Table of Contents
Introduction
- According to Gartner, 30% of online searches are expected to be AI-driven by 2025, shifting away from traditional search engines.
- Moreover, AI tools like Perplexity AI claim to reduce search time by up to 40% by delivering direct, personalized responses instead of multiple links.
- AI-driven search boosts engagement by 20–25% through quicker, personalized answers.
- AI search systems achieve 90% accuracy in understanding user queries, reducing misunderstandings.
- 97% of mobile users now rely on AI-powered voice assistants, transforming mobile search habits.
- 46% of U.S. AI platform queries lead to follow-up questions, indicating deep user engagement.
The Rise of Search Engines
In the early days of the internet, search engines functioned like digital directories, relying on exact keyword matches to deliver results.
- Google’s introduction of PageRank revolutionized this approach by ranking pages based on backlinks and relevance.
- However, early search models struggled with contextual understanding, often prioritizing keyword matches over user intent.
- The rise of AI-powered search changed everything.
- With advancements in machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and neural networks, search engines evolved beyond simple keyword dependency.
They began interpreting meaning, intent, and context, making searches more accurate, intuitive, and user-centric.
Key Milestones in AI Search Evolution
- RankBrain (2015): Google’s first AI-driven ranking algorithm, improving results for complex and unfamiliar queries.
- BERT (2019) & MUM (2021): Enhanced language understanding, allowing search engines to process queries more naturally and contextually.
- Generative AI in Search (2023–2024): The rise of AI models like ChatGPT, Bard, and Perplexity AI shifted search from ranked links to AI-generated, conversational responses.
Search has evolved from simple keyword indexing to AI-powered contextual intelligence, making it smarter, faster, and more intuitive. As AI advances, the way we search, discover, and interact with information will keep transforming.
AI-Powered Search Engines
Deepseek AI

Deepseek is positioned as a next-generation search engine that leverages deep learning and semantic search techniques. Rather than relying solely on keyword matching, it uses advanced algorithms (often including vector representations) to understand the intent behind queries and deliver contextually richer results.
Key Points:
- Semantic Understanding: Uses deep learning to capture meaning beyond keywords.
- Contextual Retrieval: Designed to return results that align with complex or nuanced queries.
- Emerging Technology: Represents the growing trend of embedding AI techniques into search to improve relevance.
Perplexity AI

- Conversational Interface: Users can ask questions in natural language and receive direct, chat-style responses.
- Source-Backed Answers: Typically provides citations for its information, enhancing transparency.
- User-Friendly: Designed to simplify information discovery by reducing the need to sift through multiple links.
Google Gemini

Google Gemini is the next-generation AI model initiative from Google. While not a standalone search engine, it is intended to power a range of Google’s services, including search. Gemini is expected to combine the strengths of language models with Google’s massive data infrastructure.
Key Points:
- Next-Gen AI: Seen as Google’s answer to generative AI competitors, integrating advanced language capabilities into its core products.
- Search Integration: Will likely enhance search results with conversational and generative features.
- Part of a Broader Ecosystem: Embedded within Google’s suite of tools and services, influencing how users interact with information.
Microsoft Copilot

Microsoft Copilot is an AI assistant integrated into Microsoft 365 applications (like Word, Excel, and Outlook) and across Windows. It leverages large language models to provide context-aware assistance—from drafting emails to summarizing documents—and is closely tied to Microsoft’s AI-enhanced Bing search.
Key Points:
- Productivity Focus: Helps users generate content, automate tasks, and gain insights within Microsoft Office products.
- Integration with Search: Ties into Bing and other Microsoft tools to pull in relevant information and data.
- Enterprise Ready: Built with business and productivity workflows in mind, streamlining everyday tasks with AI support.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT

