Table of Content
Introduction

SAP, which stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, was founded in 1972 by five former IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany. Five IBM engineers, all based in Mannheim, Germany, began working on the program – Hasso Plattner, Klaus Tschira, Claus Wellenreuther, Dietmar Hopp, and Hans-Werner Hector.
SAP’s vision was to create software that would integrate business processes in real-time, allowing companies to improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
The company’s vision is to help organizations run better by simplifying business processes and improving efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
SAP, one of the biggest players in the ERP industry, was the first company to introduce enterprise-level ERP software to the world.
Key Stats
- 86% of Fortune 500 companies use SAP software
- The United States has more than 1,400 websites currently using SAP Commerce Cloud
- There are 20 SAP labs around the world
- This is $16 trillion of consumer purchases worldwide
- SAP is a global company with over 100,000 employees & it has offices in over 180 countries.
- SAP collaborated with Walmart, Amazon, Boeing more than 21000 partner companies
- 77% of the world’s transaction revenue goes through an SAP system
- 80% of SAP’s customers are small and medium-sized companies 98% of the 100 most valued brands are SAP customers 92% of Forbes Global 2000 companies are SAP customers
History of SAP & SAP’s Impact on the Business World
SAP, which stands for Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung in German (System Analysis and Program Development in English), is a software company founded in 1972 by five former IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany. The company’s first product was a financial accounting system called R/1.
- In the 1980s, SAP expanded internationally and launched its second product, R/2, which offered improved functionality and allowed companies to integrate their business processes. This led to rapid growth for SAP, as more and more businesses adopted its software.
- In the 1990s, SAP launched R/3, which was a major improvement over its previous products.
- R/3 was a client-server system that allowed businesses to integrate their operations across multiple departments, and it became the dominant enterprise resource planning (ERP) software in the world.
- In the early 2000s, SAP continued to expand its product offerings, introducing various new applications and services for businesses.
- It also acquired several companies to expand its capabilities, including Ariba (a procurement software company) and SuccessFactors (a human resources software company).
- SAP has focused on expanding its cloud offerings, providing customers with a range of software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- This has included the launch of SAP S/4HANA, a cloud-based ERP system that offers real-time analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- In addition to its software offerings, SAP has also prioritized sustainability and social responsibility. In 2020, the company announced a commitment to become carbon neutral by 2025 and to achieve net-zero emissions by 2030.
- SAP has also pledged to increase its spending with diverse suppliers and to support education and training initiatives for underrepresented groups.
- SAP is one of the largest software companies in the world, with more than 200 million users in over 180 countries.
- Its products and services span a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and more.
- SAP has faced challenges in recent years, including criticism of its licensing and pricing models and competition from other software providers.
SAP's Impact on the Business World
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a software company that provides enterprise resource planning (ERP) software solutions for businesses. Since its inception in 1972, SAP has had a significant impact on the business world, and its software solutions are now used by thousands of businesses worldwide. Here are some ways SAP has impacted the business world:
- Improved business efficiency: SAP’s ERP software helps businesses streamline their operations, automate processes, and reduce manual work. This improves the overall efficiency of the business, allowing it to operate more smoothly and with greater accuracy.
- Increased data accuracy and visibility: SAP’s software solutions provide businesses with real-time data on their operations, which enables them to make informed decisions quickly. The software also ensures data accuracy by eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Enhanced customer experience: By providing businesses with a comprehensive view of their customers’ interactions and transactions, SAP’s software solutions help businesses to better understand and serve their customers. This enhances the overall customer experience and increases customer satisfaction.
- Improved supply chain management: SAP’s software solutions help businesses manage their supply chains more effectively by providing real-time information on inventory levels, production schedules, and logistics. This enables businesses to optimize their supply chains and reduce costs.
- Better financial management: SAP’s software solutions provide businesses with accurate financial data and enable them to manage their finances more effectively. This includes tracking expenses, forecasting revenue, and managing cash flow.
