Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s dynamic and competitive online marketing, organizations rely on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress toward their strategic objectives, monitor performance, and drive informed decision-making.
KPIs are quantifiable metrics that enable businesses to evaluate their success in achieving critical goals and targets across various areas of operation. The concept of KPIs has gained widespread recognition as a fundamental tool for performance management and business intelligence.
In this comprehensive guide to Key Performance Indicators, we will explore the significance of KPIs in business management, the different types of KPIs used across industries, best practices for selecting and defining effective KPIs, etc.
What are Key Performance Indicators?
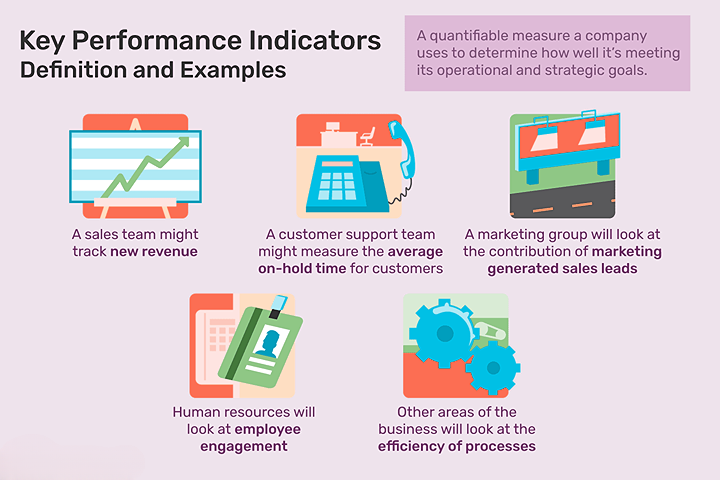
KPIs are measurable values that help businesses assess their progress toward achieving their goals. They are used to evaluate overall performance as well as departmental performance. KPIs can be used at multiple levels to gauge success, from high-level company performance to low-level departmental processes.
Key Features
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure a company’s success against targets, objectives, or industry peers.
- Financial KPIs include net profit, revenues minus expenses, and current ratio.
- Customer-focused KPIs center on per-customer efficiency, satisfaction, and retention.
- Process-focused KPIs aim to measure and monitor operational performance.
- Analytics software and reporting tools are used to measure and track KPIs in businesses.
Types of Key Performance Indicators

Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) can vary depending on the ecommerce industry, organization, and even within different departments of the same company. There are various types of KPIs used to measure the performance of other aspects of an organization. Here are some common types of KPIs:
- Financial KPIs: These KPIs measure the financial performance of an organization. They include metrics like revenue growth, profitability, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow.
- Operational KPIs: These KPIs assess the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes. Some examples are production output, cycle time, quality metrics, and inventory turnover.
- Customer KPIs: These KPIs gauge customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Common metrics include Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), customer churn rate, and customer lifetime value (CLV).
- Sales KPIs: These KPIs measure the effectiveness of sales activities and strategies. Metrics include sales revenue, sales growth, win rate, average deal size, and sales pipeline velocity.
- Supply Chain KPIs: These KPIs evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain operations. Examples include inventory turnover, order fulfillment cycle time, supplier performance, and transportation costs.
The selection of KPIs should align with the specific goals and objectives of an organization. Additionally, KPIs should follow the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to ensure they measure progress effectively and drive performance improvement.
Selecting and Defining Effective KPIs
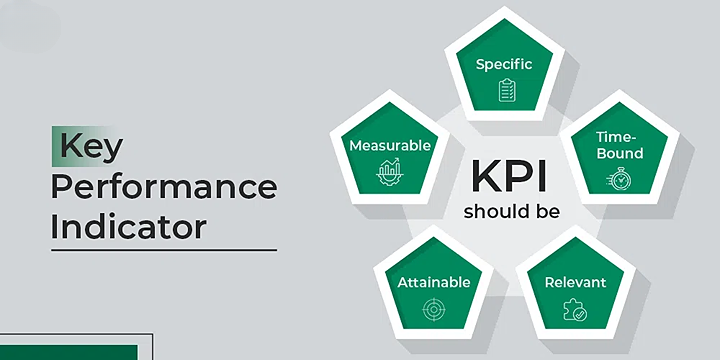
Selecting and defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is a critical process that requires careful consideration and alignment with organizational goals. Here’s a step-by-step guide to selecting and defining KPIs:
- Understand Organizational Goals: Begin by understanding the overarching goals and objectives of the organization. What does the organization aim to achieve in the short term and long term? These goals will guide the selection of relevant KPIs.
- Identify Strategic Objectives: Break down the organizational goals into specific strategic objectives. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Each objective should contribute to the overall mission of the organization.
- Set Targets: Establish targets or benchmarks for each KPI to provide a clear indication of what success looks like. Targets should be ambitious yet realistic, based on historical performance, industry benchmarks, and organizational objectives.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of KPIs and their alignment with organizational goals. Solicit feedback from stakeholders and be open to refining or adding new KPIs as the organization evolves.
By following these steps, you can effectively select and define KPIs that align with organizational goals, drive performance improvement, and enable informed decision-making.
Interpreting and Analyzing KPI Data

