Table of Contents
Introduction
Data automation is an innovative process that utilizes automated technologies to manage, upload, process, collect, clean, and store data in an organized manner, moving away from traditional manual methods.
This approach leverages computer programs, simulations, and artificial intelligence to optimize data-related tasks and enhance workflow accuracy. Techniques involved in data automation include data preparation, validation, transformation, and analytics.
The primary goal of data automation is to increase operational efficiency and reduce errors in data processing. This allows human resources to focus on analytical tasks that require advanced critical thinking and decision-making skills.
What is Data Automation?
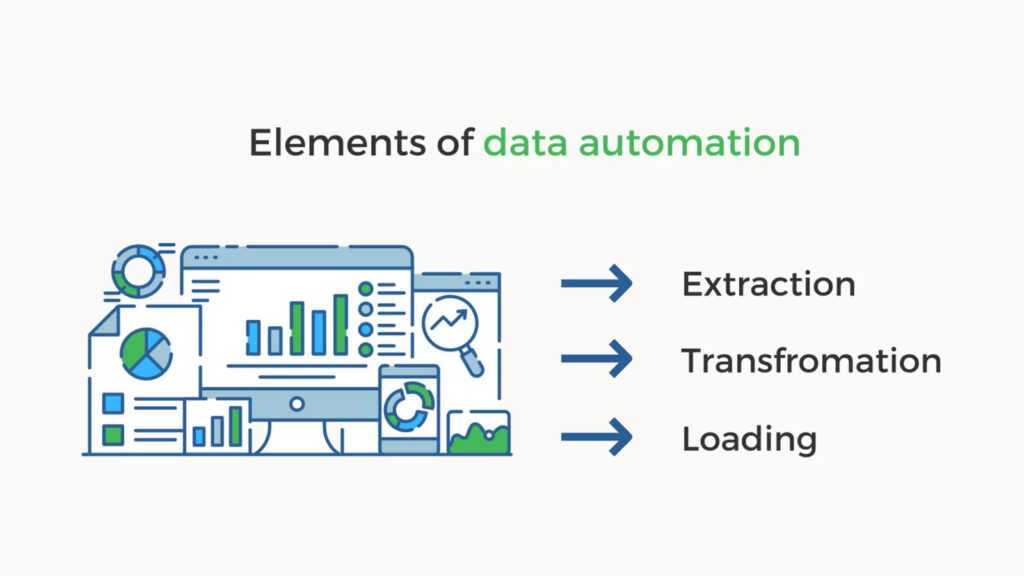
Data automation involves the strategic use of technology and software to streamline and optimize tasks and processes associated with an organization’s data management.
- This approach encompasses the deployment of algorithms, scripts, and specialized tools that facilitate the automated collection, processing, transformation, and analysis of data, often referred to as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load).
- By eliminating the need for manual human intervention, data automation enhances efficiency and accuracy, allowing organizations to manage large volumes of data with greater precision.
How Does Data Automation Work?
Data automation depends on a mix of tools, scripts, and workflows that engage with data sources to carry out established tasks. For instance:
- Data Collection: Gathering data automatically from APIs, databases, or IoT devices.
- Data Transformation: Cleaning and organizing data to make it usable.
- Data Integration: Merging data from various sources into a central hub.
- Data Utilization: Utilizing insights through analysis, visualization, and reporting.
Each phase is carried out smoothly, minimizing human involvement and speeding up decision-making.
The Importance of Data Automation
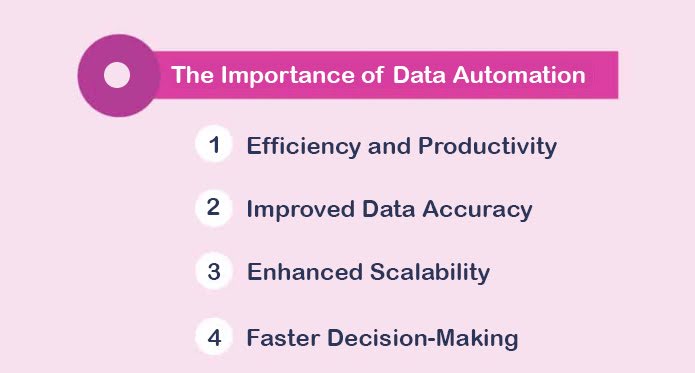
- Efficiency and Productivity: Manual processes can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and database updates, employees are freed up to focus on strategic initiatives, significantly boosting overall productivity.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Human errors in data handling can lead to costly mistakes. Automation ensures consistent and reliable data processing, which helps reduce inaccuracies.