ChatGPT is OpenAI’s flagship conversational AI model. While it isn’t a traditional search engine, it’s widely used to answer queries, provide explanations, and assist in creative tasks through interactive dialogue.
Key Points:
- Conversational AI: Enables users to engage in natural, back-and-forth dialogue for a variety of queries.
- Wide Range of Applications: Used in customer support, content generation, tutoring, and more.
- Rapid Evolution: Regular updates and improvements have kept it at the forefront of public interest in generative AI.
You.com
You.com is an AI-powered search engine designed to offer a more personalized and privacy-conscious search experience. It integrates traditional search results with AI-generated summaries and interactive elements.
Key Points:
- Customizable Experience: Offers users the ability to adjust and personalize search result formats.
- AI Integration: Blends standard search algorithms with AI tools for summarization and categorization.
- Privacy Focus: Markets itself as an alternative that respects user data compared to more traditional search engines.
Andi

Andi is an AI-powered search assistant that aims to simplify the search process by providing direct answers and context-rich responses. It is built around a conversational model that reduces the need to click through multiple results.
Key Points:
- Conversational Search: Engages users in dialogue to refine and clarify queries, often delivering summarized answers.
- User-Centric Design: Focuses on delivering clear, actionable responses quickly.
- Competitive Edge: Part of the new wave of AI search assistants designed to compete with more established engines by focusing on ease of use and interactivity.
Key Features of AI-Powered Search Engines

Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables search engines to understand and interpret human language in a way that mimics human comprehension. Traditional search engines rely on keyword matching, but AI-powered search engines use NLP to analyze the context, sentiment, and intent behind a query.
- Context Awareness: Recognizes meaning beyond individual words, reducing ambiguity.
- Conversational Understanding: Processes questions as a human would, making search results more intuitive.
- Multilingual Support: Breaks language barriers by understanding and translating queries across languages.
Example: When a user searches “best laptop for coding under $1000,” an AI-driven search engine understands the context rather than just matching keywords.
Machine Learning Algorithms
AI search engines improve over time through Machine Learning (ML), which allows them to analyze vast datasets and refine search results based on user behavior.
- Self-Learning Capabilities: Algorithms continuously learn from user interactions, improving accuracy.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifies trends and adapts search rankings accordingly.
- Spam Filtering: Detects low-quality or misleading content to maintain search result integrity.
Example: If users frequently click on a specific article for a search query, ML algorithms may rank that page higher for similar searches in the future.
Hyper-Personalization & Behavioral Learning
Modern AI search engines create tailored experiences by analyzing user behavior, preferences, and previous search history.
- User-Centric Results: Prioritizes content based on past interactions and interests.
- Adaptive Learning: Evolves based on user engagement, refining recommendations.
- Smart Content Recommendations: Suggests articles, products, or videos that match user preferences.
Example: If a user frequently searches for “vegan recipes,” the AI will start prioritizing plant-based content in their search results.
Predictive Search & Generative AI

- Proactive Suggestions: Displays potential search queries based on trends and past behavior.
- AI-Powered Answers: Generates detailed responses rather than just listing links.
- Interactive Assistance: Provides chatbot-like engagement to refine search queries.
Predictive Search & Auto-Suggestions
AI-driven auto-suggestions streamline the search process by offering real-time query completions.- Smart Query Expansion: Suggests related terms to help users refine searches.
- Real-Time Predictions: Provides dynamic results as users type.
- Error Correction: Detects and fixes spelling errors automatically.
Semantic Search
Semantic search focuses on meaning rather than exact keyword matches, delivering more relevant results.- Conceptual Understanding: Recognizes synonyms and related terms to improve accuracy.
- Entity Recognition: Identifies specific topics, people, or places within queries.
- Contextual Relevance: Matches results based on searcher intent rather than keyword density.
How AI is Revolutionizing Search Engines

AI-powered search engines are reshaping how users find information, prioritizing intent over traditional ranking factors. Instead of relying solely on backlinks and metadata, modern search algorithms analyze contextual relevance, user behavior, and predictive analytics to deliver more precise results.
Conversational Search & AI Chatbots
- Search is becoming more interactive, with AI chatbots providing direct answers instead of just listing links.
- Tools like Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), ChatGPT, and Perplexity AI enable users to ask complex questions and receive summarized, AI-generated responses—reducing the need to click through multiple websites.
Predictive Search & Personalized Results
- AI-driven algorithms analyze search history, preferences, and behavior to deliver highly personalized results.
- Instead of generic rankings, users receive tailored answers based on their interests, shifting SEO strategies from broad visibility to individual relevance.
AI-Powered Visual & Voice Search
- With tools like Google Lens, and Pinterest Lens, and voice assistants such as Alexa and Siri, users now search using images and voice commands.
- Businesses must optimize content for these formats, ensuring AI can accurately interpret and rank their information.
Search Generative Experience (SGE) & AI Summarization
- Google’s SGE uses AI to generate instant, summarized answers at the top of search results.
- As AI-driven search evolves, traditional SEO strategies must adapt to ensure content remains visible and optimized for generative search models.
Impact on SEO and Digital Marketing

