opening new avenues for countries to strengthen their roles in global commerce.
- Port Infrastructure Investments: Major ports have launched comprehensive expansion projects to support larger ships, boosting their capabilities and market competitiveness.
- Surge in Maritime Commerce: With more substantial vessels transiting the canal, there is a noticeable increase in regional maritime trade and economic opportunities.
- Future Trade Evolution: Ongoing investments in technology, logistics, and infrastructure are crucial for ports to adapt and thrive as larger vessels become the norm.
The Panama Canal’s expansion continues to influence future trade in the region. As larger vessels increasingly traverse the canal, ports in Latin America and the Caribbean must evolve to meet the changing needs of the shipping sector.
Challenges Ahead for the Panama Canal

The Panama Canal, while an extraordinary feat of engineering, encounters several issues as it looks to the future. These issues are vital for ensuring the canal’s efficient management and operations, as well as its sustainability and adaptability in the constantly evolving global trade environment.
The Transfer of Authority
- The Panama Canal faced a significant challenge when control was handed over from the United States to Panama in 1999.
- The Panama Canal Authority now manages the canal, requiring effective governance and ongoing training to ensure sustainable operations.
Increasing Shipping Industry
- As the shipping industry grows, the canal must accommodate larger vessels and increased traffic.
- The rise of neo-Panamax and post-Panamax ships strains resources, making it essential to fund renovations, such as widening the Gatun Cut and deepening Gatun Lake, to meet future demands.
Environmental Impacts
- The canal also faces environmental challenges, including deforestation and water availability.
- Deforestation leads to soil erosion, impacting operations.
- Sustainable land management and effective water resource management are vital for maintaining the delicate ecosystem and the canal’s long-term viability.
Through strategic planning, infrastructure investments, and sustainable management practices, the canal can continue to serve as a crucial link in global maritime trade, facilitating the movement of goods and supporting economic development in Panama and beyond.
Future Scenarios for the Panama Canal
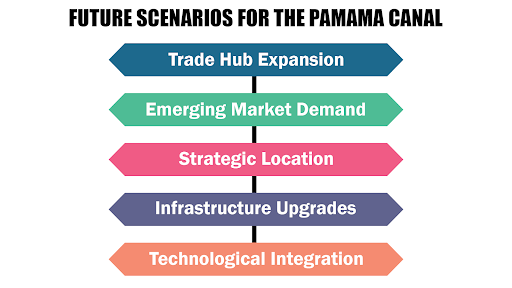
The Panama Canal is set to remain a vital artery for global commerce, evolving to meet the changing demands of international shipping through strategic upgrades, increased maritime traffic, and emerging technological innovations.
- Trade Hub Expansion: Surge in maritime traffic as trade volumes grow. This growth is propelled by dynamic global markets and evolving trade routes.
- Emerging Market Demand: Increased role with rising economies like China, India, and Brazil. The canal’s efficiency and connectivity make it a strategic choice for these burgeoning markets.
- Strategic Location: Continues to serve as a key connection between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Its prime positioning ensures enduring relevance in global shipping networks.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Ongoing enhancements to support modern shipping needs. Investments in advanced technology help the canal meet future demands and improve operational capacity.
- Technological Integration: Adaptation to advancements like autonomous vessels and alternative fuels. Embracing these innovations will enable the canal to boost efficiency and support sustainable maritime practices.
Conclusion
The Panama Canal is a remarkable engineering feat that has greatly impacted Panama’s history and economy by facilitating international trade. Its establishment marked a significant moment in Panama’s authority and offered economic opportunities.
While the canal continues to generate revenue and support the economy, it faces challenges such as increased traffic, ecological concerns, and changing trade dynamics. Effective management and strategic planning will be crucial for its continued success.
Despite these hurdles, the Panama Canal remains vital for global maritime trade. Its historical significance and revenue highlight its importance, and ongoing renovations will help it maintain its crucial role in connecting the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