- Cost Reduction: Although implementing automation systems requires an initial investment, they result in long-term savings by minimizing labor costs and decreasing the likelihood of financial errors.
- Enhanced Scalability: As organizations expand, their data needs also grow. Automation enables businesses to scale their data operations seamlessly, without the need for a proportional increase in workforce.
- Faster Decision-Making: Automated systems provide real-time data, allowing quicker and more informed decision-making. This agility is essential in industries where timing is critical.
Core Components of Data Automation
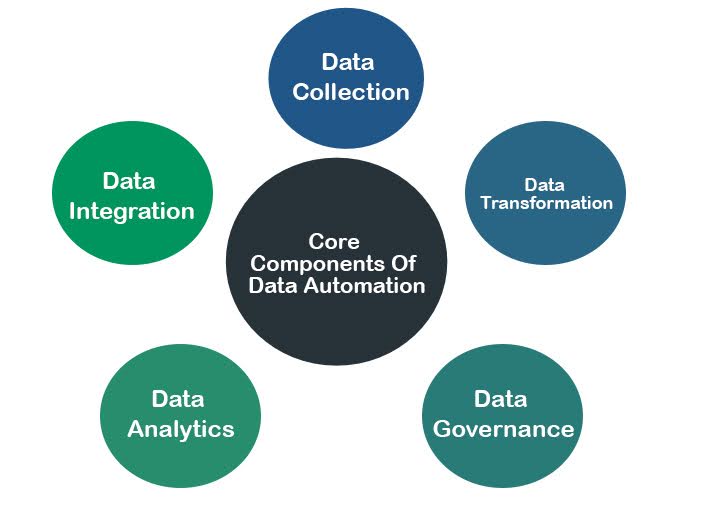
To successfully implement data automation, it’s essential to understand its core components:
- Data Collection: This is the initial step, involving the automated gathering of data from multiple sources. Tools such as APIs, web scraping software, and IoT sensors facilitate this process, eliminating the need for manual input.
- Data Transformation: Raw data often requires processing to make it useful. Automated workflows can clean, deduplicate, and reformat data to meet organizational requirements.
- Data Integration: Bringing together data from various sources into a unified system ensures that it is accessible and usable for analysis. This is particularly important for large enterprises with diverse data ecosystems.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing data and generating insights is a critical step. Automation tools can provide dashboards, predictive models, and reports to help businesses make data-driven decisions.
- Data Governance: Automating data compliance processes ensures that data handling adheres to legal and organizational standards. This is especially crucial in regulated industries such as healthcare and finance.
Tools for Data Automation

A wide variety of tools cater to data automation across its various stages. Below is a breakdown of some popular tools:
Data Collection Tools
- Zapier: Automates workflows by connecting different applications and triggering specific actions.
- Google Cloud Dataflow: Processes both batch and streaming data with scalability in mind.
- Scrapy: An open-source web scraping tool designed for extracting data from websites.
Data Integration Tools
- Apache NiFi: Facilitates seamless data flow between systems.
- Talend: Offers robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) capabilities.
- Informatica: Provides solutions for data integration, governance, and security.
Data Transformation Tools
- Alteryx: Simplifies data preparation and transformation for analytics purposes.
- Trifacta: Focuses on cleaning and preparing data for visualization.
- Data Wrangler: A browser-based tool for interactive data transformation.
Data Analytics Tools
- Tableau: A leading tool for creating interactive dashboards.
- Power BI: Offers business intelligence capabilities for data visualization.
- Looker: Provides a cloud-based platform for real-time analytics.
Data Governance Tools
- Collibra: Concentrates on data governance and stewardship.