Shift from Traditional Keyword-Based SEO to AI-Driven SEO
In the past, SEO was primarily about optimizing for keywords. Marketers would research high-volume search terms and create content stuffed with these keywords to rank higher in search engine results.- Personalized Search Results: AI uses data from user behavior, location, and past searches to customize results for individual users.
- AI-Driven Search Summaries: Featured snippets, AI-generated summaries, and direct answers are becoming more common, reducing clicks to actual websites.
- Voice Search and Natural Language Queries: With AI assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, people search using natural, spoken language rather than typing keywords.
- The Impact of AI on Content Quality: Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI search tools are favoring in-depth, well-structured content over shallow keyword-stuffed pages.
Importance of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
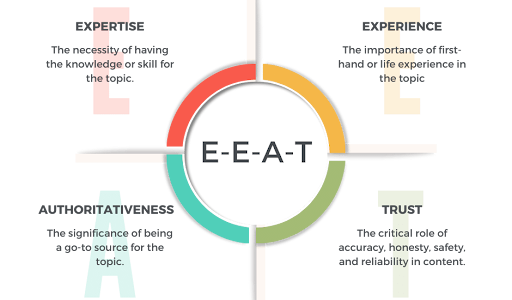
Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) framework has become even more critical in AI-driven search engines. AI algorithms now evaluate content not just for relevance but for credibility and quality.
Experience
- AI-powered search engines prioritize content created by people with real-life experience in the topic.
- Example: A fitness blog written by a certified personal trainer will rank higher than a generic article written by someone without expertise.
Expertise
- Content must demonstrate expert-level knowledge in a field.
- AI evaluates credentials, author bios, and citations to assess expertise.
- Example: A medical article by a doctor or healthcare professional is considered more credible than one from an anonymous writer.
Authoritativeness
AI determines authority based on:
- Backlinks from reputable sites
- Social proof (mentions, shares, engagement)
- Brand recognition and reputation
Trustworthiness
Trust signals include:
- Accurate, fact-checked content
- Secure website (HTTPS)
- Positive user reviews and minimal misleading information
To succeed in AI-driven SEO, businesses and content creators must focus on high-quality, well-researched, and authoritative content that adds real value to users.
AI and the Future of Search Advertising
AI-Driven PPC and Automated Bidding
Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising has long been a staple in digital marketing, allowing businesses to bid on keywords and display ads in search results. AI-driven PPC has changed the game by introducing automation, efficiency, and predictive analytics.
How AI is Revolutionizing PPC
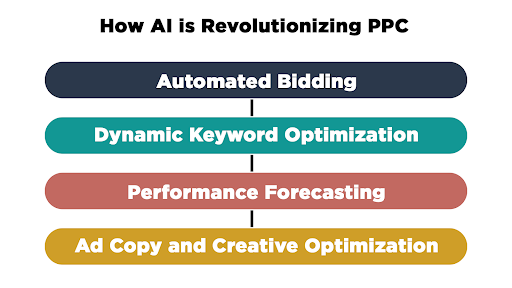
- Automated Bidding: AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to determine the optimal bid for an ad in real-time. Google Ads’ Smart Bidding, for instance, uses machine learning to adjust bids based on conversion likelihood, user behavior, and historical data.
- Dynamic Keyword Optimization: AI identifies high-performing keywords, adjusts keyword targeting, and even suggests new keywords that align with search intent.
- Performance Forecasting: AI-driven PPC platforms predict how campaigns will perform based on past data, helping advertisers make data-backed decisions.
- Ad Copy and Creative Optimization: AI tools like Google’s Responsive Search Ads (RSAs) automatically test different headlines and descriptions to find the best-performing combinations.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: Click fraud has been a significant concern in PPC advertising. AI can detect suspicious activity, such as bots generating fake clicks, and prevent ad budget wastage.
Personalized Ads and Audience Targeting