The Emergence of SAP R/2
SAP R/2 was the first fully integrated enterprise resource planning (ERP) software developed by SAP AG, a German software company. The development of SAP R/2 started in the 1970s, and it was released in 1979.
- SAP R/2 was designed to provide businesses with an integrated system that could manage all their business processes, including accounting, finance, materials management, production planning, and sales and distribution.
- SAP R/2 was based on a mainframe architecture and was designed to run on IBM mainframes. It used a hierarchical database management system (DBMS) called Adabas, which was developed by Software AG.
- The software was written in COBOL and was designed to be highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor it to their specific needs.
- One of the key features of SAP R/2 was its ability to provide real-time information on business processes.
- SAP R/2 was very successful, and by the mid-1980s, it had become the leading ERP software in Europe. It was also adopted by many businesses in other parts of the world, including the United States and Asia.
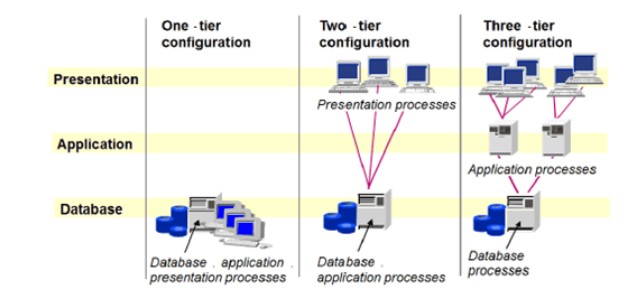
- SAP R/3 was a client-server architecture that used a relational database management system (RDBMS) and was designed to run on a variety of platforms, including UNIX, Windows, and mainframes.
SAP R/3: The Game-Change
SAP R/3 is a software application developed by the German company SAP SE. It is an enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that enables businesses to manage their operations, finance, human resources, and other important processes in a single system. The software was first introduced in 1992 and quickly became a game-changer in the business world.
Before the introduction of SAP R/3, businesses often had to use multiple software applications to manage their various processes.
- This led to data inconsistencies, inefficiencies, and a lack of visibility across different departments.
- SAP R/3 revolutionized the way businesses managed their operations by providing a single integrated system that could manage all of their processes consistently and efficiently.
SAP R/3 allowed businesses to:
Automate their processes: SAP R/3 automated many of the manual tasks that were previously required to manage business operations, including financial accounting, materials management, and sales and distribution.
- Improve decision-making: SAP R/3 provided real-time data and analytics, allowing businesses to make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
- Increase efficiency: With SAP R/3, businesses could eliminate redundancies and streamline their operations, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Standardize processes: SAP R/3 provided a standard set of processes that could be used across the entire organization, ensuring consistency and accuracy in all areas of the business.
SAP R/3 was a game-changer because it provided businesses with a powerful tool to manage their operations in a more integrated, efficient, and effective manner. SAP continues to innovate and develop new solutions to help businesses stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing business landscape.
SAP Business Suite
SAP Business Suite is a collection of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software modules that are designed to help businesses manage their operations and processes more effectively.
SAP Business Suite provides businesses with a single integrated solution for managing their operations and processes. It helps businesses to improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and make better-informed decisions.
List of SAP Modules here
- SAP FI (Financial Accounting): This module handles financial transactions, general ledger accounting, accounts payable/receivable, asset accounting, and financial reporting.
- SAP CO (Controlling): The Controlling module focuses on cost accounting, profitability analysis, and internal orders. It helps in monitoring and managing costs within an organization.
- SAP SD (Sales and Distribution): The SD module manages sales processes, including order management, pricing, delivery, and billing. It integrates with other modules to provide end-to-end sales functionalities.
- SAP MM (Materials Management): MM module deals with procurement and inventory management. It covers purchasing, goods receipt, inventory control, and invoice verification.
- SAP PP (Production Planning): PP module handles production planning and control activities. It includes functions like Bill of Materials (BOM), routing, capacity planning, and shop floor control.
- SAP HR/HCM (Human Capital Management): HR module manages human resources-related processes such as personnel administration, organization management, payroll, time management, and recruitment.