- IBM InfoSphere: Ensures data quality and compliance.
- BigID: Helps organizations discover and manage sensitive data.
Benefits of Data Automation
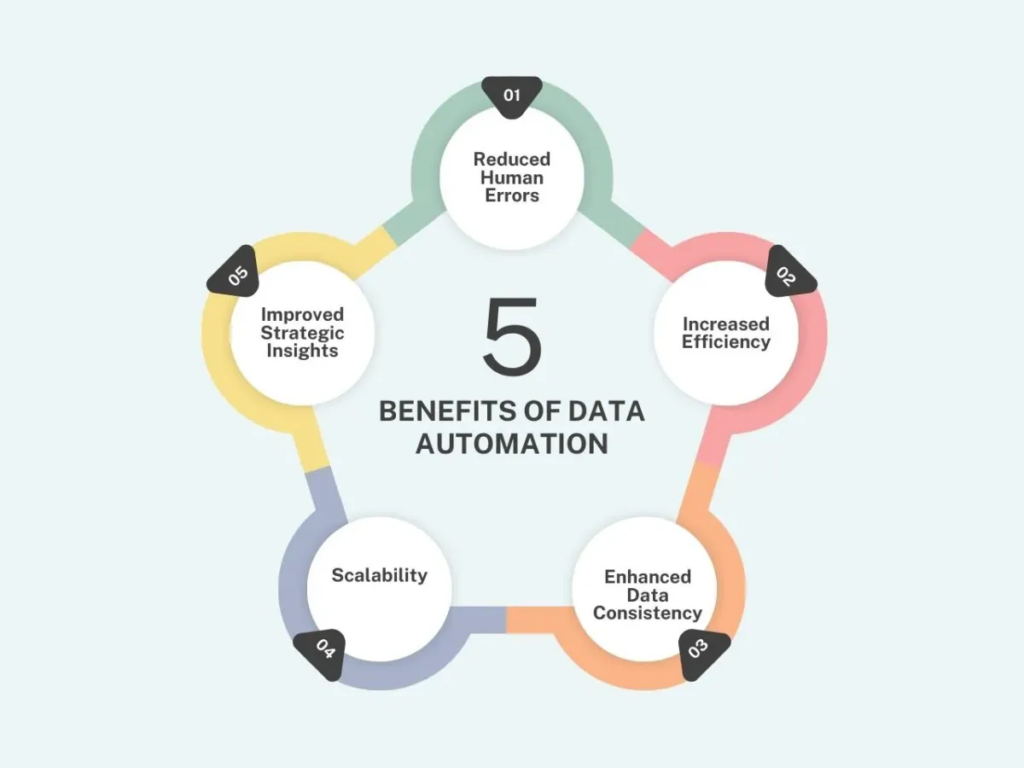
Implementing data automation presents significant benefits for organizations.
- Reduced Human Errors: Automating data processes minimizes the risk of mistakes, ensuring more accurate and reliable results.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined workflows enable faster data processing, freeing up valuable time and resources.
- Enhanced Data Consistency: Automation ensures uniformity across datasets, improving accuracy and reliability.
- Scalability: Automation allows businesses to handle growing data volumes effortlessly without compromising performance.
- Improved Strategic Insights: With automated data analysis, businesses can quickly derive actionable insights, driving smarter decision-making.
These advantages highlight the transformative impact of data automation on organizations, paving the way for enhanced efficiency and competitiveness.
Challenges in Implementing Data Automation

While data automation offers substantial benefits, it also presents several challenges:
- Data Silos: Integrating different systems and breaking down data silos requires effective tools and strategies.
- Data Quality Issues: Poor quality input data can undermine the effectiveness of automation, emphasizing the need for strong quality control measures.
- Security Risks: Automating processes can introduce potential vulnerabilities. Organizations must prioritize secure data handling practices to mitigate these risks.
- Initial Costs: The upfront investment in tools, infrastructure, and training can pose a barrier for smaller organizations.
- Change Management: Resistance to adopting new technologies can slow down implementation. Clear communication and training are essential to overcome this resistance.