Personalization has become the cornerstone of digital advertising, and AI is the driving force behind it. Traditional advertising strategies often rely on demographic data, but AI enables hyper-personalized targeting based on behavioral analysis, interests, and real-time interactions.
How AI Enhances Personalized Advertising
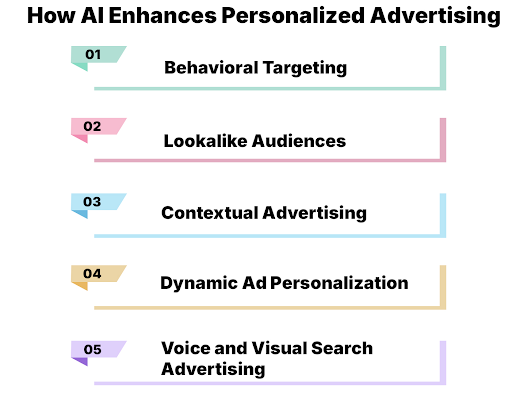
- Behavioral Targeting: AI tracks user interactions, such as search history, clicks, and website visits, to predict preferences and display relevant ads.
- Lookalike Audiences: AI identifies patterns among existing customers and finds new potential customers who share similar traits.
- Contextual Advertising: Instead of relying solely on keywords, AI analyzes page content and user intent to place ads in the most relevant contexts.
- Dynamic Ad Personalization: AI-powered platforms like Google Ads and Meta (Facebook) dynamically adjust ad creatives, copy, and offers based on individual user preferences.
- Voice and Visual Search Advertising: AI-driven search engines can now understand voice and image queries, enabling advertisers to target users beyond traditional text-based search.
AI-Powered Search Engines vs. Traditional Search Engines
With AI becoming the backbone of modern search engines, let’s explore how AI-powered search differs from traditional search models.
Key Differences in Functionality and User Experience
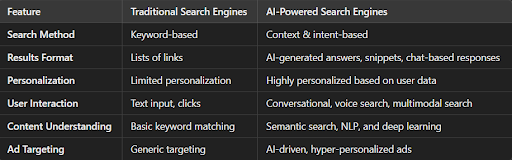
Key Differences Explained
- Search Method: Traditional search engines depend on keyword matching, whereas AI-powered ones analyze the intent behind a query, making results more relevant.
- Results Format: Conventional search engines display lists of links, while AI-powered ones generate direct answers, snippets, and chat-based responses.
- Personalization: AI search engines offer highly tailored results by analyzing user behavior and preferences, unlike traditional search engines with limited personalization.
- User Interaction: Instead of just text-based inputs and clicks, AI-powered search allows conversational queries, voice search, and multimodal inputs.
- Content Understanding: Traditional search engines rely on keyword matching, whereas AI-powered search engines utilize semantic search, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and deep learning to comprehend complex queries better.
- Ad Targeting: AI-driven search engines enable hyper-personalized advertising, making ads more relevant to users compared to the generic targeting of traditional search engines.
The Future of AI-Powered Search
AI-driven search is advancing beyond traditional text-based queries, integrating with Augmented Reality (AR), the Internet of Things (IoT), and voice assistants to provide more intuitive, real-world search experiences.
As AI-generated summaries impact website traffic, businesses must embrace AI-first content strategies, emphasizing structured data, conversational SEO, and AI-driven content optimization. The future of search is shifting from simple page rankings to delivering immediate, multimodal, and intent-driven responses.
Conclusion
AI-powered search is redefining how we access and engage with information—leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand intent and providing instant AI-generated insights. While this evolution improves search accuracy and user experience, it also raises concerns regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and content reliability.
To stay ahead in this changing landscape, businesses must align their strategies with AI-driven search trends, focusing on conversational search and structured content to ensure continued digital presence and relevance.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