Analyzing KPI data is crucial for understanding the efficacy of your DevRel training programs and making informed decisions to improve them. Here are some steps to help you analyze and interpret KPI data:
Data Collection
Ensure that you are consistently collecting accurate data for each KPI you are tracking. Utilize tools and systems, such as learning management systems (LMS), analytics software, or surveys, to automate data collection and maintain data quality.
Data Organization
Organize the collected data in a structured format to facilitate analysis. This can be done using spreadsheets, databases, or data visualization tools. Categorize the data by training type (synchronous, asynchronous), specific training sessions, participant demographics, or other relevant factors.
Data Visualization
Use data visualization tools, such as charts, graphs, or dashboards, to present the KPI data in an easily digestible format. This can help you quickly identify trends, patterns, or anomalies in the data.
Using KPIs for Performance Management and Improvement
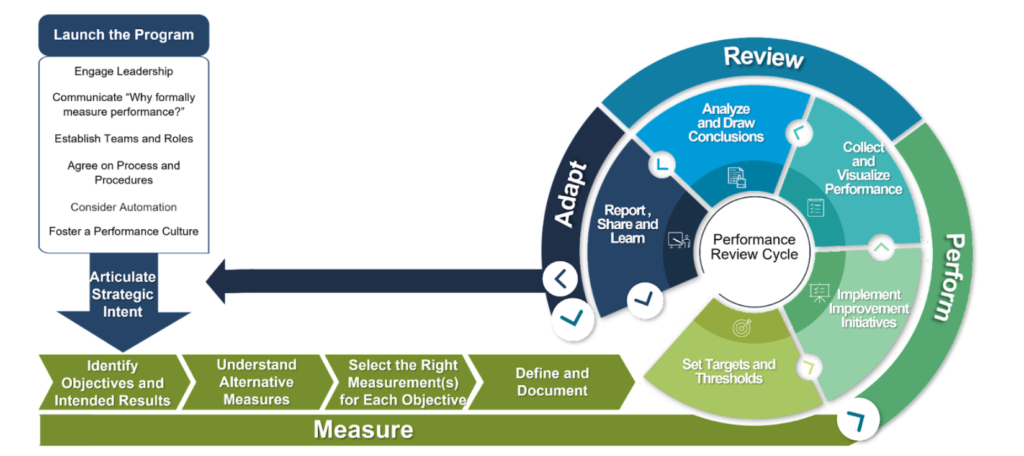
KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are a set of metrics used to measure an employee’s performance. To be effective, KPIs should be specific, measurable, and quantifiable, and they should be tracked over a certain period to indicate whether the employee has achieved their goals.
- Managers should work with employees to develop KPIs that can measure their performance.
- Process KPIs measure progress along the way to a desired outcome, while outcome KPIs measure the desired result.
- KPIs should align directly with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- KPIs should be easily quantifiable and measurable.
- Employees should be able to influence the KPI.
- KPIs should be clear, simple, and easy to understand.
- KPIs should serve as a powerful communication tool for helping employees understand specifically what is expected of them.
- KPIs should be able to be measured and communicated on time.
It’s important to note that KPIs are not the sole indicator of how well an employee is performing. KPIs should be linked to objectives and tracked over time to see how employees are performing.
Case Studies on Successful KPI Implementation
Below are some examples of successful implementations of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across various industries:

- Case Study: Google uses a set of KPIs to measure the performance of its search engine and advertising platforms.
- Approach: Google tracks various KPIs related to user engagement, advertising revenue, and product development. Key metrics include user retention, click-through rates (CTR), cost per click (CPC), and revenue per user (RPU).
- Impact: By monitoring and analyzing KPI data, Google continuously optimizes its products and services to enhance user experience and drive advertising revenue. The company’s focus on KPIs has contributed to its dominant position in the digital advertising market.
Amazon