Best Practices for Data Automation
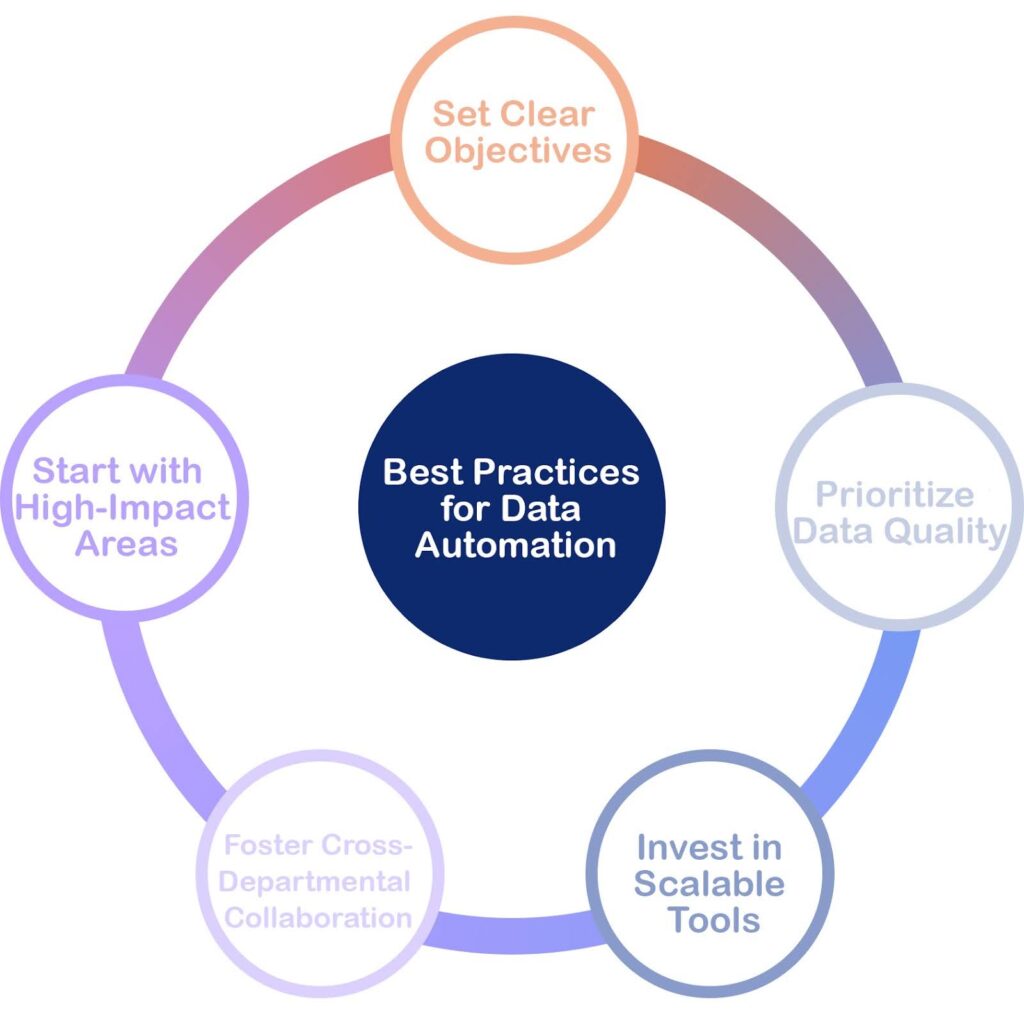
To effectively navigate the world of data automation, it’s essential to adopt certain best practices:
- Set Clear Objectives: Begin by defining specific goals and desired outcomes. This clarity will help steer the implementation process and ensure that efforts are aligned with organizational needs.
- Start with High-Impact Areas: Concentrate on automating processes that will yield the greatest return on investment. Areas such as data entry and reporting are often prime candidates due to their potential for efficiency gains.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Implement automated procedures for data cleaning and validation. Maintaining accuracy is crucial, as high-quality data underpins effective decision-making and operational success.
- Foster Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Promote alignment and communication between teams to facilitate smoother integration of automated processes. Collaboration can mitigate potential challenges and enhance adoption rates.