- SAP PM (Plant Maintenance): The PM module is responsible for managing equipment maintenance, preventive maintenance, work orders, and inspections. It helps in optimizing the maintenance activities of an organization.
- SAP QM (Quality Management): QM module ensures the quality of products throughout the manufacturing process. It covers quality planning, inspection, and control activities.
- SAP PS (Project System): PS module is used for project planning, execution, and monitoring. It includes functionalities like project structures, cost planning, resource management, and progress tracking.
- SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management): CRM module focuses on managing customer relationships, sales, marketing, and service activities. It helps organizations improve customer satisfaction and retention.
- SAP BW/BI (Business Warehouse/Business Intelligence): BW/BI module enables data extraction, transformation, and reporting. It provides tools for data analysis and decision-making.
- SAP SCM (Supply Chain Management): SCM module covers supply chain planning, logistics, and execution. It includes functions like demand planning, procurement, inventory management, and transportation management.
- SAP SRM (Supplier Relationship Management): SRM module manages supplier relationships, procurement processes, and strategic sourcing activities. It helps streamline the procurement process and supplier collaboration.
- SAP EWM (Extended Warehouse Management): EWM module focuses on advanced warehouse management processes, including inbound and outbound logistics, inventory management, and warehouse optimization.
- SAP GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance): GRC module assists in managing governance, risk assessment, and compliance activities. It helps organizations maintain regulatory compliance and mitigate risks.
With the SAP Business Suite, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce data inconsistencies, and improve visibility across different departments.
Here are some of the different SAP Business Suite products:
SAP ERP
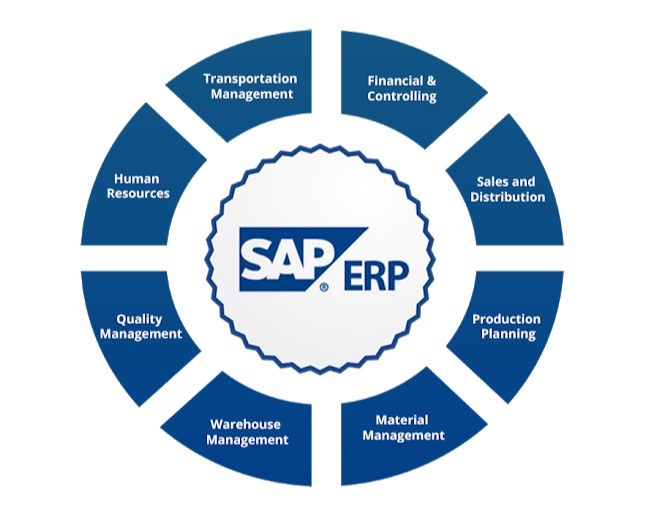
SAP ERP is the core module of the SAP Business Suite. It is an integrated enterprise resource planning software that covers various business processes such as finance, accounting, human resources, procurement, and supply chain management.
SAP Customer Relationship Management (CRM)

SAP CRM is a module that helps businesses manage their customer relationships more effectively. It covers functions such as sales management, marketing automation, customer service, and analytics.
SAP Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
SAP SRM is a module that helps businesses manage their supplier relationships and procurement processes. It covers functions such as supplier selection, contract management, and supplier performance monitoring.
SAP Supply Chain Management (SCM)
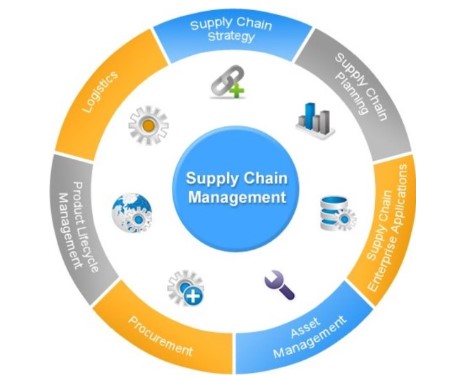
SAP SCM is a module that helps businesses optimize their supply chain processes. It covers functions such as demand planning, logistics, warehouse management, and transportation management.