- Case Study: Amazon heavily relies on KPIs to manage its e-commerce operations and logistics network.
- Approach: Amazon tracks KPIs related to customer satisfaction, order fulfillment, inventory management, and delivery performance. Key metrics include on-time delivery rates, order defect rates, inventory turnover, and customer feedback scores.
- Impact: Amazon’s relentless focus on KPIs enables the company to maintain high levels of customer service, optimize its supply chain, and drive operational efficiency. By leveraging KPI data, Amazon continuously innovates and expands its product offerings and delivery capabilities.
Netflix

- Case Study: Netflix uses KPIs to monitor subscriber growth, content consumption, and viewer engagement on its streaming platform.
- Approach: Netflix tracks KPIs such as subscriber additions, churn rates, viewing hours, and content retention. Key metrics also include user ratings, viewing preferences, and audience demographics.
- Impact: Netflix’s data-driven approach to content creation and recommendation algorithms is fuelled by KPI analysis. By leveraging insights from KPI data, Netflix produces original content tailored to viewer preferences, enhances the user experience, and retains subscribers in an increasingly competitive market.
Toyota
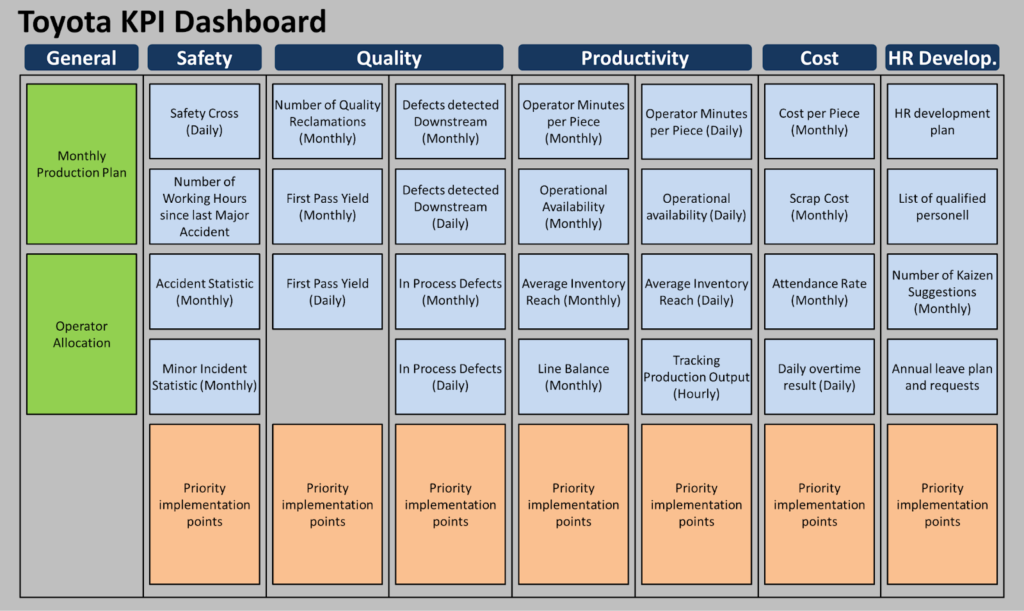
- Case Study: Toyota implements KPIs to drive continuous improvement and quality management across its manufacturing operations.
- Approach: Toyota uses KPIs such as defect rates, production efficiency, lead times, and employee engagement to measure performance at its production facilities. Key metrics also include inventory levels, supplier performance, and safety incidents.
- Impact: Toyota’s adherence to KPIs and the principles of lean manufacturing has enabled the company to achieve high levels of efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. By focusing on KPIs, Toyota minimizes waste, maximizes productivity, and maintains its reputation for producing reliable vehicles.
These case studies demonstrate how organizations across different industries utilize KPIs to drive performance improvement, achieve strategic objectives, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a crucial role in driving organizational success by providing quantifiable metrics to measure progress, assess performance, and inform decision-making.
By selecting and defining relevant KPIs that align with strategic objectives, organizations can gain valuable insights into various aspects of their operations, including financial performance, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and employee productivity.
Ultimately, KPIs serve as a valuable tool for organizations to measure success, optimize performance, and achieve their strategic objectives in an increasingly competitive and dynamic business environment.

Faisal Rafeeq is an SEO, PPC, and Digital Marketing expert. Faisal has worked on multiple e-commerce and web development projects, creating tailored and result oriented solutions. Some of the recent projects include ERPCorp, Wheelrack , TN Nursery, PROSGlobalinc, Patient9, and many more