- Invest in Scalable Tools: Select tools that are not only effective for current needs but can also adapt and scale with the organization’s evolving requirements. This foresight can save time and resources in the long run.
By adhering to these practices, organizations can enhance their data automation strategies and achieve their desired outcomes efficiently.
Future Trends in Data Automation
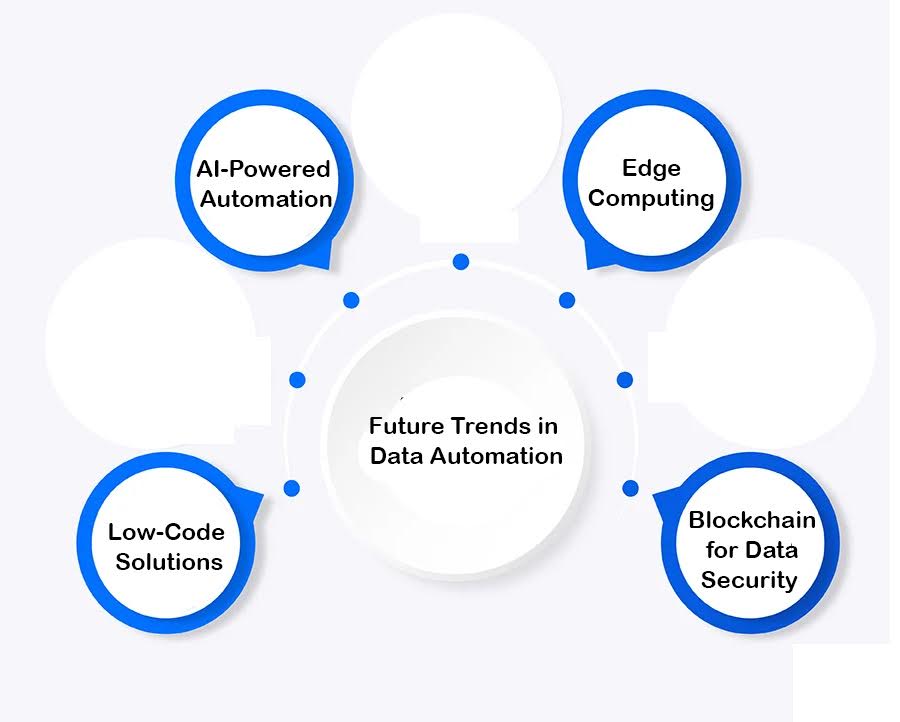
The landscape of data automation is undergoing significant transformation, largely propelled by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Below are some key trends that are shaping the future of this field:
- AI-Powered Automation: AI facilitates predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and intelligent workflows, leading to smarter and more adaptable automation processes.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes latency and enhances the capabilities for real-time data analysis.
- No-Code/Low-Code Solutions: The rise of no-code and low-code platforms simplifies the creation of automation workflows, empowering individuals without technical backgrounds to design and manage automated processes effectively.
- Blockchain for Data Security: Incorporating blockchain technology provides secure and tamper-proof data transactions, significantly increasing trust in automated systems.
These trends highlight the ongoing evolution of data automation and its increasing importance in various sectors.
Conclusion
Data automation is more than just a tool; it represents a transformative approach to managing information in the digital age. By streamlining workflows, businesses can enhance efficiency, improve accuracy, and achieve greater scalability, allowing them to thrive in competitive markets.
Whether you are just starting your automation journey or looking to refine your strategies, this guide offers the insights you need to succeed. Embrace the power of data automation and elevate your organization to the next level.
Deepak Wadhwani has over 20 years experience in software/wireless technologies. He has worked with Fortune 500 companies including Intuit, ESRI, Qualcomm, Sprint, Verizon, Vodafone, Nortel, Microsoft and Oracle in over 60 countries. Deepak has worked on Internet marketing projects in San Diego, Los Angeles, Orange Country, Denver, Nashville, Kansas City, New York, San Francisco and Huntsville. Deepak has been a founder of technology Startups for one of the first Cityguides, yellow pages online and web based enterprise solutions. He is an internet marketing and technology expert & co-founder for a San Diego Internet marketing company.