SAP Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
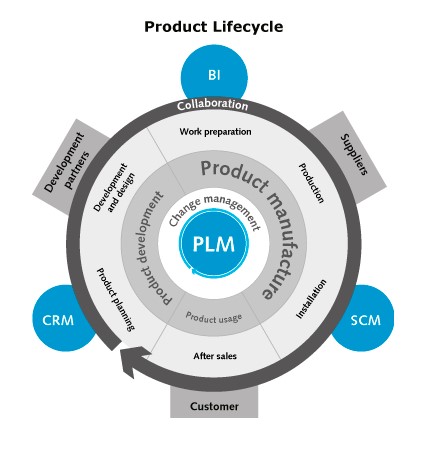
SAP PLM is a module that helps businesses manage their product development processes from ideation to retirement. It covers functions such as product design, engineering, and change management.
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM)
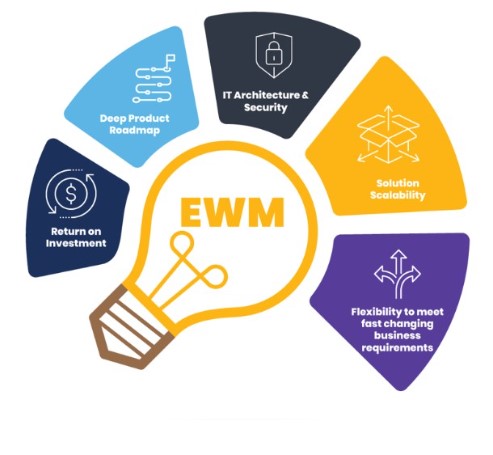
SAP EWM is a module that provides advanced warehouse management capabilities, such as inventory tracking, goods receipt, and dispatching.
SAP Financial Services Network (FSN)
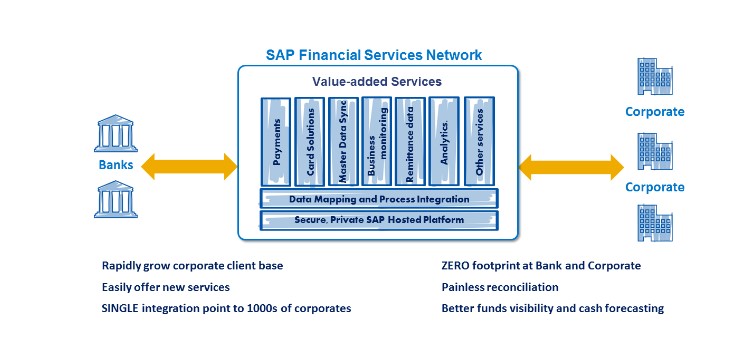
SAP FSN is a module that helps financial services companies automate their business processes and collaborate more effectively with their customers and partners.
SAP S/4HANA: The Next Generation ERP
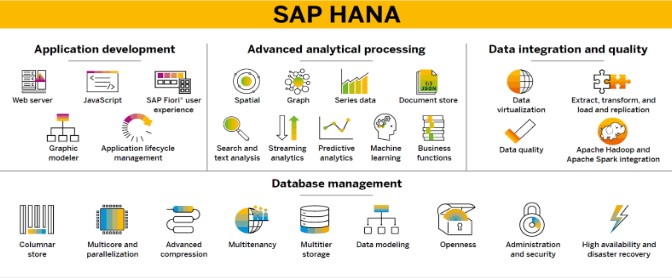
SAP S/4HANA is the next-generation enterprise resource planning (ERP) system from SAP. It is a revolutionary software platform that is designed to help businesses run simpler and faster in the digital economy.
S/4HANA is built on SAP’s in-memory computing platform, SAP HANA, and provides real-time processing capabilities for transactional and analytical data. With S/4HANA, businesses can simplify their operations, reduce costs, and accelerate growth, making it a game-changer for the ERP industry.

Some of the key features and benefits of SAP S/4HANA include:
- Simplification: S/4HANA simplifies business processes and reduces complexity by providing a streamlined and intuitive user interface, embedded analytics, and a simplified data model.
- Real-time insights: S/4HANA provides real-time access to data from across the enterprise, allowing businesses to make better-informed decisions and respond quickly to changing business conditions.
- Speed and performance: S/4HANA delivers lightning-fast performance for data processing, analytics, and reporting, enabling businesses to process large volumes of data in real-time.
- Agility and flexibility: S/4HANA is designed to be highly adaptable and flexible, enabling businesses to quickly respond to changing market conditions and new business opportunities.
- End-to-end business processes: S/4HANA provides end-to-end business processes, including finance, procurement, sales, inventory management, manufacturing, and more, enabling businesses to operate with greater efficiency and effectiveness.
- Cloud deployment: S/4HANA can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud, providing businesses with greater flexibility and scalability.
SAP S/4HANA is designed to help businesses meet the demands of the digital economy. It provides a powerful, integrated platform for managing core business processes, delivering real-time insights, and driving business innovation.
SAP FICO
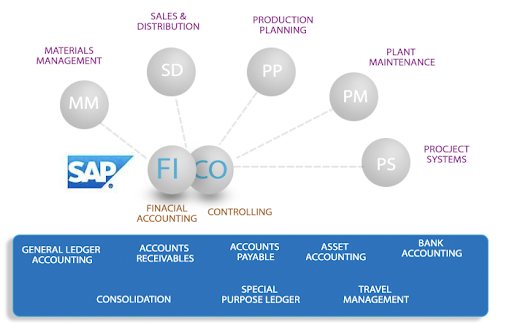
SAP FICO, which stands for Financial Accounting and Controlling, is a core module of SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software. It is designed to manage an organization’s financial transactions, reporting, and analysis. SAP FICO integrates various financial processes, such as general ledger accounting, accounts payable/receivable, asset accounting, cost center accounting, and profitability analysis.
Here are some key features and functionalities of SAP FICO:
- General Ledger Accounting: SAP FICO provides a centralized system for managing financial transactions and recording them in the general ledger. It enables organizations to create, update, and analyze financial statements, balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements.
- Accounts Payable/Receivable: SAP FICO facilitates the management of accounts payable and accounts receivable processes. It enables organizations to track and process vendor invoices, manage payments and collections, and generate reports for outstanding payments and customer balances.
- Asset Accounting: SAP FICO helps organizations manage their fixed assets effectively. It allows for the creation and management of asset master data, depreciation calculations, asset acquisitions, and disposals, and periodic reporting on asset values and depreciation expenses.
- Cost Center Accounting: With SAP FICO, organizations can track and allocate costs to different cost centers within the company. It enables cost planning, budgeting, and monitoring of expenses for various departments or projects. Cost center accounting provides valuable insights into cost control and performance evaluation.
- Profitability Analysis: SAP FICO enables organizations to analyze profitability at various levels, such as product, customer, or business segment. It helps in identifying the most profitable areas and making informed business decisions based on revenue, costs, and profitability data.
- Financial Reporting: SAP FICO offers robust reporting and analysis capabilities. It provides pre-configured financial reports and customizable reporting tools to generate real-time insights into financial data. These reports can be used for internal management reporting, statutory reporting, and compliance requirements.
- Integration with Other Modules: SAP FICO integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules, such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM), and Production Planning (PP). This integration enables smooth data flow between different functional areas of an organization, ensuring accurate financial information across the enterprise.
- Controlling: SAP FICO’s controlling functionality allows for cost controlling, profitability analysis, and internal orders. It helps organizations monitor and control costs, track variances, and analyze profitability by comparing planned and actual figures.
SAP FICO is a powerful financial management solution that provides organizations with the tools and capabilities to effectively manage their financial processes, gain insights into financial performance, and make informed business decisions. It enhances financial transparency, efficiency, and accuracy, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.
SAP Industry 4.0
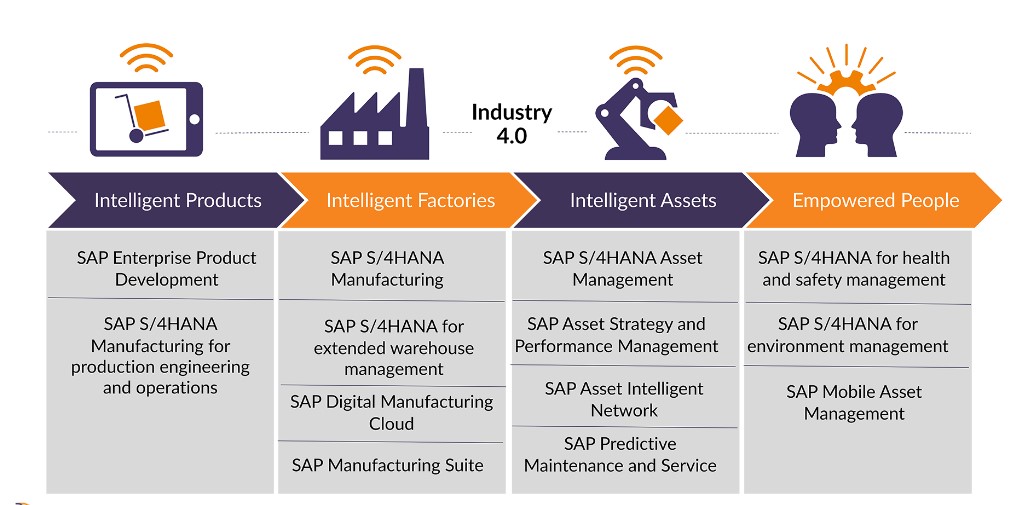
SAP Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the integration of digital technologies with traditional industrial processes to create more efficient, automated, and intelligent systems.
Here are some important points about SAP Industry 4.0:
- Digital Transformation: SAP Industry 4.0 enables companies to digitally transform their operations by leveraging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud computing.
- Connected Ecosystem: It promotes the concept of a connected ecosystem where machines, devices, sensors, and systems are interconnected, enabling real-time data sharing and collaboration across the entire value chain.
- Smart Manufacturing: SAP Industry 4.0 revolutionizes manufacturing processes by incorporating smart technologies and automation. It enables predictive maintenance, optimized production planning, real-time monitoring, and adaptive manufacturing based on data-driven insights.
- Real-time Data Analytics: By capturing and analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, SAP Industry 4.0 empowers organizations to make informed decisions and gain valuable insights for improving operational efficiency, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Improved Customer Experience: With SAP Industry 4.0, companies can personalize products and services, offer innovative solutions, and enhance customer experiences through technologies like digital twins, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR).
- Agile and Responsive Supply Chain: SAP Industry 4.0 enables end-to-end supply chain visibility, seamless integration, and efficient logistics management. It allows for dynamic demand forecasting, optimized inventory levels, and improved delivery reliability.
- Enhanced Safety and Sustainability: Industry 4.0 technologies help create safer working environments through automated processes, remote monitoring, and advanced safety protocols. It also enables sustainability initiatives by optimizing resource utilization, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency.
- New Business Models: SAP Industry 4.0 facilitates the development of new business models, such as servitization and outcome-based models. It enables companies to offer value-added services, predictive maintenance contracts, and pay-per-use options.
- Workforce Transformation: Industry 4.0 requires a skilled and adaptable workforce. SAP provides training and upskilling programs to help employees adapt to new technologies and roles, ensuring their participation in the digital transformation journey.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: SAP Industry 4.0 emphasizes collaboration and partnerships between companies, technology providers, and academia. It encourages open innovation, knowledge sharing, and ecosystem development to drive continuous improvement and innovation.
Leading Companies use SAP
Several leading companies across various industries have adopted SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) software to streamline their business processes and enhance operational efficiency. Here are some prominent companies that use SAP:
Coca-Cola

The Coca-Cola Company, a global beverage giant, utilizes SAP solutions to manage its supply chain, manufacturing, finance, and sales processes.
IBM

IBM, a multinational technology company, implements SAP software for its enterprise resource planning (ERP) needs, including finance, human resources, and procurement.
Siemens

Siemens, a diversified engineering and technology company, leverages SAP solutions for managing its financial operations, supply chain, and project management.
Amazon

Amazon, the world’s largest e-commerce company, employs SAP software to handle its logistics, order fulfillment, and inventory management processes.
Nestlé

Nestlé, a leading food and beverage company, uses SAP to manage its operations, including supply chain management, production planning, and financial management.
Partnerships & Collaborations
SAP, as a global leader in enterprise software solutions, has formed numerous partnerships and collaborations with various organizations to enhance its offerings and provide comprehensive solutions to its customers. Here are some notable partnerships and collaborations involving SAP:
Microsoft

SAP has a strategic partnership with Microsoft to provide integrated solutions that combine SAP’s cloud platform, SAP S/4HANA, and Microsoft Azure. This collaboration enables customers to run SAP applications in a secure and scalable cloud environment.
Google Cloud

SAP has partnered with Google Cloud to provide customers with a secure and scalable cloud infrastructure for running SAP applications. This collaboration allows organizations to leverage Google Cloud’s advanced capabilities and SAP’s industry-specific solutions.
Apple

SAP and Apple have partnered to develop mobile applications for the enterprise using Apple’s iOS platform. This collaboration aims to empower businesses with user-friendly and intuitive mobile solutions that leverage SAP’s software capabilities.
OpenText

SAP collaborates with OpenText, a leader in enterprise information management, to deliver solutions for managing unstructured content and digital assets within SAP systems. This partnership helps organizations streamline their document management processes and enhance information governance
These partnerships and collaborations demonstrate SAP’s commitment to driving innovation, expanding its product offerings, and delivering value-added solutions to its customers across various industries. By leveraging the expertise and capabilities of these partner organizations, SAP aims to provide comprehensive solutions that address the evolving needs of the digital economy.
Future of SAP S/4HANA: The Next Generation ERP
The future of SAP and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is promising as technology continues to advance and businesses require more sophisticated software solutions to manage their operations. Here are some trends that may shape the future of SAP and ERP:
- Cloud-based solutions: The shift to cloud-based solutions is likely to continue, as businesses seek to reduce their IT infrastructure costs and increase scalability. SAP has already developed cloud-based solutions like SAP S/4HANA Cloud, and this trend is expected to accelerate.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: The integration of AI and machine learning in ERP software solutions can improve the accuracy of data and provide more intelligent insights for decision-making. SAP has already integrated AI capabilities into some of its solutions, and this trend is expected to grow.
- Increased focus on user experience: ERP software solutions have traditionally been complex and difficult to use. However, the focus is now shifting towards user experience, with more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. SAP has already made significant investments in improving user experience, and this trend is expected to continue.
- Integration with other technologies: The integration of ERP software solutions with other technologies like IoT, blockchain, and big data analytics can provide even more powerful insights for businesses. SAP has already made some strides in this area, and it is likely to continue.
- Customization and personalization: Businesses increasingly want ERP solutions tailored to their needs. Customization and personalization of ERP software solutions are likely to become more common in the future, allowing businesses to optimize their operations even further.
The future of SAP and ERP is bright, with cloud-based solutions, AI, user experience, integration with other technologies, and customization likely to shape the future of ERP software solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, With the development of the world’s first enterprise ERP system in the 1970s, SAP revolutionized the way businesses manage their operations, and it has continued to innovate and evolve ever since.SAP is a global leader in enterprise software solutions, serving businesses of all sizes and industries around the world. As technology continues to advance, SAP’s ongoing innovation in cloud-based solutions, AI, user experience, integration with other technologies, and customization is likely to shape the future of ERP software solutions, enabling businesses to become more efficient and agile.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



